For most individual traders, there is absolutely no forex tax in Dubai. This zero-tax policy on personal income, capital gains, and forex profits is a primary reason the city has become a global magnet for traders. However, the rules can change depending on your residency status and whether you operate as a business. As a trader who made the move, I can tell you the landscape is incredibly favorable, but understanding the nuances is key. This guide will cover the essential laws on forex tax in Dubai for individuals, foreigners, and companies, including the specifics of operating within a forex tax in Dubai free zone.

Key Takeaways
- Zero Personal Tax: Individuals and sole traders in Dubai are not subject to income tax or capital gains tax on their forex trading profits. This is the biggest draw for retail traders.
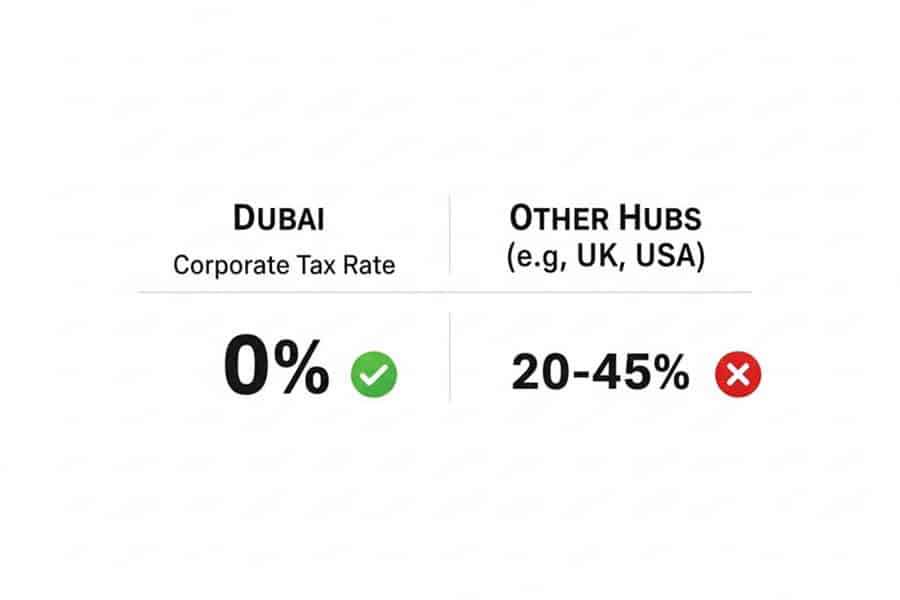
- Corporate Tax Exists: While personal trading is tax-free, forex trading businesses or companies established in the UAE mainland may be subject to a 9% corporate tax on profits exceeding AED 375,000 per year.
- Free Zones Offer Benefits: Setting up a company in a designated Free Zone, like the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) or Dubai Multi Commodities Centre (DMCC), can provide a 0% corporate tax rate, making it an ideal structure for professional trading entities. This is the main appeal of the forex tax in Dubai free zone model.
- Residency is Crucial: To benefit from Dubai’s tax laws, you must establish tax residency in the UAE. This prevents your home country from claiming tax on your global income, although international reporting standards like CRS still apply.
- Regulation is Strong: Forex trading is legal and well-regulated in Dubai by bodies like the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) and the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA), ensuring a secure trading environment.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and was last reviewed for accuracy in August 2025. Tax laws are subject to change and can be complex. The author is a financial market specialist, not a tax advisor. Please consult with a qualified tax professional or legal consultant in the UAE to receive advice tailored to your specific situation before making any financial decisions.
Forex Tax in Dubai – Essential Overview
Navigating the financial landscape of a new country is the first challenge every trader faces. When I first considered moving my trading operations, the question of forex tax in Dubai was my number one priority. The rumors of a tax-free haven seemed too good to be true. After extensive research and eventually making the move, I found that while the core benefit is real, the details are what truly matter for long-term success and compliance. This initial overview clarifies the foundational concepts you need to grasp.
What is Forex Trading?
At its core, forex (foreign exchange) trading is the act of speculating on the fluctuating values of currency pairs. You might buy the Euro (EUR) hoping it will strengthen against the US Dollar (USD), or sell the British Pound (GBP) if you believe it will weaken against the Japanese Yen (JPY). For traders like us, it’s a dynamic, 24/5 market driven by geopolitics, economic data, and market sentiment. The profits (or losses) are generated from these price movements. In Dubai, this activity is not just permitted; it’s actively supported by a robust financial infrastructure.
Is Forex Taxed in Dubai? (Current Laws, Myths & Facts)
This is the most critical question, and the answer is a clear and resounding “no” for most people. As of 2025, the UAE does not levy any personal income tax. This means that as an individual retail trader, your profits from forex trading are not taxed. There is no capital gains tax, no income tax return to file for your trading activities, and no complicated paperwork to track for personal tax purposes. This is a fact, not a myth.
The myth, however, is that this applies universally to everyone under all circumstances. The crucial distinction lies between personal activity and corporate activity. If you establish a formal business entity for your trading, then the new Corporate Tax law, introduced in 2023, could apply. The key is that the absence of a forex tax in Dubai primarily benefits individuals.
Why Dubai Attracts Forex Traders: Tax and Legal Advantages
From my experience, traders flock to Dubai for a powerful combination of reasons that go beyond just the tax benefits. While the lack of a forex tax in Dubai is the headline attraction, the supporting environment is what makes it a sustainable hub.
- Zero-Tax Environment: The most significant advantage. Keeping 100% of your trading profits provides an unparalleled boost to capital compounding compared to trading in high-tax jurisdictions like the UK, Germany, or Canada.
- World-Class Regulatory Framework: Dubai is not an unregulated “wild west.” Reputable brokers are licensed by either the mainland’s Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) or the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) within the DIFC free zone. This provides a layer of security and trust that is essential for serious traders.
- Strategic Location: Positioned between the Asian, European, and American trading sessions, Dubai’s time zone (GMT+4) allows traders to comfortably participate in the market’s most active hours without sacrificing sleep.
- Economic Stability and Modern Infrastructure: The UAE’s stable economy, pro-business government policies, and state-of-the-art infrastructure create a seamless living and working environment. High-speed internet, modern banking, and a cosmopolitan lifestyle are all part of the package.
Read More: Forex Tax in Dubai
Forex Tax for Individuals, Residents, and Expats
This is where the rubber meets the road for most people reading this. You’re likely an individual trader, perhaps an expat or someone considering becoming one, and you need to know exactly how the rules apply to you. The nuances of residency and international obligations are where many aspiring Dubai-based traders get confused. Let’s break down the forex tax in Dubai for individuals and how it impacts different groups.

Do Individuals Pay Tax on Forex Profits in Dubai?
Let me state this as clearly as possible: If you are a resident of the UAE and trading forex with your own personal funds as a retail trader, you do not pay any tax on your profits. This applies whether you make $1,000 or $1,000,000. The concept of personal income tax simply does not exist in the UAE federal framework. This is the cornerstone of the financial freedom that attracts so many of us here.
This principle holds true regardless of the online forex broker you use, whether they are based locally or internationally. The tax obligation (or lack thereof) is determined by your tax residency status, not the location of your broker. My personal setup involves accounts with multiple brokers, some in Europe and some regulated locally, and the tax treatment on my personal income remains the same: zero.
Residency & Taxation: What Counts as Your Tax Home?
This is the most critical piece of the puzzle. Simply having a bank account in Dubai or trading while on a tourist visa is not enough to claim tax-free status. To truly escape the tax net of your home country, you must become a tax resident of the UAE. If you don’t, your home country will likely still have the right to tax your worldwide income, including your forex profits.
To establish tax residency in the UAE, you generally need to meet one of these conditions:
- Spend 183 days or more in the UAE within a consecutive 12-month period.
- Obtain a residence visa (e.g., through employment, property investment, or by setting up a company) and have a permanent place of residence (like a rented or owned apartment) and an employment contract or business in the UAE.
- The “center of your financial and personal interests” is in the UAE.
Once you meet these criteria, you can apply for a Tax Residency Certificate (TRC) from the UAE’s Federal Tax Authority (FTA). This certificate is the official document you can present to the tax authorities in your home country to prove your new tax home and potentially benefit from Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs).
Foreigners & Expats: Reporting Forex Profits
For foreigners and expats, understanding the rules on forex tax in Dubai for foreigners involves a two-part equation: UAE law and your home country’s law. As we’ve established, the UAE side is simple—no tax. The complex part is your international obligation.
Many countries, like the United States, tax their citizens on worldwide income regardless of where they live. An American citizen moving to Dubai would still need to file a US tax return and report their forex profits. However, they may be able to use the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) to exclude a significant portion of their income, though this typically applies to earned income, and rules for investment profits can be different. Other countries have similar “exit tax” or trailing tax liability rules.
Furthermore, under the Common Reporting Standard (CRS), an automatic global information exchange system, your UAE bank and broker will likely report your financial account details to the tax authority of your home country (or country of citizenship). This makes it impossible to simply “hide” your profits. The key is not to hide, but to legally structure your affairs by properly establishing UAE tax residency. This is the legitimate path to enjoying the benefits of the forex tax in Dubai system.
Forex Tax For Businesses & Free Zones

While individual trading is straightforwardly tax-free, the game changes once your trading activities are structured as a formal business. This is a path many professional traders take to separate personal and business liabilities, manage larger capital pools, or create a more formal operational structure. Here, the introduction of UAE Corporate Tax in 2023 becomes a central consideration, and understanding the role of free zones is paramount. This section delves into the corporate side of forex tax in Dubai.
Tax Implications for Corporate Traders and Companies
If you set up a Limited Liability Company (LLC) on the UAE mainland to conduct your forex trading activities, your company is now a distinct legal entity. As such, it falls under the purview of the UAE’s Corporate Tax law. The law states:
- A 0% tax rate applies to annual taxable profits up to AED 375,000 (approximately $102,000 USD).
- A 9% tax rate applies to annual taxable profits that exceed AED 375,000.
This means that if your trading company makes a profit of AED 500,000 in a year, the first AED 375,000 is taxed at 0%, and the remaining AED 125,000 is taxed at 9% (resulting in a tax bill of AED 11,250). While 9% is still extremely competitive globally, it’s a stark difference from the 0% tax enjoyed by individual traders. This is a critical factor when deciding whether to incorporate your trading on the mainland.
Example: Corporate Tax Calculation
Let’s imagine your mainland trading company, “Dubai Pro Traders LLC,” has a successful year.
- Total Trading Profit: AED 1,200,000
- Taxable Profit Threshold: AED 375,000
- Profit Subject to 9% Tax: AED 1,200,000 – AED 375,000 = AED 825,000
- Corporate Tax Due: AED 825,000 * 9% = AED 74,250
This demonstrates how the tax applies only to the portion of profit above the threshold, not the entire amount.
How Dubai Free Zones Affect Forex Taxation
This is where it gets interesting for serious trading businesses. Dubai and the broader UAE have numerous “Free Zones,” which are special economic areas designed to attract foreign investment with their own independent regulatory frameworks. Setting up in one of these zones can change the tax equation completely. The key benefit is that a company established in a Free Zone (a “Free Zone Person”) can potentially qualify for a 0% Corporate Tax rate, even on profits exceeding AED 375,000.
To qualify for this 0% rate, the Free Zone company must maintain adequate substance in the UAE and derive “Qualifying Income.” While the specifics can be detailed, income from trading in commodities (which often includes currency derivatives) on a recognized exchange is typically considered Qualifying Income. This makes a forex tax in Dubai free zone structure the ultimate goal for many professional trading firms. Prominent free zones for financial activities include:
- Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC): The premier financial hub in the region, with its own internationally recognized legal system and regulator (the DFSA). It’s the gold standard for financial service companies.
- Dubai Multi Commodities Centre (DMCC): A popular and versatile free zone that licenses a wide range of activities, including proprietary trading in commodities and currencies.
- Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM): Abu Dhabi’s equivalent to the DIFC, offering a similar world-class regulatory environment for financial businesses.
Company Setup: Zero-Tax Structures for Forex Activity
Based on my observations and discussions with other professional traders, the choice of structure boils down to your scale and objectives:
- Individual Trader (No Company): The simplest path. No setup costs, no corporate tax. You live in Dubai as a resident and trade your personal account. This is the best route for most retail traders and the purest form of enjoying the zero forex tax in Dubai.
- Free Zone Company (Proprietary Trading): The optimal structure for serious, full-time traders who want a formal entity. You form a company in a free zone like DMCC or ADGM. The company trades its own capital. This structure provides limited liability and access to the 0% corporate tax regime, making it the most efficient model for a forex tax in Dubai free zone strategy.
- Mainland LLC: This is generally less attractive for a pure trading business due to the 9% corporate tax on profits over the threshold. It’s more suitable for businesses that need to transact directly with the UAE mainland economy, which isn’t usually a requirement for a forex trader.
Choosing the right path requires careful consideration of setup costs, annual renewal fees, visa eligibility, and compliance requirements associated with each structure.
Read More: Tax Implications of Forex Trading
Forex Trader Tax Compliance in Dubai

While the phrase “tax-free” sounds liberating, it doesn’t mean “rule-free.” Operating successfully as a forex trader in Dubai requires a clear understanding of the regulatory environment and compliance obligations. From my experience, being diligent with compliance is what separates a sustainable career from a risky venture. The authorities here value transparency and adherence to international standards. Ignoring these rules is the fastest way to undermine the benefits of the zero forex tax in Dubai.
UAE Regulatory Bodies & Financial Licensing
The UAE’s financial market is overseen by strong, reputable regulators. Knowing who they are and what they do is essential for choosing a trustworthy regulated forex broker.
- Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA): This is the federal regulator responsible for licensing and supervising financial markets on the UAE mainland. Brokers with an SCA license are authorized to serve clients across the UAE.
- Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA): The DFSA is the independent regulator for the DIFC free zone. It operates based on a legal framework modeled on international best practices, similar to those in London and New York. DFSA-regulated brokers are held to exceptionally high standards.
- Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM): Similar to the DIFC, the ADGM has its own financial regulator, the Financial Services Regulatory Authority (FSRA), which also maintains top-tier international standards.
As a trader, your primary interaction with these bodies is indirect—by choosing to trade with a broker they license. Doing so ensures your funds are segregated and you have recourse in case of disputes.
KYC, AML, and Record-Keeping Requirements
Even though you may not file a personal tax return, you are still subject to strict Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. When you open an account with a broker or a bank in Dubai, you will need to provide:
- Proof of Identity (Passport)
- Proof of Residence (Utility bill, tenancy contract)
- Information on the Source of Your Funds/Wealth
This is a global standard, and Dubai enforces it rigorously to maintain its reputation as a legitimate financial center. For traders, this means keeping good records of your financial activities is crucial. Even without a tax obligation, having a clear paper trail of your capital sources and trading performance is a best practice, especially if you plan to move large sums of money or set up a corporate structure later on. The absence of a forex tax in Dubai for individuals does not mean an absence of financial scrutiny.
Corporate vs. Personal Taxation Thresholds
To summarize the key compliance threshold: the line is drawn at your operational structure.
- Personal Trading: No profit threshold. Your earnings are not considered taxable income. This applies to forex tax in Dubai for foreigners who have established residency.
- Corporate Trading (Mainland): A tax threshold of AED 375,000 in annual net profit. Anything above this is taxed at 9%.
- Corporate Trading (Qualifying Free Zone): A potential 0% tax rate, provided the company meets substance and “Qualifying Income” requirements.
This distinction is the single most important compliance point to understand regarding the forex tax in Dubai framework.
Advantages & Caveats of Zero-Forex-Tax in Dubai
The allure of a zero-tax environment is powerful, but a successful international trading career is built on a balanced perspective. It’s crucial to weigh the incredible advantages against the potential pitfalls and international responsibilities that come with being a global citizen. I’ve seen traders thrive here, but I’ve also seen some get caught off guard by rules they overlooked. Here’s a pragmatic look at the pros and cons.
Global Comparisons: Dubai vs. Other Major Hubs
To truly appreciate what Dubai offers, it helps to see it in context. A simple comparison shows why the lack of a forex tax in Dubai is such a game-changer.
| Feature | Dubai (UAE) | United Kingdom | United States |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Tax on Forex | 0% (No income or capital gains tax) | Capital Gains Tax (10-20%) or Income Tax (20-45%) depending on activity level. | Section 988 (ordinary income rates) or Section 1256 (60/40 rule, lower blended rate). Can be complex. |
| Corporate Tax Rate | 9% (on profits > AED 375k), 0% in Free Zones. | 25% | 21% (Federal) + State Taxes |
| Annual Filing | None for individuals. Required for corporations. | Required for both individuals (Self Assessment) and corporations. | Required for both individuals and corporations. |
| Regulatory Environment | Strong (SCA, DFSA) | Very Strong (FCA) | Very Strong (CFTC, NFA) |
This table makes it visually clear. The capital you save from the zero forex tax in Dubai can be reinvested into your trading account, accelerating your growth at a rate that’s mathematically impossible in most other developed countries.
Potential Pitfalls: International Reporting and Double Taxation
The biggest mistake a new expat trader can make is thinking that moving to Dubai makes them invisible to their home country’s tax authority. As mentioned, the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) ensures that financial information flows between countries.
The key is to properly sever your tax ties with your previous country of residence. This might involve:
- Selling your primary residence or renting it out long-term.
- Closing the majority of your bank accounts and credit cards there.
- Spending less than the statutory number of days required to be considered a resident.
If you don’t do this correctly, you could be liable for double taxation—where both the UAE (if you’re a company) and your home country try to tax the same income. While the UAE has over 140 Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs), relying on them is more complicated than simply establishing clean tax residency in Dubai from the outset.
Read More: What Is Prop Firm in Forex
Recent and Upcoming Tax Law Changes or Risks
The UAE financial landscape is evolving. The introduction of Corporate Tax in 2023 was a landmark change. While there are currently no plans to introduce a personal income tax, traders must stay informed. The government’s revenue needs could change, and global pressures for tax harmonization (like the OECD’s global minimum tax initiative) could influence future policies.
The risk is low in the short to medium term, but it’s not zero. This is why I always advise fellow traders to structure their affairs correctly from day one. A proper forex tax in Dubai free zone setup, for example, is more resilient to potential changes than a less formal arrangement. Always keep an eye on announcements from the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Authority.
Elevate Your Trading with a Leading Broker
Choosing the right broker is as important as your tax strategy. Opofinance, regulated by ASIC, provides the tools and security serious traders demand. Benefit from a comprehensive trading ecosystem designed for performance and peace of mind.
- Advanced Trading Platforms: Choose from MT4, MT5, cTrader, and the proprietary OpoTrade platform.
- Innovative AI Tools: Gain an edge with the AI Market Analyzer, AI Coach, and instant AI Support.
- Flexible Trading Styles: Explore opportunities with Social Trading and Prop Trading programs.
- Secure & Flexible Transactions: Enjoy safe and convenient deposits and withdrawals, including crypto payments with zero fees.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the landscape for forex tax in Dubai remains one of the most attractive in the world. For individual traders who establish residency, the 0% tax rate on profits is a powerful and legitimate advantage that can significantly accelerate wealth creation. For businesses, the path through a forex tax in Dubai free zone offers a compliant way to achieve a similar 0% tax outcome. The key is to act with intention—understand the rules, establish proper residency, and choose the right structure for your scale of operations.
Can I trade forex in Dubai on a tourist visa?
Yes, you can physically trade while on a tourist visa, but your profits would likely still be taxable in your home country. To legally benefit from the zero-tax environment, you must establish UAE tax residency.
Is there a difference in tax treatment between forex, crypto, and stocks?
For individual residents in Dubai, there is no difference. Profits from trading forex, cryptocurrencies, and stocks are all considered personal capital gains and are not taxed.
How much does it cost to set up a free zone company for trading?
Costs vary by free zone and package, but you can typically expect setup costs to range from $5,000 to $15,000 USD, with annual renewal fees thereafter. This usually includes the trade license and visa eligibility.
Do I need a local UAE bank account to trade?
While not strictly necessary to trade (you can fund an international broker from anywhere), having a local UAE bank account is essential for establishing residency and managing your finances within the country seamlessly and cost-effectively.
Will the UAE introduce an income tax in the future?
While there are no current official plans to introduce a personal income tax, it’s impossible to predict long-term government policy. However, the UAE’s economic model has long been built on its tax-free appeal, making any such change a major policy shift.
Is Forex Trading Legal in Dubai?
Yes, absolutely. Forex trading is 100% legal in Dubai and the UAE. It is a well-regulated activity, with strong oversight from bodies like the SCA and DFSA to protect traders and ensure market integrity. You can trade with confidence, provided you use a reputable and licensed forex trading broker.
Are Forex Earnings Repatriation-Friendly?
Yes. The UAE has no currency controls. You are free to move your profits out of the country to your home bank account or anywhere else in the world. As a trader, this financial freedom is paramount. You can deposit funds into your trading account and withdraw your earnings without government restrictions, making capital management seamless.
Does Corporate Tax Apply to High-Volume Traders?
This is a common point of confusion. The corporate tax is not based on trading volume, number of trades, or even revenue. It applies to net profit and only if you are operating as a registered corporate entity on the mainland. A high-volume individual trader making millions in profit still pays 0% tax. A company on the mainland making over AED 375,000 in profit pays 9%. The structure, not the volume, is the determining factor.







