In the dynamic world of forex trading, staying ahead of the curve is crucial for success. Choosing the right forex trading broker can significantly impact your journey. Enter forex intermarket analysis, a powerful technique that can give traders a significant edge in predicting currency movements. This comprehensive guide will demystify intermarket analysis in forex, providing you with the tools and knowledge to potentially enhance your trading strategies and boost your profits.

Forex intermarket analysis is the study of relationships between various financial markets and how they influence currency movements. This approach recognizes that forex markets don’t exist in isolation but are interconnected with other asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and commodities. By understanding these correlations, traders can gain valuable insights into potential currency trends and make more informed trading decisions.
The key to effective forex intermarket analysis lies in recognizing and interpreting the complex web of relationships between different markets. Here’s a direct answer to what forex intermarket analysis entails:
- It involves examining the interactions between four primary markets: currencies, commodities, bonds, and stocks.
- Traders use this analysis to identify potential opportunities and risks in the forex market.
- It helps in understanding how economic events in one market can ripple through to affect currency valuations.
- Forex intermarket analysis enables traders to anticipate currency movements by observing trends in related markets.
By implementing intermarket analysis in forex trading, you can:
- Gain a broader perspective on market dynamics
- Identify potential trend reversals before they occur
- Improve the timing of your entries and exits
- Enhance your risk management strategies
Let’s dive deep into the world of forex intermarket analysis and discover how it can transform your trading approach.
Read More: 5-3-1 trading strategy
Understanding the Basics of Forex Intermarket Analysis
What is Forex Intermarket Analysis?
Forex intermarket analysis is a holistic approach to understanding currency movements by examining the relationships between various financial markets. This method recognizes that no market operates in isolation and that changes in one market can have significant impacts on others.
Key aspects of forex intermarket analysis include:
- Correlation analysis between different asset classes
- Identifying leading indicators in related markets
- Understanding global economic cycles and their impact on currencies
- Recognizing the interconnectedness of global financial systems
Read More: trading strategies for commodities
The Four Key Markets in Intermarket Analysis
To effectively implement intermarket analysis in forex trading, it’s crucial to understand the four main markets and their relationships:
1. Currency Market
The forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6.6 trillion. Currency pairs are influenced by a wide range of factors, including economic data, geopolitical events, and trends in other markets.
Key points about the currency market:
- It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week
- Major currency pairs account for the majority of trading volume
- Central bank policies play a significant role in currency valuations
2. Commodity Market
Commodities, especially gold and oil, have strong correlations with certain currencies. For example, the Canadian dollar (CAD) is often influenced by oil prices due to Canada’s significant oil exports.
Important commodity-currency relationships:
- Gold and the US Dollar (USD) often have an inverse relationship
- Oil prices can significantly impact currencies of oil-exporting nations
- Agricultural commodities can affect currencies of major agricultural exporters
3. Bond Market
Bond yields, particularly those of government bonds, can provide insights into economic expectations and interest rate trends. These factors directly impact currency valuations.
Key aspects of the bond market in intermarket analysis:
- Higher yields often attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency
- Yield differentials between countries can drive currency movements
- Bond markets often reflect economic health and inflation expectations
4. Stock Market
Equity markets often reflect investor sentiment and economic health. Strong stock markets can indicate risk appetite, which may influence currency pairs.
How stock markets impact forex:
- Risk-on sentiment often weakens safe-haven currencies
- Strong equity performance in a country can attract foreign capital, boosting the local currency
- Global stock market trends can indicate overall economic sentiment
Key Relationships in Forex Intermarket Analysis
Understanding the relationships between these markets is crucial for effective intermarket analysis in forex. Let’s explore some key correlations:

Currency and Commodity Relationships
- Oil and CAD: As mentioned earlier, the Canadian dollar often moves in tandem with oil prices. When oil prices rise, the CAD typically strengthens against other currencies, especially the USD.
- Gold and USD: Gold is often seen as a safe-haven asset, and its price typically has an inverse relationship with the US dollar. When the USD weakens, gold prices tend to rise, and vice versa.
- Copper and AUD: Australia is a major copper exporter, so the Australian dollar often correlates positively with copper prices.
Currency and Bond Yield Relationships
- USD and US Treasury Yields: Higher yields often lead to a stronger dollar, as they attract foreign investment. This relationship is particularly important for carry trades.
- JPY and Global Bond Yields: The Japanese yen typically strengthens when global bond yields fall, due to its status as a safe-haven currency. This relationship is often observed during periods of economic uncertainty.
- Interest Rate Differentials: Currencies of countries with higher interest rates tend to appreciate against those with lower rates, all else being equal.
Currency and Stock Market Relationships
- Risk-on vs. Risk-off: During periods of economic uncertainty, investors often move away from riskier assets (like stocks) and into safer currencies like the USD or JPY. Conversely, during periods of optimism, riskier currencies and assets tend to perform well.
- Carry Trade: In a strong equity market, investors may borrow low-yielding currencies to invest in higher-yielding assets, impacting currency valuations. This can lead to significant trends in currency pairs.
- Equity Market Performance and Local Currency: Strong performance in a country’s stock market can attract foreign investment, potentially strengthening the local currency.
Read More: Best Trading Strategy for GBPJPY
Implementing Forex Intermarket Analysis in Your Trading Strategy
Now that we understand the basics, let’s explore how to incorporate intermarket analysis into your forex trading approach:
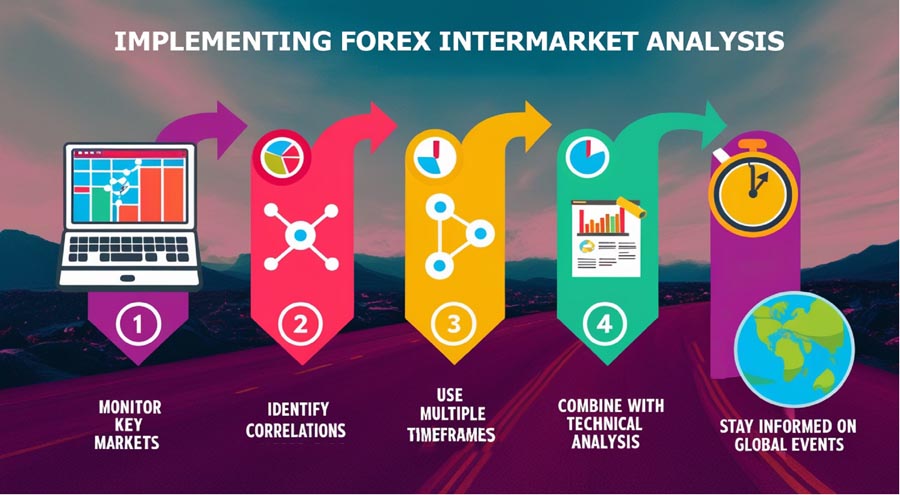
Step 1: Monitor Key Markets
Regularly track the performance of major stock indices, commodity prices, and bond yields. Tools like financial news websites and economic calendars can be invaluable for this purpose.
Recommended markets to monitor:
- Major stock indices (S&P 500, FTSE 100, Nikkei 225)
- Commodity prices (gold, oil, copper)
- Government bond yields (US Treasuries, German Bunds, Japanese Government Bonds)
Step 2: Identify Correlations
Look for consistent relationships between different markets. For example, if you notice that the AUD/USD pair tends to move in the same direction as the S&P 500, this could be a valuable correlation to track.
Tips for identifying correlations:
- Use correlation coefficients to quantify relationships
- Look for both positive and negative correlations
- Be aware that correlations can change over time
Step 3: Use Multiple Timeframes
Analyze correlations across different timeframes to identify both short-term and long-term trends. This can help you distinguish between temporary fluctuations and more significant shifts in market dynamics.
Suggested timeframes:
- Short-term: 1-hour and 4-hour charts
- Medium-term: Daily charts
- Long-term: Weekly and monthly charts
Step 4: Combine with Technical Analysis
Use intermarket analysis in conjunction with traditional technical analysis tools. For instance, if intermarket analysis suggests a bullish trend for a currency pair, look for confirming technical signals before entering a trade.
Complementary technical tools:
- Moving averages
- Relative Strength Index (RSI)
- Fibonacci retracements
- Chart patterns
Step 5: Stay Informed on Global Events
Keep abreast of major economic and geopolitical events that could impact multiple markets simultaneously. These events can often lead to significant shifts in intermarket relationships.
Key events to monitor:
- Central bank meetings and policy announcements
- Major economic data releases (GDP, inflation, employment reports)
- Geopolitical developments (elections, trade agreements, conflicts)
Advanced Techniques in Forex Intermarket Analysis
As you become more comfortable with the basics, consider incorporating these advanced techniques:
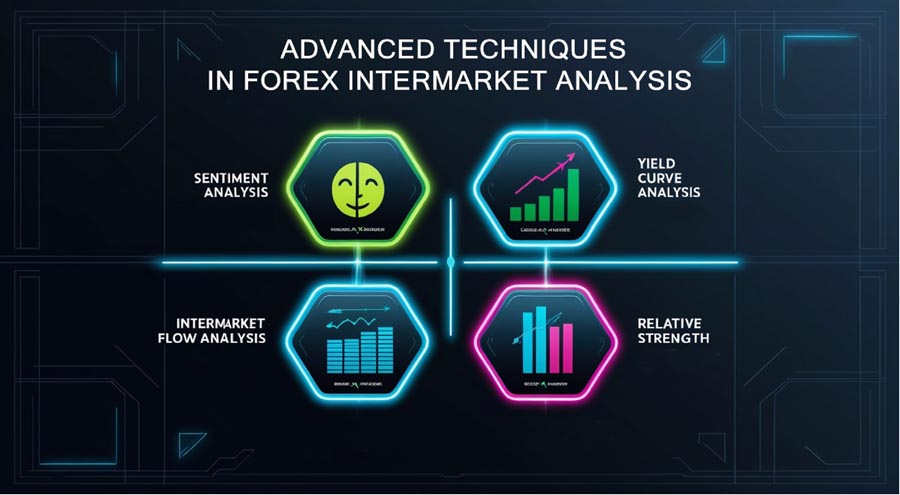
1. Sentiment Analysis
Monitor market sentiment across different asset classes to gauge overall risk appetite. Tools like the VIX (Volatility Index) can provide valuable insights.
Sentiment indicators to consider:
- Put/Call ratio
- Commitment of Traders (COT) reports
- Consumer confidence indices
2. Yield Curve Analysis
Study the yield curve of major economies to anticipate potential economic trends and their impact on currencies.
Key aspects of yield curve analysis:
- Normal vs. inverted yield curves
- Yield curve steepness
- Comparing yield curves across different countries
3. Intermarket Flow Analysis
Track the flow of capital between different markets to identify potential currency trends. For example, a significant inflow into US equities might signal strength for the USD.
Tools for flow analysis:
- Capital flow data from central banks
- Exchange-traded fund (ETF) flow data
- Cross-border investment reports
4. Relative Strength Comparisons
Compare the relative strength of different markets to identify potential trading opportunities. For instance, if commodities are outperforming stocks, commodity-linked currencies might be poised for gains.
Techniques for relative strength analysis:
- Ratio charts (e.g., Gold/S&P 500 ratio)
- Relative performance charts
- Relative strength indicators
Common Pitfalls in Forex Intermarket Analysis
While powerful, intermarket analysis is not without its challenges. Be aware of these potential pitfalls:
- Over-reliance on historical correlations: Market relationships can and do change over time. Always be prepared to reassess and adapt your analysis.
- Ignoring fundamental factors: Intermarket analysis should complement, not replace, fundamental analysis. Economic data and policy decisions remain crucial.
- Analysis paralysis: Don’t get overwhelmed by tracking too many markets simultaneously. Focus on the most relevant relationships for your trading style.
- Neglecting risk management: Even with strong intermarket signals, always adhere to sound risk management principles. Use stop-losses and proper position sizing.
- Misinterpreting short-term fluctuations: Not every correlated move is significant. Learn to distinguish between noise and meaningful trends.
- Failing to consider time lags: Some intermarket relationships may have delayed effects. Be patient and allow time for correlations to play out.
Conclusion
Forex intermarket analysis is a powerful tool for enhancing your trading strategy by providing a comprehensive view of market dynamics. By understanding relationships between currencies, commodities, bonds, and stocks, you can gain valuable insights into potential currency movements.
Remember, it’s not a guarantee of success but a sophisticated technique requiring continuous learning and adaptation. Stay disciplined, manage risks, and be prepared to adjust your strategy as markets evolve.
Key takeaways:
- Develop a systematic approach to monitoring multiple markets
- Educate yourself on global economic trends
- Combine intermarket insights with technical and fundamental analysis
- Prioritize risk management
Are you ready to elevate your forex trading with intermarket analysis? Start monitoring market relationships, practice your analysis skills, and gradually incorporate these insights into your trading decisions. Your journey to more informed, strategic, and potentially profitable forex trading begins now!
References: +
How often do intermarket relationships change, and how can I stay updated?
Intermarket relationships can evolve due to economic shifts or market changes. Stay updated by:
Regularly reviewing observed correlations
Following financial news and expert analyses
Using statistical tools to track correlations
Being prepared to adjust your strategy as needed
Can intermarket analysis be applied to all currency pairs equally?
While broadly applicable, effectiveness varies:
Major pairs have complex global relationships
Commodity currencies correlate strongly with specific commodities
Emerging market currencies are influenced by global risk sentiment
Tailor your approach to each currency pair’s characteristics
How can I incorporate intermarket analysis into my existing trading system?
Integrate gradually:
Use it as a confirming indicator initially
Increase its weight in decision-making as you gain confidence
Refine entry and exit points using intermarket insights
Create custom indicators combining intermarket data with technical indicators
Always backtest changes before trading live







