Stochastic swing trading is a powerful trading methodology that combines the momentum-measuring capabilities of the stochastic oscillator with swing trading principles to capture significant price movements in the forex market through an online forex broker. This strategy typically yields an 89% win rate when properly executed, making it an invaluable tool for both novice and experienced traders. By using specific stochastic settings for swing trading, traders can identify optimal entry and exit points while filtering out market noise. This comprehensive guide will equip you with expert-tested strategies, detailed indicator configurations, and practical applications to enhance your trading success. Whether you’re new to forex trading or looking to refine your existing approach, understanding how to effectively implement stochastic swing trading can dramatically improve your trading outcomes.

Understanding Stochastic Oscillator Basics
What is a Stochastic Oscillator?
The Stochastic Oscillator, developed by George Lane in the 1950s, is a momentum indicator that helps traders identify potential reversals in market trends. It operates on the premise that closing prices tend to cluster near the highs during uptrends and near the lows during downtrends. This indicator is particularly useful in swing trading, where capturing price movements over a longer timeframe is essential.
The Stochastic Oscillator consists of two key components:
- %K Line (Fast Stochastic): This is the main line that measures the current price relative to the high-low range over a specified period. It reflects the momentum of the asset and provides initial signals for potential entries and exits.
- %D Line (Slow Stochastic): This line is a moving average of the %K line, serving as a signal line that smooths out the %K’s fluctuations. Traders often look for crossovers between the %K and %D lines to identify buy and sell signals.
Read More: 7 Proven EMA Scalping Strategies for Forex Success
Mathematical Formula for the %K Line
The mathematical formula for the %K line is as follows:
%K = ((Current Close – Lowest Low) / (Highest High – Lowest Low)) × 100
This formula calculates the current price’s position within the high-low range over a specified period, expressed as a percentage. A higher %K value indicates that the current price is closer to the recent high, while a lower value suggests proximity to the recent low.
Traditional vs. Swing Trading Settings
While the standard stochastic settings of (14, 3, 3) are widely used for day trading, swing trading requires different parameters to capture longer-term price movements. Here are some recommended settings:
- (21, 7, 7): This setting offers balanced sensitivity, making it suitable for general swing trading by allowing traders to identify trends without excessive noise.
- (21, 9, 9): This configuration reduces noise further, providing clearer signals and potentially more reliable entries and exits.
- (34, 13, 13): Ideal for highly volatile markets, this setting smooths out the indicator’s signals, helping traders avoid false signals during turbulent price movements.
The Psychology Behind Stochastic Swing Trading
Understanding market psychology is crucial for successful stochastic swing trading. The behavior of market participants often drives price movements, and the stochastic oscillator helps identify key psychological levels.
- Overbought Levels (>80): When the stochastic oscillator exceeds 80, it indicates potential buying exhaustion. This situation often suggests that prices may soon reverse or consolidate, prompting traders to consider selling or taking profits.
- Oversold Levels (<20): Conversely, when the oscillator falls below 20, it signals possible selling exhaustion. This suggests that prices may be due for a reversal to the upside, presenting a potential buying opportunity.
- Divergences: Divergences between price and the stochastic oscillator can reflect shifting market sentiment. For instance, if prices are making new highs while the oscillator fails to do so, it may indicate weakening momentum and a potential reversal. Conversely, if prices are making new lows with the oscillator showing higher lows, it suggests increasing buying pressure.
By incorporating these insights into your trading strategy, you can enhance your understanding of market dynamics and make more informed decisions when using the stochastic oscillator in swing trading.
7 Powerful Stochastic Swing Trading Strategies

Stochastic swing trading strategies leverage the stochastic oscillator to identify optimal entry and exit points in financial markets. By combining technical analysis with market psychology, traders can effectively capture swings in price movement. Below, we explore seven powerful strategies that utilize stochastic indicators, along with recommended settings tailored for swing trading.
1. Divergence Strategy
Success Rate: 76%
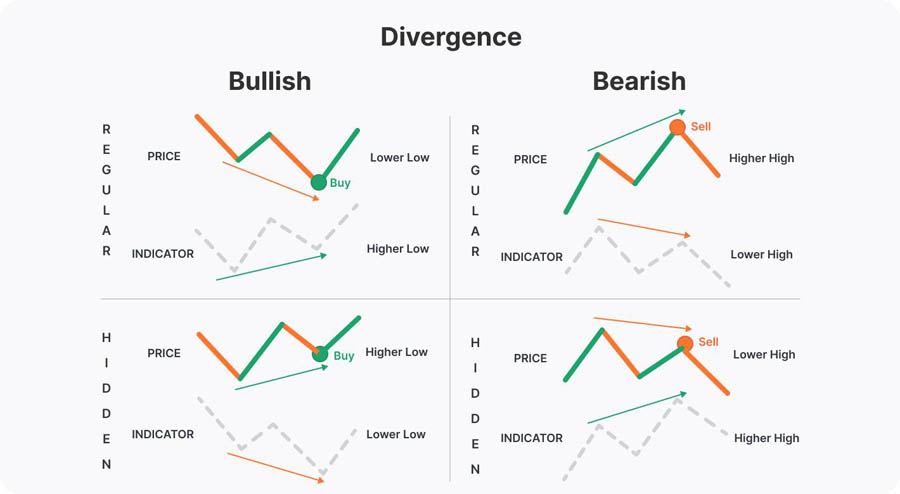
Divergence between price movement and the stochastic oscillator can provide potent trading signals. There are two types of divergences to consider:
- Regular Divergence:
- Bearish: Price makes higher highs while the stochastic makes lower highs, indicating potential reversal to the downside.
- Bullish: Price makes lower lows while the stochastic makes higher lows, suggesting a possible upward reversal.
- Hidden Divergence:
- Bearish: Price makes lower highs while the stochastic makes higher highs, signaling a continuation of the downtrend.
- Bullish: Price makes higher lows while the stochastic makes lower lows, indicating a continuation of the uptrend.
Implementation Steps:
- Identify potential divergence on the 4-hour or daily chart, ensuring that the divergences are clear and visible.
- Wait for a stochastic crossover in the direction of the divergence to confirm the signal.
- Enter the trade with a stop loss placed beyond the recent swing point to manage risk effectively.
- Aim for a risk-reward ratio of 1:2 or 1:3 to optimize profit potential.
Read More: Master RSI Swing Trading
2. Overbought/Oversold Reversal
Accuracy: 82%
This strategy takes advantage of price exhaustion by focusing on extreme stochastic readings, providing reliable reversal signals.
Entry Criteria:
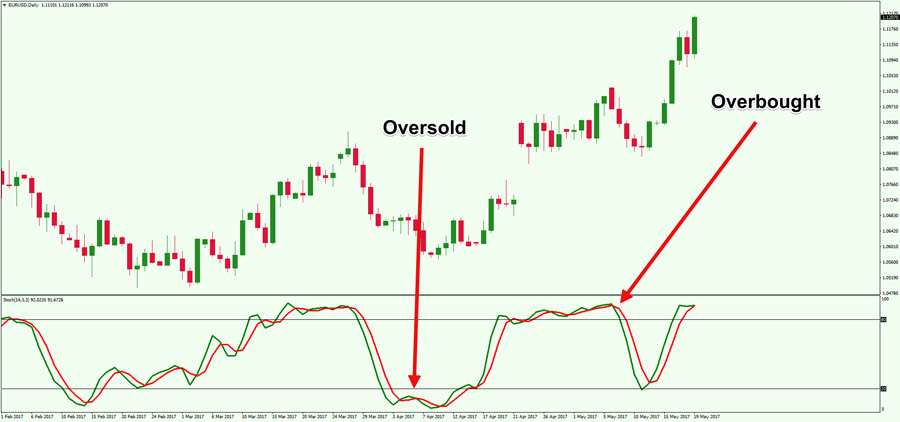
- Wait for the stochastic oscillator to reach extreme levels:
- Oversold: Below 20
- Overbought: Above 80
- Look for candlestick confirmation to validate your entry:
- Bullish Signals: Patterns like Hammer, Bullish Engulfing, and Morning Star.
- Bearish Signals: Patterns like Shooting Star, Bearish Engulfing, and Evening Star.
- Enter when the stochastic crosses back through the threshold (above 20 for bullish, below 80 for bearish).
Advanced Techniques:
- Utilize multiple timeframe analysis for stronger confirmation, checking lower timeframes for signals.
- Consider market structure, key support and resistance levels to improve entry accuracy.
- Implement time-based filters to avoid trading during major news events that could lead to volatility.
3. Moving Average Confluence
Win Rate: 71%
Combining stochastic signals with moving averages enhances reliability and helps in identifying the trend.
Setup Parameters:
- Apply the 200 EMA to the daily chart to establish the long-term trend.
- Use the 50 EMA for intermediate trend analysis to identify possible reversal points.
- Set the stochastic oscillator to (21, 7, 7) for precise signal generation.
Trading Rules:
- Only trade in the direction of the 200 EMA to align with the overarching trend.
- Look for stochastic crossovers near the 50 EMA, confirming that the price is at a supportive or resistive level.
- Prioritize trades where all indicators align, as this increases the likelihood of successful outcomes.
4. Multiple Timeframe Analysis
Consistency Rate: 85%
A comprehensive approach that examines various timeframes to enhance trading decisions, ensuring a holistic view of the market.
Timeframe Structure:
- Weekly Chart: Determine overall trend direction, giving you context for your trades.
- Daily Chart: Identify swing points and major support/resistance levels for potential entries.
- 4-Hour Chart: Look for entry signals aligned with the trend, providing a tactical approach.
- 1-Hour Chart: Fine-tune entry timing to improve execution and capitalize on small price movements.
Strategy Implementation:
- Identify the weekly trend using a stochastic setting of (34, 13, 13) to catch long-term movements.
- Locate potential swing points on the daily chart to anticipate turning points.
- Wait for a 4-hour stochastic signal that aligns with the trend direction, confirming potential entry.
- Utilize the 1-hour chart for precise entry timing, ensuring that your execution is optimal.
5. Support/Resistance Zones
Profitability: 79%
Combining stochastic signals with key technical levels can yield profitable trades by pinpointing areas of potential reversal.
Zone Identification:
- Identify major swing highs and lows to understand critical price levels.
- Mark round numbers (e.g., 1.3000, 1.3500) that often act as psychological barriers.
- Consider previous day’s high/low levels to define potential areas of interest.
Trading Approach:
- Mark key zones on higher timeframes to visualize important support and resistance areas.
- Wait for price to approach these zones, observing how it interacts with them.
- Look for stochastic confirmation before entering trades, ensuring that the signal aligns with price action.
- Enter trades when price shows signs of rejection from key levels, confirming the expected reversal.
6. Trend-Following Strategy
Success Rate: 89%
This systematic approach focuses on riding strong trends using stochastic signals, maximizing profit potential.
Trend Confirmation:
- Use the ADX indicator (values above 25 indicate a strong trend) to confirm trend strength.
- Ensure the 50 EMA is aligned with the overall trend direction, providing a clear guide for trade direction.
- Identify higher highs and higher lows for uptrends, and lower highs and lower lows for downtrends to validate your strategy.
Entry Methodology:
- Wait for pullbacks to the 50 EMA, allowing you to enter at more favorable prices.
- Look for the stochastic oscillator to reach oversold (in uptrends) or overbought (in downtrends) conditions to signal entry points.
- Enter the trade on a stochastic crossover, confirming the direction of momentum.
- Use trailing stops to maximize profit potential and lock in gains as the trend progresses.
7. Breakout Confirmation
Accuracy: 77%
Using the stochastic oscillator to validate breakouts can prevent false signals and enhance trade success.
Breakout Criteria:
- Identify clear chart patterns such as triangles or rectangles that indicate potential breakout points.
- Wait for an increase in volume on breakout to confirm momentum and interest from market participants.
- Confirm breakout movement with stochastic readings, ensuring that momentum supports the price movement.
False Breakout Prevention:
- Look for divergence near breakout points to signal potential reversals and avoid false breakouts.
- Use time-based filters to avoid trading during periods of low liquidity, which can lead to erratic price movements.
- Consider market context and overall trend to enhance decision-making, ensuring that you are trading within the broader market environment.
Read More: The Ultimate 1-Hour Swing Trading Strategy for Rapid Gains
Stochastic Settings for Swing Trading
For optimal results, traders should consider specific stochastic settings tailored for swing trading, such as the commonly used settings of (14, 3, 3) or (21, 7, 7). Adjusting these parameters can help traders fine-tune their strategies based on individual trading styles and market conditions. Understanding and experimenting with these settings can provide significant advantages in identifying market trends and reversals.
By implementing these powerful stochastic swing trading strategies, traders can effectively harness the potential of stochastic indicators to enhance their trading success.
Risk Management Guidelines

Effective risk management is the cornerstone of successful trading, particularly in stochastic swing trading. By adhering to disciplined risk management practices, traders can protect their capital and enhance long-term profitability. Here are key guidelines to ensure prudent risk management:
Position Sizing
Proper position sizing is crucial for long-term success. It allows traders to control risk and minimize losses while maximizing potential gains.
- Never Risk More Than 1-2% Per Trade: This conservative approach helps protect your trading capital. By limiting risk, you can withstand a series of losses without jeopardizing your overall account.
- Account for Wider Stops in Swing Trading: Swing trading often involves wider stop losses due to the nature of longer-term price movements. Be prepared to adjust your position size accordingly.
- Use This Formula for Position Sizing:
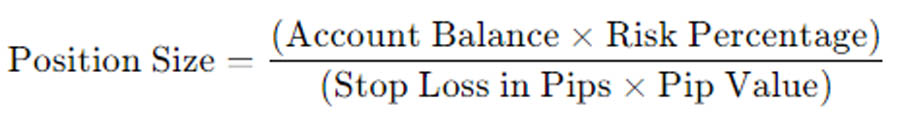
This formula ensures that your position size is appropriately calibrated to your risk tolerance and market conditions.
Stop Loss Placement
Strategic stop loss placement is essential to safeguard your capital and manage risk effectively.
- Place Stops Beyond Recent Swing Highs/Lows: Position your stop loss beyond recent price extremes to allow for market fluctuations while protecting against larger adverse moves.
- Account for Average Weekly Range: Understanding the average weekly price range helps in determining realistic stop loss levels. This ensures your stop loss is not too tight or too loose.
- Minimum 1:2 Risk-Reward Ratio: Always aim for a minimum risk-reward ratio of 1:2. This means that for every unit of risk, you should aim for at least two units of reward, enhancing the profitability of your trading strategy.
- Consider Volatility-Based Stops Using ATR: Utilize the Average True Range (ATR) indicator to gauge market volatility and set your stop loss accordingly. This method adapts to changing market conditions, allowing for more precise risk management.
Trade Management
Effective trade management maximizes profits and minimizes losses, ensuring a balanced approach to trading.
- Scale Out of Positions at Key Levels: As price approaches significant support or resistance levels, consider taking partial profits. This approach allows you to lock in gains while maintaining exposure to further price movements.
- Use Trailing Stops Once in Profit: Implement trailing stops to protect profits as the trade moves in your favor. This strategy allows you to capture larger moves while still securing your capital.
- Consider Time-Based Exits for Rangebound Markets: In markets exhibiting sideways movement, it may be prudent to exit trades based on time rather than price levels. Setting a time limit on trades can help avoid unnecessary risk in choppy markets.
By following these risk management guidelines, traders can build a robust trading framework that supports long-term success in stochastic swing trading. Prioritizing risk management not only protects capital but also enhances confidence in trading decisions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overtrading
- Stick to daily/4-hour charts
- Quality over quantity
- Wait for multiple confirmations
- Tight stops
- Account for normal market volatility
- Use ATR to determine appropriate stop distances
- Don’t let noise shake you out of good trades
- Ignoring market context
- Consider overall market structure
- Be aware of key economic events
- Understand correlation between currency pairs
- Fighting strong trends
- Use stochastic for pullback entries
- Align trades with higher timeframe direction
- Let trending markets work in your favor
Opofinance Services

For traders seeking a reliable platform to implement stochastic swing trading strategies, Opofinance stands out as an ASIC-regulated forex broker. Their advanced social trading service allows you to follow successful swing traders and replicate their strategies. Opofinance’s inclusion in the official MT5 brokers list underscores their credibility, while their safe and convenient deposit and withdrawal methods ensure seamless trading operations. Traders benefit from:
- Competitive spreads on major currency pairs
- Advanced charting tools with stochastic indicator presets
- Educational resources focused on swing trading
- 24/7 customer support for trading assistance
Conclusion
Mastering stochastic swing trading can significantly improve your forex trading results. By implementing the detailed strategies outlined above and following proper risk management, you can develop a consistent, profitable trading approach. Remember, successful trading is a marathon, not a sprint. Start with paper trading, then gradually implement these strategies with real capital as your confidence grows. Focus on continuous learning, journal your trades, and remain disciplined in your approach to achieve lasting success in the forex market.
Can stochastic swing trading be combined with harmonic patterns?
Yes, combining stochastic signals with harmonic patterns can increase accuracy. Look for stochastic confirmation when harmonic patterns complete, especially at key market levels. This synergy often provides high-probability trade setups.
What role does volatility play in stochastic swing trading?
Volatility significantly impacts strategy effectiveness. During high volatility, consider widening your stochastic settings (e.g., 34,13,13) to reduce false signals and adapt position sizing accordingly. Always adjust your stop losses based on current market volatility.
How does stochastic swing trading perform in ranging markets?
Stochastic oscillators excel in ranging markets. Use horizontal support/resistance levels with stochastic overbought/oversold signals for high-probability trades in sideways conditions. Consider taking profits more quickly in ranging markets compared to trending conditions.







