ICT smart money reversal is a powerful forex trading strategy that allows traders to identify and capitalize on price movements initiated by institutional players. As an online forex broker, we’ve seen firsthand how mastering this approach can dramatically improve trading results. At its core, ICT smart money reversal involves recognizing key market structures and order flow patterns that indicate where large institutional traders, or “smart money,” are likely to enter or exit the market.

This advanced technique, rooted in the Inner Circle Trader (ICT) methodology, provides traders with a framework to anticipate potential market turning points. By understanding concepts such as order blocks, liquidity pools, and fair value gaps, traders can align their positions with the actions of these influential market participants. This alignment often leads to more accurate trade entries, better risk management, and potentially higher profitability.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the intricacies of ICT smart money reversal. We’ll explore its key components, discuss practical implementation strategies, and examine critical market reversal patterns. Whether you’re a novice trader looking to enhance your skills or an experienced professional seeking to refine your approach, this article will equip you with the knowledge and tools to leverage ICT smart money reversal in your forex trading journey.
Understanding ICT Smart Money Reversal
What is ICT Smart Money Reversal?
ICT smart money reversal is a sophisticated trading concept developed by the Inner Circle Trader (ICT) that aims to identify and capitalize on price reversals initiated by large institutional traders. These institutional players, backed by substantial capital and market influence, have the power to move markets significantly.
The core principle behind this strategy is that retail traders can benefit by aligning their trades with the actions of these institutional players. By identifying key levels where smart money is likely to enter or exit the market, traders can position themselves for potentially profitable trades.
Key Components of ICT Smart Money Reversal
- Order Blocks: Areas on the chart where significant buying or selling pressure has occurred, often resulting in a sharp price movement.
- Liquidity Pools: Zones of concentrated stop losses or pending orders, which smart money often targets to fuel their trades.
- Fair Value Gaps (FVGs): Imbalances in price that occur when the market moves rapidly, leaving unfilled orders behind.
- Breaker Blocks: Areas where price has broken through a significant level and is likely to return to test that level.
- Mitigation Points: Levels where price is expected to return to “mitigate” or fill orders left behind during rapid price movements.
Eight Critical ICT Market Reversal Patterns

Understanding and recognizing specific market reversal patterns is crucial for successful implementation of ICT smart money reversal strategies. Let’s explore eight critical patterns that traders should be aware of:
1. Previous Day High/Low Reversals
This pattern involves identifying potential reversals when the market breaches the previous day’s extreme levels.
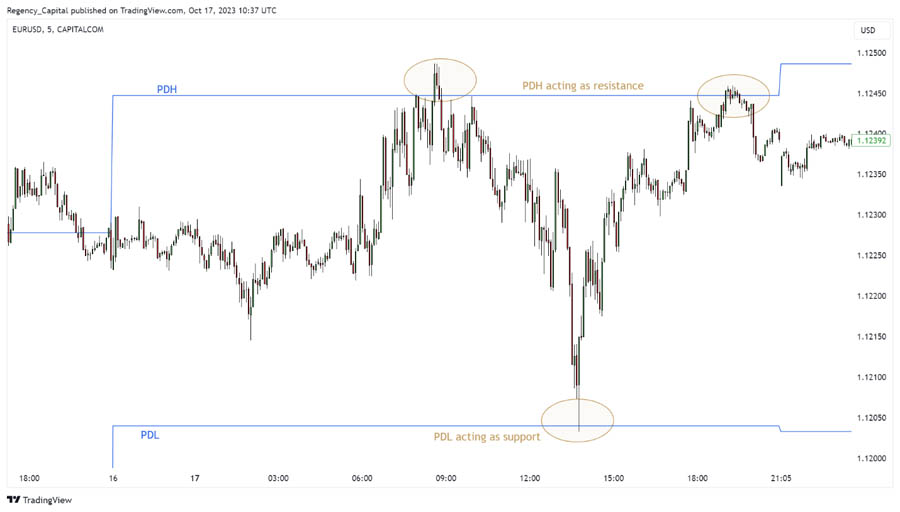
Key characteristics:
- Price moves beyond the previous day’s high or low
- A quick spike followed by immediate rejection
- Often occurs in conjunction with higher timeframe levels
Trading approach:
- Look for momentum as price approaches the previous day’s extreme
- Enter trades when price shows clear rejection from these levels
- Set stops beyond the newly formed swing high/low
2. Weekly Range Breakout Reversals
These reversals occur when the market breaks out of the current week’s range, only to reverse sharply.
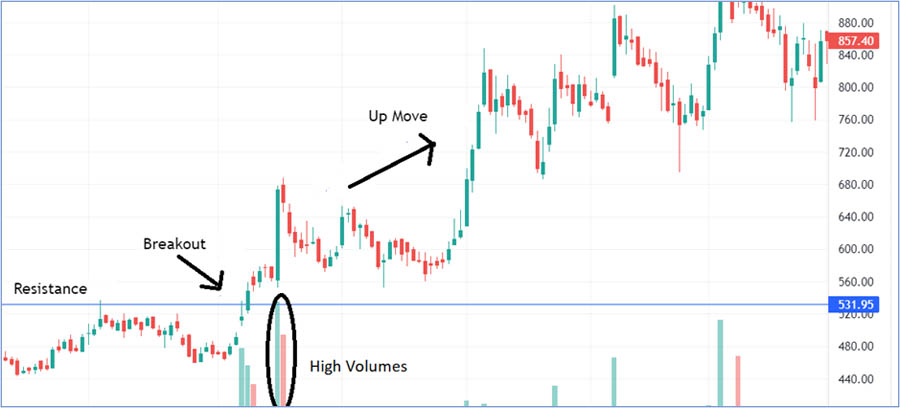
Identifying factors:
- Price breaks above the week’s high or below the week’s low
- Strong rejection candles form after the breakout
- Often coincides with significant support/resistance levels
Implementation strategy:
- Monitor weekly high and low levels
- Look for false breakouts, especially late in the trading week
- Enter trades when price action confirms the reversal
3. Monthly Pivot Point Reversals
Monthly pivot points are significant levels where institutional traders often initiate reversals.
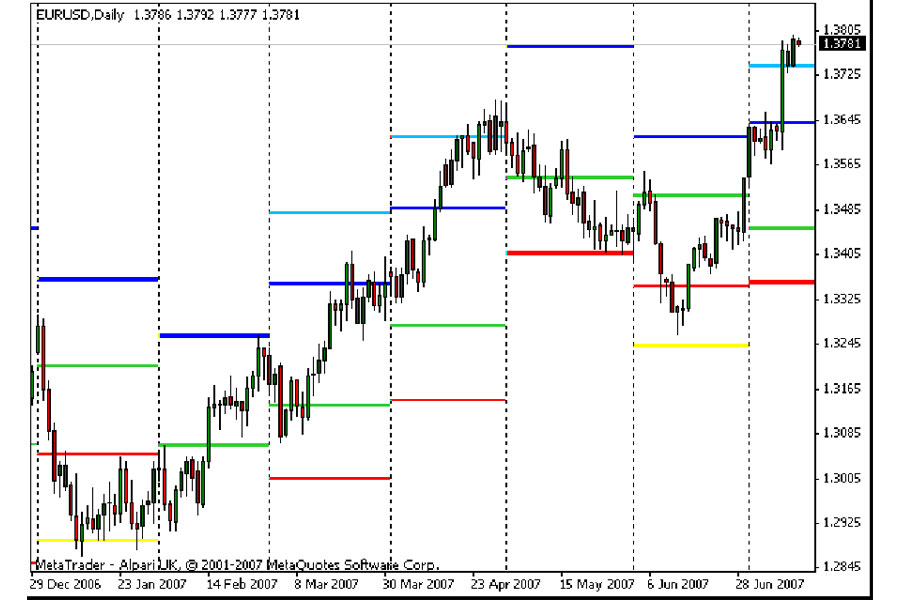
Key points:
- Price reaches or slightly overshoots monthly pivot levels
- Strong rejection candles form at these levels
- Often accompanied by divergence on momentum indicators
Trading approach:
- Calculate and plot monthly pivot points
- Watch for price reaction as it approaches these levels
- Enter trades when clear reversal signals appear
4. Liquidity Grab Reversals
These reversals occur when smart money manipulates price to grab liquidity before reversing the market.
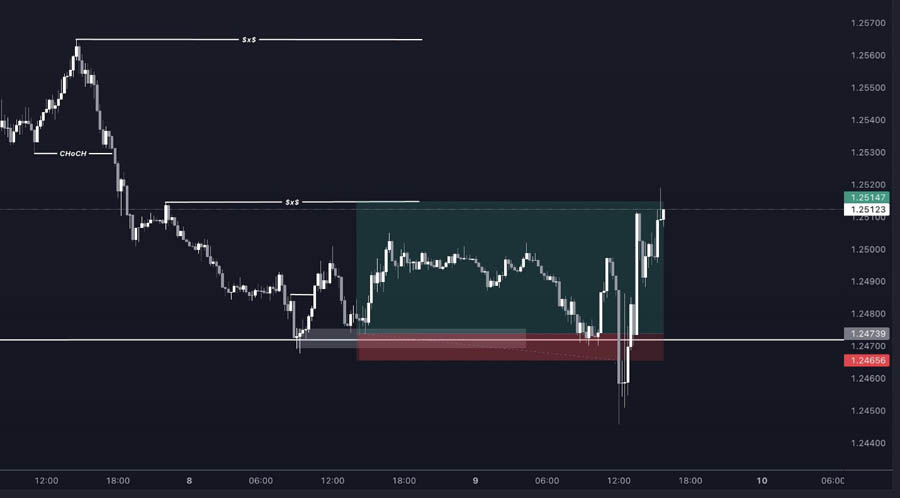
Characteristics:
- Sharp price movement beyond a key level
- Quick reversal after stop losses are triggered
- Often occurs at the beginning of major trading sessions
Strategy implementation:
- Identify areas of concentrated stop losses
- Look for sharp price movements beyond these areas
- Enter trades when price shows clear signs of reversal
Read More: Mastering ICT Trend Reversal
5. Order Block Reversal Pattern
This pattern forms when price returns to a significant order block and shows signs of reversal.
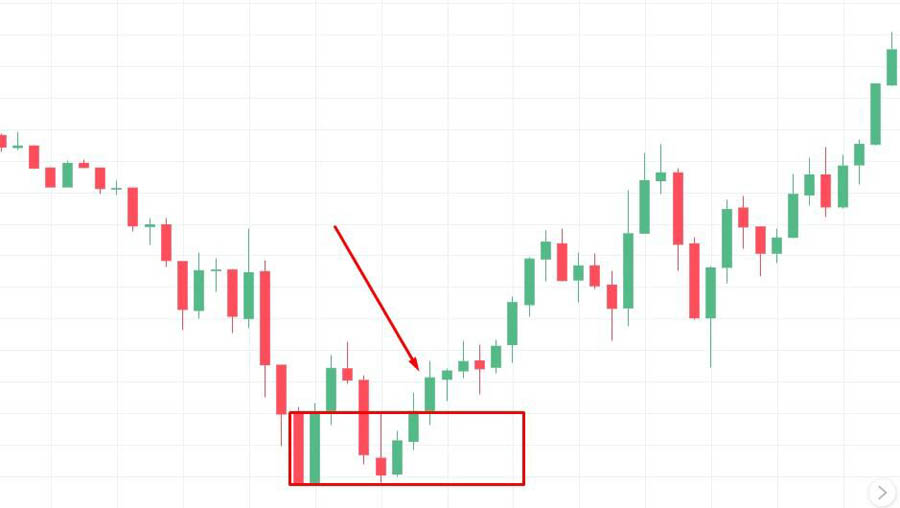
Key elements:
- Price retraces to a previously identified order block
- Strong rejection candles form at the order block
- Often occurs in line with the higher timeframe trend
Trading approach:
- Identify and mark significant order blocks
- Monitor price action as it returns to these levels
- Enter trades when rejection is confirmed with strong candles
6. Fair Value Gap (FVG) Reversals
FVG reversals occur when price returns to fill a fair value gap and then reverses.
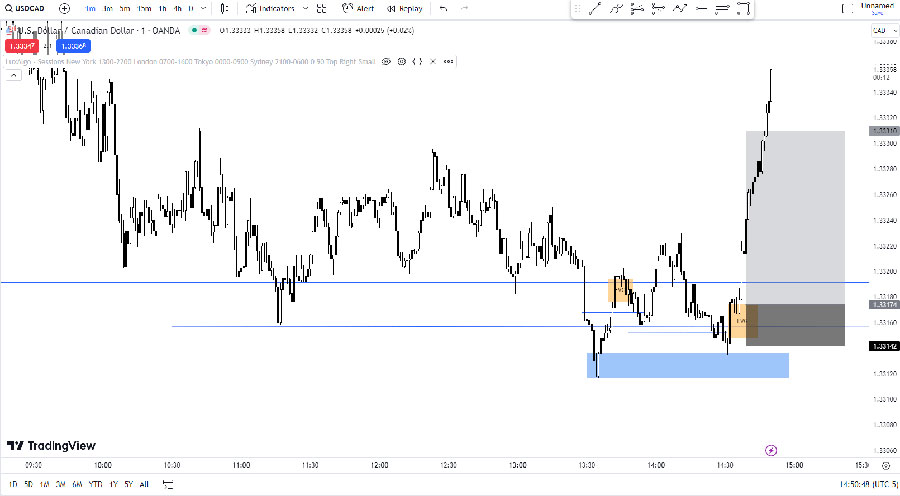
Identifying factors:
- Price moves rapidly, creating a gap in the chart
- Price returns to fill this gap
- Strong rejection occurs once the gap is filled
Implementation strategy:
- Identify FVGs on your charts
- Watch for price to return to these areas
- Enter trades when price shows clear rejection from the FVG
7. Institutional Trap Reversals
These reversals occur when smart money sets up a trap to catch retail traders on the wrong side of the market.
Characteristics:
- Price makes a convincing move in one direction
- A sudden, sharp reversal traps traders
- Often occurs at key support/resistance levels
Trading approach:
- Identify potential trap setups at key levels
- Look for divergence between price and volume/momentum
- Enter trades when the trap is sprung and reversal is confirmed
8. Session Overlap Reversals
These reversals take advantage of increased volatility during the overlap of major trading sessions.
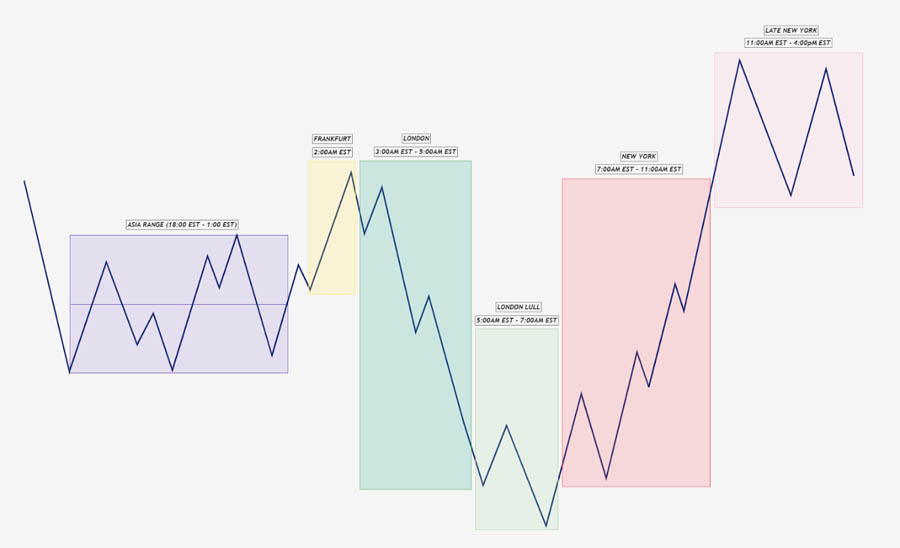
Key points:
- Occurs during the overlap of London/New York sessions
- Often accompanied by increased volume and volatility
- Can lead to significant trend reversals
Implementation strategy:
- Focus on major currency pairs during session overlaps
- Look for strong rejection candles or engulfing patterns
- Enter trades when clear reversal signals appear
By mastering these eight critical ICT market reversal patterns, traders can significantly enhance their ability to identify and capitalize on high-probability reversal opportunities in the forex market.
Implementing ICT Smart Money Reversal Strategies

To effectively implement ICT smart money reversal strategies, it’s crucial to understand and apply smart money concepts techniques. These techniques are designed to help traders identify and capitalize on the actions of institutional players. Let’s explore some key strategies:
1. Liquidity Engineering
Liquidity engineering involves identifying areas where large amounts of liquidity (stop losses and pending orders) are concentrated. Smart money often targets these areas to initiate significant moves.
How to implement:
- Identify swing highs and lows on higher time frames
- Look for areas just above recent highs or below recent lows
- Pay attention to round numbers (e.g., 1.3000, 1.3500) as potential liquidity zones
2. Order Block Analysis
Order blocks are areas on the chart where significant buying or selling has occurred, often preceding a strong move in price.
Implementation steps:
- Identify the last candle before a strong move (this is the order block)
- Mark the high and low of this candle
- Watch for price to return to this area for potential reversals or continuations
3. Fair Value Gap Trading
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) represent areas where price has moved quickly, leaving unfilled orders behind. These gaps often act as magnets, pulling price back to “fill” the missing orders.
How to trade FVGs:
- Identify gaps between the close of one candle and the open of the next
- Look for price to return to these areas
- Consider entering trades when price reacts at FVG levels
4. Breaker Block Strategy
Breaker blocks are formed when price breaks a significant support or resistance level. These areas often become important reversal points.
Strategy implementation:
- Identify areas where price has broken through a key level
- Watch for price to return to these levels
- Look for rejection or acceptance at breaker blocks for potential trade entries
5. Mitigation Point Trading
Mitigation points are levels where price is likely to return to fill orders left behind during rapid movements. These points often coincide with significant swing highs or lows.
Trading mitigation points:
- Identify swing highs and lows on higher time frames
- Watch for price to return to these levels
- Look for rejection or acceptance at mitigation points for potential trades
Read More: Master ICT High-Probability Scalping
6. Multi-Time Frame Analysis
Combining multiple time frames is crucial in ICT smart money reversal trading. It helps traders understand the broader market context and identify high-probability setups.
Implementation:
- Use higher time frames to identify the overall trend and key levels
- Drop down to lower time frames to fine-tune entries and exits
- Ensure that your trades align with the higher time frame structure
Risk Management in ICT Smart Money Reversal Trading
Effective risk management is paramount when implementing ICT smart money reversal strategies:
- Set Proper Stop Losses: Place stops beyond key levels or order blocks
- Use Appropriate Position Sizing: Never risk more than 1-2% of your account on a single trade
- Implement Asymmetric Risk-Reward: Aim for a minimum risk-reward ratio of 1:2 or better
- Use Trailing Stops: Move your stop loss to lock in profits as the trade moves in your favor
- Take Partial Profits: Consider closing part of your position at predetermined levels
Advanced ICT Smart Money Concepts
Institutional Order Flow
Understanding institutional order flow is crucial in ICT smart money reversal trading. This involves identifying areas where large players are likely to enter or exit the market.
Key considerations:
- Look for areas of high volume and price rejection
- Pay attention to key psychological levels and round numbers
- Analyze the market structure to identify potential accumulation or distribution zones
Wyckoff Method Integration
The Wyckoff Method complements ICT smart money concepts by providing a framework for understanding market cycles and institutional behavior.
Wyckoff phases to consider:
- Accumulation
- Markup
- Distribution
- Markdown
By identifying these phases, traders can align their strategies with the actions of smart money.
OpoFinance Services: Your Trusted ASIC-Regulated Forex Broker
When implementing ICT smart money reversal strategies, having a reliable and regulated forex broker is crucial. OpoFinance, an ASIC-regulated broker, offers a comprehensive suite of services tailored to meet the needs of both novice and experienced traders.
With OpoFinance, you can benefit from:
- Advanced Trading Platforms: Access cutting-edge platforms optimized for ICT smart money reversal analysis.
- Competitive Spreads: Enjoy tight spreads to maximize your trading potential.
- Educational Resources: Enhance your ICT smart money reversal knowledge with expert-led webinars and tutorials.
- Robust Risk Management Tools: Implement effective risk management with advanced order types and tools.
- Social Trading Service: Leverage the wisdom of successful traders through OpoFinance’s innovative social trading feature.
By choosing OpoFinance as your forex broker, you’re not just getting a trading platform – you’re gaining a partner committed to your success in mastering ICT smart money reversal strategies.
Read More: Mastering ICT Stop Runs
Conclusion
Mastering ICT smart money reversal strategies can significantly enhance your forex trading performance. By understanding the key concepts, such as order blocks, liquidity pools, and fair value gaps, and recognizing the eight critical market reversal patterns, you can align your trades with the actions of institutional players and potentially increase your profitability.
Remember, successful implementation of ICT smart money reversal requires practice, patience, and discipline. Continuously refine your skills, stay updated with market dynamics, and always prioritize risk management in your trading approach.
As you embark on your journey to master ICT smart money reversal, consider leveraging the advanced tools and resources offered by regulated brokers like OpoFinance. With the right knowledge, tools, and support, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the forex markets and capitalize on smart money reversals.
How long does it typically take to become proficient in ICT smart money reversal trading?
Becoming proficient in ICT smart money reversal trading varies from person to person, but generally, it takes several months to a year of consistent practice and study. The key is to focus on understanding the underlying principles rather than just memorizing patterns. Start by paper trading to gain experience without risking real capital, then gradually transition to live trading with small positions as you build confidence.
Can ICT smart money reversal strategies be applied to other financial markets besides forex?
Yes, ICT smart money reversal strategies can be applied to various financial markets, including stocks, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. The underlying principles of order flow and institutional trading behavior are relevant across different asset classes. However, it’s important to note that each market has its own unique characteristics, so you may need to adjust your approach slightly depending on the specific market you’re trading.
Are there any specific economic indicators that complement ICT smart money reversal analysis?
While ICT smart money reversal primarily focuses on price action and market structure, certain economic indicators can complement this analysis. Key indicators to consider include:
Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) for USD pairs
Interest rate decisions from central banks
GDP reports
Consumer Price Index (CPI) for inflation data
These indicators can provide context for potential smart money movements and help you anticipate significant market reactions. However, always prioritize your ICT analysis and use these indicators as supplementary information rather than primary decision-making tools.







