Are you tirelessly searching for a powerful edge in the exciting world of trading? Do you want to decode market inefficiencies and pinpoint high-probability trading opportunities? The secret might lie in understanding and leveraging the Fair Value Gap (FVG). In essence, a Fair Value Gap is a price inefficiency that occurs when there are significant imbalances between buyers and sellers, leading to rapid price movements and leaving behind unfilled orders. Think of it as a momentary lapse in market equilibrium, a fleeting opportunity for astute traders to capitalize on.

This article will serve as your comprehensive guide to mastering the Fair Value Gap, a powerful concept within Smart Money Concepts (SMC) and price action trading, and how you can use it to potentially enhance your trading strategy, especially when navigating the dynamic forex market with a regulated forex broker. We will delve deep into what a Fair Value Gap truly is, how to identify a Fair Value Gap on your charts, effective trading strategies for Fair Value Gap, and crucial risk management techniques to help you confidently integrate this potent tool into your trading arsenal.
Get ready to unlock hidden profit potential and elevate your trading game by understanding the power of the Fair Value Gap. If you are looking for a reliable online forex broker, understanding Fair Value Gap can be incredibly beneficial.
Understanding Fair Value Gaps in Trading
To truly grasp the significance of a Fair Value Gap, we must first understand the fundamental principle of market efficiency. In theory, financial markets are supposed to be efficient, meaning prices should reflect all available information, and buying and selling pressures should be balanced. However, in reality, markets are far from perfectly efficient. Rapid price movements, often driven by large institutional orders or sudden shifts in market sentiment, can create temporary imbalances. This is where the Fair Value Gap comes into play. Many traders using a broker for forex trading are starting to incorporate Fair Value Gap analysis into their strategies.
What Exactly is a Fair Value Gap?
In the context of financial markets, a Fair Value Gap represents a zone on a price chart where price has moved so rapidly that it has left behind a gap in trading activity. This gap signifies an inefficiency, an area where price has not traded, and thus, fair value has not been established. Imagine a sudden surge of buying pressure in the forex market. Large institutions executing massive buy orders can propel the price upwards with such force that there isn’t enough selling pressure to create overlapping price action. This results in a gap between price candles, visually representing the Fair Value Gap. Understanding what is Fair Value Gap is the first step to leveraging it in your trading.
The Price Inefficiency Explained by Fair Value Gap
This price inefficiency arises because the rapid price movement skips over certain price levels. Ideally, for a market to be truly efficient, price should trade at every level, ensuring that all buy and sell orders are matched in a balanced manner. When a Fair Value Gap forms, it indicates that this balanced exchange hasn’t occurred. The market, in its inherent drive towards efficiency, often seeks to revisit these gaps to “fill” them, meaning price tends to retrace back to trade within the gapped area and establish fair value. This concept of Fair Value Gap is crucial for understanding market dynamics.
Liquidity and Fair Value Gaps: A Crucial Relationship
Liquidity, the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without causing significant price movement, plays a vital role in the formation of Fair Value Gaps. During periods of low liquidity, even relatively smaller institutional orders can have a disproportionately large impact on price, making the formation of FVGs more likely. Conversely, in highly liquid markets, it takes significantly larger orders to create such gaps. Therefore, understanding market liquidity conditions is crucial when analyzing and trading Fair Value Gaps. For traders using a broker for forex, liquidity is always a key consideration.
Institutional Footprints: The Origin of Gaps
Large institutional players, such as hedge funds, banks, and investment firms, are often the primary drivers behind the creation of Fair Value Gaps. Their massive trading volumes can overwhelm the market, especially during specific trading sessions or news events, leading to swift and decisive price movements that forge these gaps. Recognizing that these gaps often represent institutional footprints can provide valuable insights into potential future price direction. Analyzing Fair Value Gap in SMC often involves understanding institutional order flow.
Fair Value Gaps Across Markets: Forex, Stocks, and Crypto
The concept of Fair Value Gaps is not limited to a single market. You can observe them across various financial instruments, including:
- Forex: In the fast-paced forex market, Fair Value Gaps are common due to high leverage and global trading activity. Currency pairs often exhibit gaps, particularly during the overlap of major trading sessions or after significant economic news releases. Choosing the right forex trading broker is essential for accessing tools to identify these gaps.
- Stocks: Stock markets also experience Fair Value Gaps, often around earnings announcements, major company news, or market-wide events. These gaps can provide clues about institutional sentiment towards a particular stock.
- Cryptocurrency: The highly volatile cryptocurrency market is rife with Fair Value Gaps. The 24/7 nature of crypto trading and the presence of both retail and institutional participants contribute to frequent gap formations.
Read More: The Smart Money Concept
Identifying Fair Value Gaps on a Chart
Identifying Fair Value Gaps on a price chart is a crucial skill for any trader looking to incorporate this concept into their strategy. It’s a visual process that involves understanding the relationship between consecutive price candles. Mastering the identification of Fair Value Gap SMC is key to successful trading.
Step-by-Step Identification Process for Fair Value Gap
- Examine Three Consecutive Candles: The key to identifying a Fair Value Gap lies in analyzing three consecutive candles on your chosen timeframe.
- Look for Non-Overlapping Wicks: A Fair Value Gap exists when the low of the first candle does not overlap with the high of the third candle. Essentially, the middle candle’s range creates a gap between the first and third candles.
- Visualize the Gap Zone: The Fair Value Gap is the space between the high of the first candle and the low of the third candle. This area represents the price inefficiency.
Key Characteristics of a Fair Value Gap
- Non-Overlap is Essential: The defining characteristic is the lack of overlap between the first and third candle’s wicks. This signifies the “gap” in price action, the essence of a Fair Value Gap.
- Institutional Imbalance: FVGs often signal strong institutional buying or selling pressure. A bullish FVG typically indicates strong buying, while a bearish FVG suggests strong selling. Understanding this imbalance is core to Fair Value Gap smc analysis.
- Timeframe Matters: Fair Value Gaps can be observed on various timeframes. Higher timeframes (e.g., daily, 4-hour) generally carry more weight and significance than lower timeframes (e.g., 15-minute, 1-minute). Stronger, more reliable FVGs are often found on higher timeframes.
Utilizing Timeframes to Detect Strong Fair Value Gaps
While Fair Value Gaps can appear on any timeframe, their reliability and strength increase on higher timeframes. Traders often use a multi-timeframe approach to analyze Fair Value Gap:
- Higher Timeframe Context: Start by identifying Fair Value Gaps on higher timeframes like the daily or 4-hour chart to understand the overall market structure and potential long-term biases.
- Lower Timeframe Refinement: Then, drop down to lower timeframes like the 1-hour or 15-minute chart to refine your entry points within the higher timeframe FVG zones. This allows for more precise entries and tighter stop-loss placement when trading Fair Value Gap.
Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy

Once you can confidently identify Fair Value Gaps, the next step is to develop strategies to trade them effectively. FVGs offer several trading opportunities based on the market’s tendency to revisit and “fill” these inefficient price zones. A solid Fair Value Gap trading strategy can significantly improve your trading outcomes.
Anticipating Price Retracements with Fair Value Gap
The core principle behind FVG trading is the anticipation of price retracement. Because Fair Value Gaps represent unfilled orders and price inefficiencies, the market often gravitates back to these zones to establish equilibrium. Traders use FVGs to predict potential areas where price might reverse or find support/resistance. This anticipation is at the heart of any effective Fair Value Gap smc strategy.
Common Fair Value Gap Trading Strategies
- Gap Fill Strategy (The Retracement Play):
- Concept: This is the most common FVG strategy. It involves entering a trade when price retraces back to test or fill the Fair Value Gap.
- Entry: Look for price to retrace into the FVG zone. Entry can be triggered when price touches the edge of the FVG or shows signs of rejection within the gap.
- Stop-Loss: Place your stop-loss just outside the FVG zone, beyond the high of the first candle (for bullish FVGs) or below the low of the first candle (for bearish FVGs).
- Take-Profit: Targets can be set at previous swing highs/lows, significant support/resistance levels, or based on a risk-to-reward ratio when trading Fair Value Gap.
- Continuation Strategy (Riding the Momentum):
- Concept: This strategy is more aggressive and assumes that the initial momentum that created the Fair Value Gap will continue.
- Entry: Enter a trade in the direction of the initial momentum shortly after the FVG forms, anticipating further price movement in that direction.
- Stop-Loss: Place your stop-loss just below a bullish FVG or just above a bearish FVG.
- Take-Profit: Targets can be based on Fibonacci extensions, previous trend continuation patterns, or a predetermined risk-to-reward ratio when using a Fair Value Gap strategy.
- Support & Resistance Role (FVGs as Zones):
- Concept: Fair Value Gaps can act as dynamic support and resistance zones. Bullish FVGs often become support after price retraces to them, while bearish FVGs can act as resistance on subsequent rallies.
- Trading: Observe how price reacts when it approaches a previously formed FVG. Look for bullish price action (e.g., candlestick patterns, bounces) at bullish FVGs for potential long entries, and bearish price action (e.g., rejections, reversals) at bearish FVGs for potential short entries. This is a nuanced approach to Fair Value Gap trading.
Entry, Stop-Loss, and Take-Profit Precision in Fair Value Gap Trading
- Entry Refinement: Don’t blindly enter trades as soon as price enters an FVG. Look for confirmation signals like candlestick patterns (e.g., pin bars, engulfing patterns), order block rejections, or momentum shifts within the FVG zone. Precision is key in Fair Value Gap entries.
- Stop-Loss Placement: Strategic stop-loss placement is crucial. Avoid placing stops too tightly within the FVG, as price might briefly wick into the gap before reversing. Give your trade some breathing room while still managing risk effectively when trading Fair Value Gap.
- Take-Profit Strategies: Consider using multiple take-profit levels to secure partial profits and let the remaining position run. Fibonacci retracement and extension levels can be valuable tools for identifying potential take-profit zones in Fair Value Gap setups.
Read More: Market Structure Break (MSB)
Fair Value Gap Indicator & Tools
Manually identifying Fair Value Gaps can be time-consuming, especially when analyzing multiple charts and timeframes. Fortunately, various Fair Value Gap indicators are available on popular trading platforms like TradingView and MetaTrader to automate this process. These tools can greatly assist in Fair Value Gap smc analysis.
Overview of FVG Indicators
These indicators are designed to automatically scan price charts and highlight potential Fair Value Gaps based on the defined criteria. They typically draw boxes or shaded areas on the chart to visually represent the FVGs. Using a Fair Value Gap indicator can streamline your analysis.
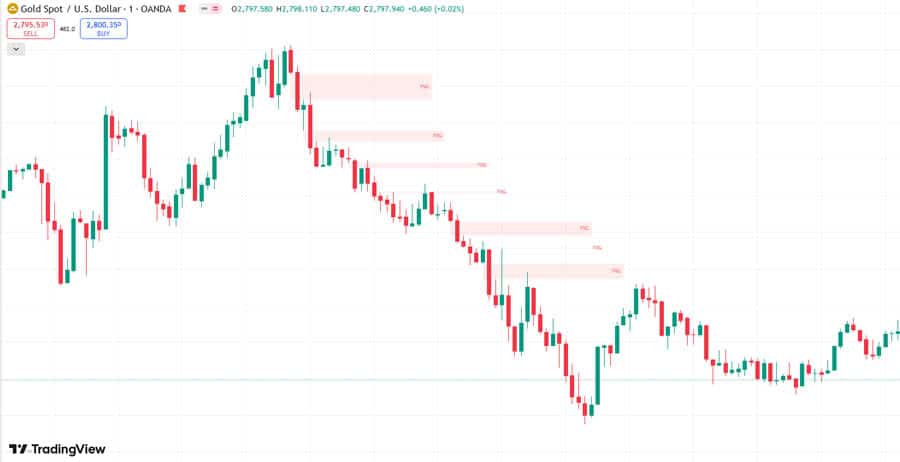
Benefits of Automated Fair Value Gap Indicators
- Efficiency: Save time and effort by automating the FVG identification process.
- Objectivity: Indicators provide a consistent and objective way to identify FVGs, reducing subjective interpretation.
- Backtesting and Analysis: Indicators facilitate backtesting and historical analysis of FVG strategies.
Combining FVGs with Other Technical Tools
While Fair Value Gap indicators are helpful, relying solely on them is not recommended. For robust trading decisions, it’s essential to combine FVG analysis with other technical tools and concepts. A holistic approach to Fair Value Gap trading is always best.
- Fibonacci Retracement Levels: Use Fibonacci retracement levels to identify potential retracement targets within Fair Value Gaps. Confluence of FVG zones and Fibonacci levels can strengthen trade setups.
- RSI & MACD for Confirmation: Employ momentum indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to confirm potential reversals within FVGs. Divergence between price and momentum can signal high-probability turning points when trading Fair Value Gap.
- Order Blocks & Supply/Demand Zones: Combine Fair Value Gaps with order blocks and supply/demand zones. FVGs often form in conjunction with these zones, further reinforcing the significance of these areas. An FVG within a strong order block or supply/demand zone can create powerful trading opportunities. This integration is key to advanced Fair Value Gap smc strategies.
Pro Tips for Advanced Traders
- Refined FVG Definition: Explore variations of FVG definitions, such as considering body-to-body gaps or wick-to-body gaps, to fine-tune your analysis of Fair Value Gap.
- FVG Confluence: Look for confluence of FVGs across multiple timeframes. A Fair Value Gap that aligns across different timeframes (e.g., daily and 4-hour) is generally more significant.
- Context is King: Always analyze FVGs within the broader market context. Consider the overall trend, market structure, and news events when evaluating Fair Value Gap setups.
- Backtesting is Non-Negotiable: Rigorously backtest any FVG strategy before deploying it in live trading. Understand its performance characteristics and optimize parameters for different market conditions.
Read More: choch in smart money concept
Advantages and Limitations of Fair Value Gaps in Trading
Like any trading tool or concept, Fair Value Gaps have both advantages and limitations. Understanding these aspects is crucial for realistic expectations and effective application of Fair Value Gap strategies.
Advantages (Pros) of Fair Value Gap
- Potential Reversal Zones: FVGs effectively highlight potential areas where price might reverse or find significant support/resistance. This can be invaluable for identifying high-probability entry points using Fair Value Gap.
- Price Action Synergy: FVGs seamlessly integrate with other price action trading strategies. They complement concepts like order blocks, supply/demand zones, and candlestick patterns, enhancing the overall analysis of Fair Value Gap setups.
- High Risk-Reward Setups: When properly identified and traded, FVGs can offer favorable risk-reward ratios. Entering trades within FVG zones with well-defined stop-losses can lead to significant profit potential relative to the risk taken in Fair Value Gap trading.
Limitations (Cons) of Fair Value Gap
- Not All Gaps Fill: A critical limitation is that not all Fair Value Gaps get filled. Price may sometimes move away from an FVG and continue in the original direction, leaving the gap unfilled. Relying solely on the assumption of gap filling can lead to losses when trading Fair Value Gap.
- Confirmation is Key: FVGs are not standalone signals. They require additional confirmation from other technical indicators, price action patterns, or fundamental analysis to increase their accuracy and reliability in Fair Value Gap strategies.
- False Signals in Volatility: In highly volatile markets, Fair Value Gaps can produce false signals. Rapid and erratic price movements can create numerous FVGs, some of which may be less significant or lead to whipsaws. Be cautious of Fair Value Gap signals during high volatility.
Risk Management When Trading Fair Value Gaps
Effective risk management is paramount when trading Fair Value Gaps, just as it is with any trading strategy. Proper risk management techniques will protect your capital and ensure long-term trading success in Fair Value Gap strategies.

Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels in Fair Value Gap Trading
- Stop-Loss Discipline: Always use stop-loss orders when trading FVGs. Place your stop-loss strategically outside the FVG zone to limit potential losses if the trade goes against you when trading Fair Value Gap.
- Take-Profit Targets: Define your take-profit levels before entering a trade. Use realistic targets based on market conditions, risk-reward ratios, and potential support/resistance zones in your Fair Value Gap trades.
Managing Risk-to-Reward Ratio in Fair Value Gap Strategies
- Aim for Favorable Ratios: Strive for a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2 or 1:3 when trading FVGs. This means you are aiming to make at least twice or three times your potential loss on each trade using Fair Value Gap.
- Calculate Risk Per Trade: Determine the percentage of your trading capital you are willing to risk on each trade (e.g., 1-2%). Size your positions accordingly to adhere to your risk management rules when trading Fair Value Gap.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in Fair Value Gap Trading
- Over-Leveraging: Avoid using excessive leverage when trading FVGs. Leverage magnifies both profits and losses. Start with conservative leverage and gradually increase as you gain experience and confidence in Fair Value Gap trading.
- Ignoring Confirmation: Don’t trade FVGs in isolation. Always seek confirmation from other technical tools and price action signals before entering a trade based on Fair Value Gap.
- Emotional Trading: Stick to your trading plan and avoid emotional decision-making. Fear and greed can lead to impulsive actions that violate your risk management rules when trading Fair Value Gap.
Backtesting and Demo Trading: Essential Preparation for Fair Value Gap
- Backtesting Rigorously: Before trading FVGs with real capital, thoroughly backtest your strategies on historical data. This will help you understand their performance characteristics and identify potential weaknesses of your Fair Value Gap strategy.
- Demo Account Practice: Practice trading FVGs on a demo account to familiarize yourself with the strategy and refine your execution skills in a risk-free environment before live Fair Value Gap trading.
Opofinance: Your Partner in Forex Trading
Looking for a reliable and regulated forex broker to implement your Fair Value Gap trading strategies? Consider Opofinance, an ASIC-regulated broker committed to providing a secure and efficient trading environment. Opofinance is a great choice for traders interested in Fair Value Gap strategies.
Opofinance Services:
- ASIC Regulation: Trade with confidence knowing Opofinance is regulated by the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC), a reputable regulatory body.
- MT5 Platform: Access the powerful MetaTrader 5 (MT5) platform, officially featured on the MT5 brokers list, equipped with advanced charting tools and indicators, including potential FVG indicators.
- Social Trading: Explore social trading features to learn from and potentially copy the trades of experienced traders, enhancing your understanding of market dynamics and FVG application. Social trading can be a valuable tool for learning Fair Value Gap strategies.
- Safe and Convenient Deposits & Withdrawals: Enjoy a seamless trading experience with a variety of safe and convenient deposit and withdrawal methods.

Ready to elevate your forex trading with a trusted broker?
Start Trading with Opofinance Today!
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Fair Value Gap is a powerful concept in technical analysis that unveils market inefficiencies and provides valuable insights into potential price movements. By understanding what is Fair Value Gap, how to identify a Fair Value Gap, and how to incorporate Fair Value Gap into your trading strategies, you can significantly enhance your ability to spot high-probability trading opportunities.
Remember that while FVGs offer numerous advantages, they are not foolproof and require confirmation and robust risk management. Embrace continuous learning, practice diligently, and always test your strategies before deploying them in live markets. With dedication and a solid understanding of Fair Value Gaps, you can unlock a new dimension of trading proficiency and navigate the financial markets with greater confidence. Mastering Fair Value Gap analysis can be a game-changer for your trading.
Key Takeaways
- Fair Value Gaps represent price inefficiencies caused by rapid price movements and unfilled orders.
- Identifying FVGs involves analyzing three consecutive candles and looking for non-overlapping wicks.
- Common FVG trading strategies include gap fill, continuation, and using FVGs as support/resistance.
- FVG indicators can automate detection, but combining them with other tools is crucial for effective Fair Value Gap trading.
- Risk management, including stop-loss orders and risk-reward ratios, is essential for FVG trading.
- Backtesting and demo trading are vital steps before live trading FVG strategies.
Can Fair Value Gaps be used in scalping strategies?
Yes, Fair Value Gaps can be applied to scalping, particularly on lower timeframes like the 1-minute or 5-minute charts. Scalpers often look for quick gap fills or short-term reactions within FVGs to capitalize on rapid price movements. However, scalping with FVGs requires even faster execution and tighter risk management due to the increased volatility on lower timeframes. When scalping with Fair Value Gap, speed and precision are paramount.
How do economic news events affect Fair Value Gaps?
Economic news events, especially high-impact releases, can significantly influence the formation and behavior of Fair Value Gaps. News events often trigger rapid price movements and increased volatility, leading to the creation of larger and more pronounced FVGs. Trading FVGs around news events can be potentially profitable but also carries higher risk due to increased market uncertainty and potential for whipsaws. Be cautious when trading Fair Value Gap around major news releases.
Are Fair Value Gaps more effective in trending or ranging markets?
Fair Value Gaps can be effective in both trending and ranging markets, but their application might differ. In trending markets, continuation strategies based on FVGs can be particularly potent as they align with the prevailing trend momentum. In ranging markets, gap fill strategies within the range boundaries can be effective as price tends to revert to the mean and fill inefficiencies within the range. The key is to adapt your FVG trading approach to the specific market conditions. Adapt your Fair Value Gap strategy to market conditions for optimal results.







