The ATR indicator (Average True Range) is a fundamental tool in forex trading that measures market volatility. Created by J. Welles Wilder, it helps traders determine the degree of price movement in the market and enables more informed decisions regarding entry, exit, and risk management. Understanding how to use the ATR indicator in forex is essential, as it can give traders an edge in volatile markets by adjusting stop-losses, profit targets, and trading strategies based on current market conditions. To maximize the effectiveness of the ATR and other tools, working with a regulated forex broker can provide added security and ensure that your trading activities are in a safe and compliant environment.

This comprehensive guide explains how to use the ATR indicator in forex, covering its definition, calculations, practical applications, and strategies for trading with it. Additionally, we’ll explore how traders can incorporate the ATR indicator on platforms like MetaTrader and provide advanced tips to maximize trading outcomes.
Introduction to the ATR Indicator in Forex
The Average True Range (ATR) is a volatility indicator designed to show the range of price movement over a specific period. It doesn’t predict trends or price direction, but instead, it measures the degree of market volatility, providing insight into potential price fluctuations. Whether you are a beginner or advanced trader, understanding how to use the ATR indicator in forex is crucial for refining your trading strategies.
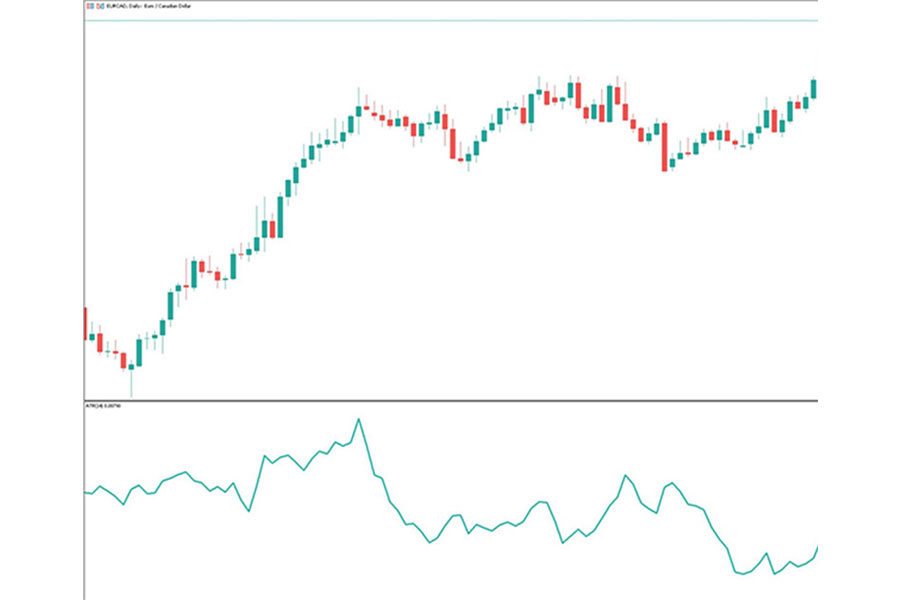
Forex markets can exhibit sudden shifts in volatility, especially around major economic events, making the ATR indicator valuable for risk management. By identifying periods of high or low volatility, traders can adjust their stop-losses and profit targets accordingly, helping them avoid premature exits or missed opportunities in both calm and turbulent markets.
The ATR indicator helps traders:
- Identify market volatility to determine the best risk management strategy.
- Set appropriate stop-losses based on market conditions to avoid premature exits.
- Understand potential price movement to estimate profit targets.
Incorporating ATR into your forex trading strategy with a reliable forex trading broker is essential, as they provide access to efficient trading platforms like MT4 or MT5, where you can easily set up and customize the ATR indicator.
What is the ATR Indicator and How Does It Work?
The ATR indicator is based on the concept of True Range, which takes into account the most comprehensive range of price movement over a given period. It calculates the greatest of the following three values:
- Current high minus the current low.
- The absolute value of the current high minus the previous close.
- The absolute value of the current low minus the previous close.
Once the True Range is calculated for each period, the Average True Range (ATR) is determined by taking the average of the True Range values over a specified period, typically 14 periods by default. The higher the ATR, the more volatile the market, while a lower ATR suggests more stable conditions.
Key Features of the ATR Indicator:
- Measures volatility, not price direction.
- High ATR values indicate increased market volatility.
- Low ATR values suggest stable or calm market conditions.
How to Use the ATR Indicator in Forex Trading
The ATR indicator in forex is highly versatile and can be integrated into various trading strategies. Here are some of the primary uses of the ATR indicator:
Setting Stop-Losses Using ATR
One of the most practical applications of the ATR indicator is in setting stop-losses. Rather than using fixed stop-loss distances, traders can use ATR to adjust their stop-loss levels based on current market volatility. This ensures that stop-losses are wide enough to account for price fluctuations without getting hit too early, which is especially important in volatile forex markets.
How to Set Stop-Losses with ATR:
- Identify the current ATR value.
- Multiply the ATR by a factor (commonly 1.5x or 2x).
- Place the stop-loss this distance away from the current price, allowing the trade room to breathe.
For example, if the ATR value is 50 pips and you multiply it by 2, your stop-loss should be placed 100 pips away from the current price. This method allows traders to customize their risk tolerance according to market volatility.
Read More: how to use bollinger bands in forex trading
Profit Targeting with ATR
Using ATR for profit targeting is another powerful strategy. When the ATR is high, it signals increased volatility, suggesting that there is potential for larger price movements. In contrast, when the ATR is low, it might be wise to avoid entering trades or set more conservative profit targets, as price movement may be limited.
How to Set Profit Targets with ATR:
- Identify the current ATR value.
- Estimate potential price movement based on the ATR.
- Set profit targets within the anticipated price range.
For example, if the ATR indicates a 100-pip range for the day, your profit target can be set within this range, ensuring that your trade remains realistic and in line with market conditions.
Pro Tips for Advanced Traders:
- Combine ATR with Other Indicators: Use the ATR in conjunction with trend-following indicators like Moving Averages or Relative Strength Index (RSI) to confirm entry and exit points. For instance, if the RSI is signaling an overbought market and the ATR shows high volatility, it could be a good time to exit the trade.
- Trailing Stops Using ATR: As the market moves in your favor, use the ATR to trail your stop-loss. By recalculating the ATR and moving your stop-loss further away, you can lock in profits while giving the trade room to grow.
- Position Sizing with ATR: Use ATR to adjust your position size based on volatility. In highly volatile markets, reduce your position size to limit risk, while in calmer markets, you may increase it for more profit potential.
ATR Indicator Strategies for Forex Traders

To effectively harness the power of the Average True Range (ATR) indicator in your forex trading, it’s essential to implement strategies that are both actionable and adaptable to various market conditions. Below are several practical ATR-based strategies designed to enhance your trading performance:
ATR-Based Breakout Strategy
Objective: Capitalize on significant price movements following periods of low volatility.
How It Works:
- Identify Consolidation: Use the ATR to spot periods where market volatility is low (ATR is declining), indicating consolidation.
- Set Breakout Levels: Determine key support and resistance levels based on recent price action.
- Confirm Breakout with ATR: When the price breaks above resistance or below support, ensure that the ATR is increasing, signaling rising volatility.
- Enter the Trade: Initiate a long position on a breakout above resistance or a short position on a breakdown below support.
- Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit:
- Stop-Loss: Place it a multiple of the ATR (e.g., 1.5x ATR) below the breakout point for longs or above for shorts.
- Take-Profit: Aim for a reward-to-risk ratio of at least 2:1, adjusting based on ATR to capture larger moves in volatile conditions.
Example: Suppose EUR/USD has been trading in a tight range with an ATR of 30 pips. A breakout occurs to the upside with the ATR rising to 45 pips. Enter a long position with a stop-loss set 1.5x ATR (45 pips) below the breakout point and a take-profit target 2x ATR (90 pips) above.
ATR Trailing Stop Strategy
Objective: Protect profits by dynamically adjusting stop-loss levels as the trade moves in your favor.
How It Works:
- Enter the Trade: Use your preferred entry signal (e.g., moving average crossover).
- Initial Stop-Loss: Set an initial stop-loss based on a multiple of the ATR (e.g., 2x ATR) from the entry price.
- Implement Trailing Stop:
- As the trade moves in your favor, adjust the stop-loss to trail the price by a set ATR multiple.
- For example, if ATR is 40 pips, trail the stop-loss 1.5x ATR (60 pips) behind the highest price reached in a long position.
- Exit the Trade: The trade closes when the price reverses and hits the trailing stop, locking in profits while allowing for potential further gains.
Example: You enter a long trade on GBP/JPY at 150.00 with an ATR of 50 pips. Set an initial stop-loss at 149.00 (2x ATR). As the price moves to 151.50, adjust the stop-loss to 150.00 (1.5x ATR below the new high). If the price continues to 153.00, move the stop-loss to 151.50, securing a 1.5 ATR profit while allowing the trade to run.
ATR and Position Sizing Strategy
Objective: Manage risk by adjusting your position size based on current market volatility.
How It Works:
- Determine Risk Per Trade: Decide the percentage of your trading capital you are willing to risk on a single trade (e.g., 1%).
- Calculate ATR-Based Risk: Use the ATR to assess the market’s volatility. Higher ATR implies higher volatility and suggests taking smaller positions to manage risk.
- Compute Position Size:
- Formula: Position Size = (Account Risk in Pips) / (ATR × Pip Value)
- Account Risk in Pips: Defined by your risk percentage and ATR.
- Adjust Position Size Accordingly: Scale your trade size up or down based on the ATR to maintain consistent risk across different volatility environments.
Example: With a $10,000 account and a 1% risk per trade ($100), if the ATR for USD/CHF is 20 pips:
- Risk in Pips: $100 / 20 pips = $5 per pip
- Position Size: $5 per pip corresponds to a position size of 0.05 lots (since 1 lot typically equals $10 per pip).
In a more volatile market where ATR is 40 pips:
- Risk in Pips: $100 / 40 pips = $2.50 per pip
- Position Size: $2.50 per pip corresponds to a position size of 0.025 lots.
ATR Divergence Strategy
Objective: Detect potential reversals by identifying divergences between price movement and ATR.
How It Works:
- Monitor ATR and Price Trends: Observe the relationship between ATR and price direction.
- Identify Divergence:
- Bullish Divergence: Price makes lower lows while ATR makes higher lows, indicating decreasing volatility despite falling prices.
- Bearish Divergence: Price makes higher highs while ATR makes lower highs, suggesting decreasing volatility despite rising prices.
- Confirm with Additional Indicators: Use trend indicators like Moving Averages or momentum indicators like RSI to validate potential reversal signals.
- Enter the Trade: Initiate a position in the direction opposite to the prevailing trend, anticipating a reversal.
- Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit: Use ATR multiples to determine appropriate levels based on the new volatility landscape.
Example: Assume USD/CAD has been in a downtrend with price making lower lows and ATR increasing. Suddenly, price makes a new lower low, but ATR starts to decline, indicating weakening volatility. This bullish divergence may signal a potential reversal. Confirm with an RSI moving above 30 and enter a long position, setting a stop-loss at 1.5x ATR above the entry point.
Read More: atr scalping strategy
ATR Range-Based Scalping Strategy
Objective: Utilize ATR to execute quick trades within a defined range during low volatility periods.
How It Works:
- Identify Low Volatility Periods: Look for periods where ATR is below a certain threshold, indicating a tight trading range.
- Set Range Boundaries: Define upper resistance and lower support levels based on recent price consolidation.
- Execute Scalps:
- Buy at Support: Enter long positions when the price touches the lower boundary, anticipating a bounce.
- Sell at Resistance: Enter short positions when the price reaches the upper boundary, expecting a pullback.
- Use ATR for Tight Stop-Losses: Place stop-loss orders just outside the trading range using a small ATR multiple (e.g., 0.5x ATR) to minimize risk.
- Quick Take-Profits: Aim for small, consistent profits by exiting trades quickly as price reverses within the range.
Example: EUR/GBP is trading between 0.8500 (support) and 0.8550 (resistance) with an ATR of 10 pips. Enter a long position at 0.8500 with a stop-loss at 0.8500 – (0.5 × ATR) = 0.8450 and a take-profit at 0.8550. Conversely, enter a short position at 0.8550 with a stop-loss at 0.8550 + (0.5 × ATR) = 0.8600 and a take-profit at 0.8500.
Multi-Timeframe ATR Strategy
Objective: Enhance trade accuracy by analyzing ATR across different timeframes.
How It Works:
- Select Multiple Timeframes: Choose at least two different timeframes (e.g., daily and 1-hour charts).
- Analyze ATR on Each Timeframe:
- Higher Timeframe ATR: Provides a broader view of market volatility and trends.
- Lower Timeframe ATR: Offers detailed insights for precise entry and exit points.
- Align Trading Signals: Ensure that signals from both timeframes align to increase the probability of successful trades.
- Execute the Trade: Enter trades when both timeframes indicate favorable volatility conditions based on ATR.
- Manage the Trade with ATR: Use the lower timeframe ATR to set dynamic stop-losses and take-profits, ensuring adaptability to real-time volatility.
Example: On the daily chart, GBP/USD has an ATR of 80 pips, indicating a strong trend. On the 1-hour chart, ATR is 20 pips, showing manageable volatility for intraday trading. Enter a long position when the 1-hour ATR signals a favorable setup aligned with the daily trend, setting stop-loss and take-profit based on the 1-hour ATR to capture intraday moves while adhering to the broader market trend.
Implementing ATR Strategies: Practical Tips
- Backtest Your Strategies: Before applying any ATR-based strategy in live trading, backtest it on historical data to assess its effectiveness.
- Combine with Price Action: Use ATR in conjunction with price action techniques (e.g., candlestick patterns) to enhance signal reliability.
- Stay Adaptable: Market conditions change, so be prepared to adjust your ATR settings and strategies accordingly.
- Use Alerts: Set up ATR-based alerts on your trading platform to notify you of significant volatility changes, helping you to act swiftly.
- Maintain Discipline: Adhere strictly to your ATR-based rules for stop-losses and take-profits to ensure consistent risk management.
By incorporating these practical ATR strategies into your trading routine, you can better navigate different market environments, manage risk effectively, and improve your overall trading performance.
How to Use ATR on Trading Platforms (MT4/MT5)
One of the advantages of using ATR is its availability on most forex trading platforms like MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5). Here’s a quick guide to setting up the ATR indicator on these platforms:
Setting Up ATR on MT4/MT5:
- Open a chart for the currency pair you want to trade.
- Click on the Insert menu, select Indicators, and then choose Oscillators.
- From the Oscillators section, select Average True Range (ATR).
- Customize the period (14 is the default), but you can adjust it according to your strategy.
- The ATR line will appear below the chart, showing the volatility in pip values.
Customizing the ATR Indicator:
- You can change the period length depending on your trading timeframe (shorter periods for scalping, longer periods for swing trading).
- Visual customization is also available, such as changing the color or thickness of the line to make it more visible.
Pro Tip: Advanced traders can create custom ATR alerts on MT4/MT5 to notify them when volatility rises above or falls below a certain threshold.
Read More: How to Use the Momentum Indicator in Forex
Limitations and Considerations When Using ATR
While the ATR indicator is an invaluable tool in forex trading, it’s important to be aware of its limitations:
Lagging Nature of ATR
ATR is a lagging indicator, meaning it reflects past volatility and does not predict future price movements. This can sometimes lead to missed opportunities if you rely solely on ATR for trade entry decisions.
False Signals in Low-Volume Markets
ATR can provide false signals in low-volume markets, such as during holidays or off-peak trading hours. During these times, volatility may appear low, but the market could still move unpredictably when volume returns.
Events and ATR
Avoid relying on ATR during significant economic events like central bank announcements, as these can cause sudden spikes in volatility that ATR may not accurately capture in real-time.
Opofinance Services: A Trusted Broker for Forex Traders
When using the ATR indicator in forex, it’s essential to have a reliable broker. Opofinance, an ASIC-regulated broker, provides a secure and transparent trading environment for traders at all levels. Opofinance is officially featured on the MT5 brokers list, offering access to advanced trading platforms like MetaTrader 5 (MT5), which is perfect for using the ATR indicator effectively.

Why Choose Opofinance?
- Safe and Convenient Deposits and Withdrawals: Opofinance ensures fast and secure transactions, so traders can focus on their strategies without worrying about fund safety.
- Social Trading Services: Opofinance offers social trading, allowing traders to follow and copy the strategies of successful professionals. This is ideal for traders looking to learn how to use indicators like ATR more effectively by watching seasoned experts in action.
Opofinance is a trusted partner for traders seeking a regulated forex broker with top-tier tools and services.
Conclusion
The ATR indicator is a vital tool in forex trading, providing traders with a clear view of market volatility. By understanding how to use the ATR indicator in forex, traders can set better stop-losses, adjust profit targets, and adapt to different market conditions. ATR’s ability to gauge market volatility makes it a powerful asset for traders looking to fine-tune their risk management strategies.
However, it’s important to remember that ATR should be used alongside other indicators for a more comprehensive view of the market. By practicing these strategies on demo accounts and refining them, traders can harness the full potential of ATR in their live trading.
Key Takeaways
- ATR measures market volatility, not trend direction, helping traders adjust their strategies based on current market conditions.
- Setting stop-losses and profit targets using ATR allows traders to account for volatility, reducing the likelihood of premature exits or missed opportunities.
- Combining ATR with other indicators like Moving Averages or RSI can improve trading decisions.
- Opofinance, an ASIC-regulated broker, provides an ideal platform for using the ATR indicator with MT5 and offers social trading services.
Can ATR be used in short-term forex trading strategies?
Yes, ATR can be adjusted for shorter periods, making it suitable for scalping and other short-term trading strategies by reflecting immediate volatility changes.
What’s the ideal ATR period for forex trading?
The default period is 14, but traders can adjust the period based on their trading style. Short-term traders may prefer a period of 7, while long-term traders might choose a period of 21 or more.
How does ATR help with risk management?
ATR helps traders measure volatility, enabling them to place stop-losses and adjust position sizes based on market conditions, thus reducing risk in volatile markets.







