Inflation is a silent force that can either erode wealth or create massive trading opportunities. For forex traders, it plays a crucial role in shaping currency values, influencing exchange rates, and driving central bank policies. But how exactly does inflation impact forex market movements?

When inflation rises unexpectedly, it disrupts market stability, causing wild fluctuations in currency prices. Traders often struggle to predict central bank reactions, leading to increased volatility and uncertainty in the forex market.
This uncertainty can result in rapid losses if traders fail to anticipate inflation-driven shifts. Without the right knowledge, even experienced traders can find their strategies upended by inflation-fueled interest rate changes or sudden capital outflows.
Understanding the inflation impact on forex market can help traders make informed decisions, manage risk, and capitalize on profitable trends. Whether it’s identifying high-inflation economies, tracking central bank policies, or choosing a regulated forex broker for a secure trading environment, mastering inflation’s effects is key to staying ahead.
In this article, we’ll explore how inflation influences currency movements, how central banks react, and the best strategies to trade during inflationary cycles. Let’s dive in.
Understanding the Basics of Inflation
Inflation simply means a general increase in prices over time, causing each unit of currency to buy fewer goods and services. But while the definition is straightforward, the forces that drive inflation are more complex. Before you can truly grasp the inflation impact on forex market, it’s essential to know what causes inflation and how it integrates into the broader economy.
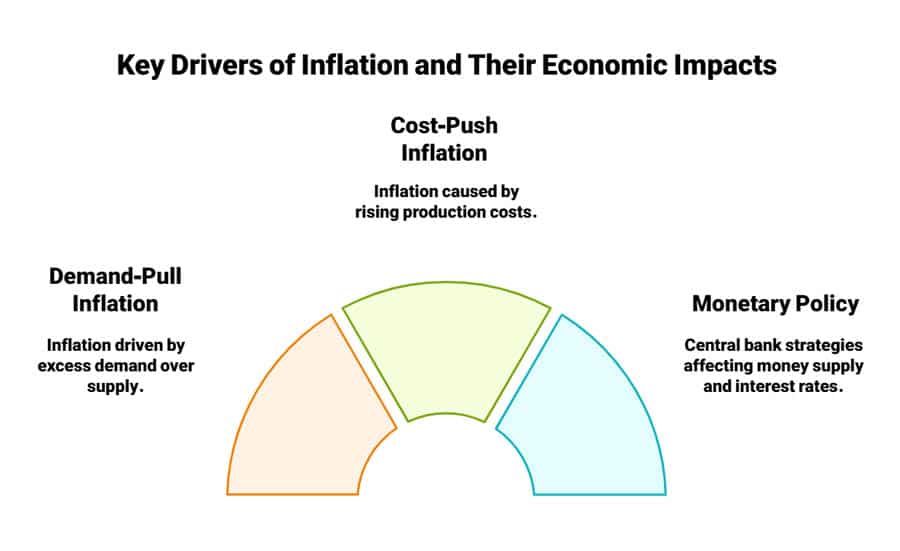
Demand-Pull and Cost-Push
Two primary drivers of inflation stand out:
- Demand-Pull Inflation: Occurs when demand for goods and services outstrips supply. When consumers and businesses have excess purchasing power, they compete for limited resources, driving up prices.
- Cost-Push Inflation: Happens when costs of production—such as labor or raw materials—go up. Producers transfer these extra costs to consumers via higher prices.
In reality, both demand-pull and cost-push factors can operate simultaneously. A booming economy might experience rising wages (fueling demand) while grappling with expensive raw materials (increasing production costs). When these two forces converge, inflation can accelerate quickly.
Monetary Policy and Money Supply
Inflation is also tied to how much money circulates in an economy relative to its output. If a central bank keeps interest rates too low for too long or pumps excessive liquidity into the market (for instance, through quantitative easing), it could stoke inflation. More money chasing the same set of goods leads to higher prices.
- Loose Monetary Policy: Encourages spending and investment, which is great for growth but can lead to higher inflation if not calibrated properly.
- Tight Monetary Policy: Restricts money supply, often lifting interest rates to cool an overheating economy and curb inflation.
Why Forex Traders Should Care
Currencies are priced relative to one another. A surge in a country’s inflation often devalues its currency on the global market. That’s because:
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Investors want currencies that hold their value over time, so if they see inflation eroding this value, they may shift to more stable currencies.
- Central Bank Responses: When inflation rises, markets often anticipate future interest rate hikes, which can momentarily strengthen a currency. But if economic growth falters under tight monetary conditions, the currency could eventually weaken.
Inflation, therefore, isn’t just a background stat; it’s a dynamic force that can propel or hinder currency valuations. Understanding its foundation helps traders anticipate shifts in foreign exchange rates and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Read More: Fundamental Analysis in Forex
The Chain Reaction of Inflation in Forex
When inflation accelerates, it initiates a domino effect that reverberates throughout the forex market. The interplay of rising prices, shifting consumer behavior, and evolving central bank policies can drastically reshape how currencies move.
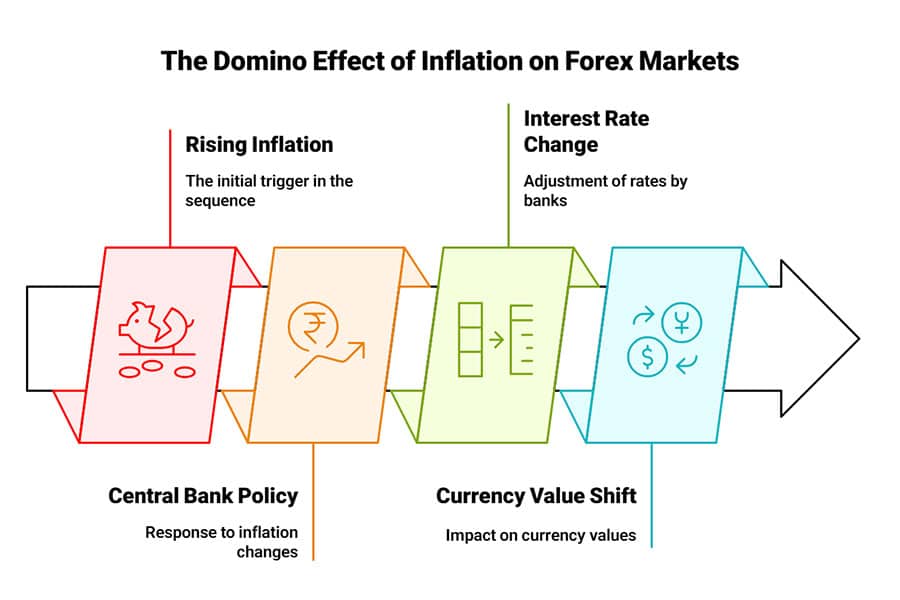
Currency Valuation
High inflation in a country typically leads to a weaker currency over the long term because people and businesses look for more stable stores of value. However, short-term effects can be counterintuitive. For instance, if traders expect more interest rate hikes, they might buy that currency now, temporarily driving it higher. The ultimate direction depends on whether the central bank can curb inflation without stifling growth.
Trade Balances
When local goods become pricier due to inflation, exports can suffer, and imports become relatively cheaper. This can lead to trade imbalances:
- Wider Trade Deficits: Money flows out to buy cheaper foreign goods, reducing demand for domestic currency.
- Weakened Currency: Over time, this deficit can further degrade the currency’s value, especially if there’s no concurrent rise in exports.
Investment Climate
Foreign direct investment (FDI) and portfolio investments often shy away from high-inflation economies because the returns might be undermined by future currency depreciation. In contrast, stable economies with controlled inflation draw long-term capital, supporting their currency.
Market Psychology
Forex markets are heavily influenced by sentiment. Even a rumor that a central bank might tighten monetary policy to fight rising inflation can send traders scurrying to buy a currency. Conversely, if inflation data disappoints (staying too high or unexpectedly low), traders might quickly dump that currency. Understanding this knee-jerk psychological aspect is crucial for timing entries and exits.
These interconnected factors illustrate the inflation effect on foreign exchange market: it’s not just about a single metric but rather the chain reaction triggered across economic activities, trading behaviors, and fiscal strategies. Knowing where each domino lands can give traders a significant edge.
Central Banks: The Puppeteers of Currency
Central banks stand at the forefront of managing inflation. Through various policy tools, they attempt to keep prices in check while fostering economic growth. Their decisions, in turn, have a direct and profound influence on the inflation impact on forex market.

Interest Rate Manipulation
The most common tool in a central bank’s arsenal is adjusting benchmark interest rates:
- Raising Rates: Aims to slow down an overheating economy. By making borrowing more expensive, consumer spending and business expansion can cool off, taming inflation. In the short term, this often leads to currency appreciation, as investors seek higher yields.
- Lowering Rates: Stimulates economic growth by encouraging cheaper loans for businesses and consumers. If inflation is under control or too low, rate cuts can help spur spending. However, lower rates usually make a currency less attractive to yield-seeking investors.
Open Market Operations
Central banks buy or sell government securities to regulate the money supply:
- Buying Securities: Injects liquidity into the economy, potentially sparking inflation if it overheats.
- Selling Securities: Drains liquidity, helping to reduce inflationary pressures.
Forward Guidance
Often overlooked but immensely powerful, forward guidance involves central banks signaling future policy moves. Traders parse every word of policy statements for hints of the next rate hike or rate cut. If the language points toward heightened vigilance against inflation, market participants may position themselves accordingly, leading to abrupt currency shifts.
Quantitative Easing and Tightening
During severe economic downturns, central banks may resort to quantitative easing (QE)—massive bond-buying programs intended to lower long-term interest rates and inject money into the system. While QE can stave off deflation or recession, it also raises the risk of higher inflation down the road. Conversely, tapering or ending QE can create upward pressure on the currency if done swiftly, as markets see it as a signal of economic recovery and a clampdown on inflation.
For forex traders, tracking central bank signals is non-negotiable. Because inflation drives many of these policy maneuvers, understanding how authorities might respond to rising prices or economic stagnation can guide better trading decisions. Stay updated with policy announcements and always factor in potential surprises—central banks sometimes act sooner or more aggressively than the market expects.
Read More: Economic Indicators for Forex
Measuring Inflation: Key Indicators for Forex Traders
Inflation can feel nebulous without tangible metrics to gauge its trajectory. Fortunately, economists rely on a range of indicators to quantify price movements. For anyone seeking to comprehend the inflation effect on foreign exchange market, these metrics provide invaluable insights.
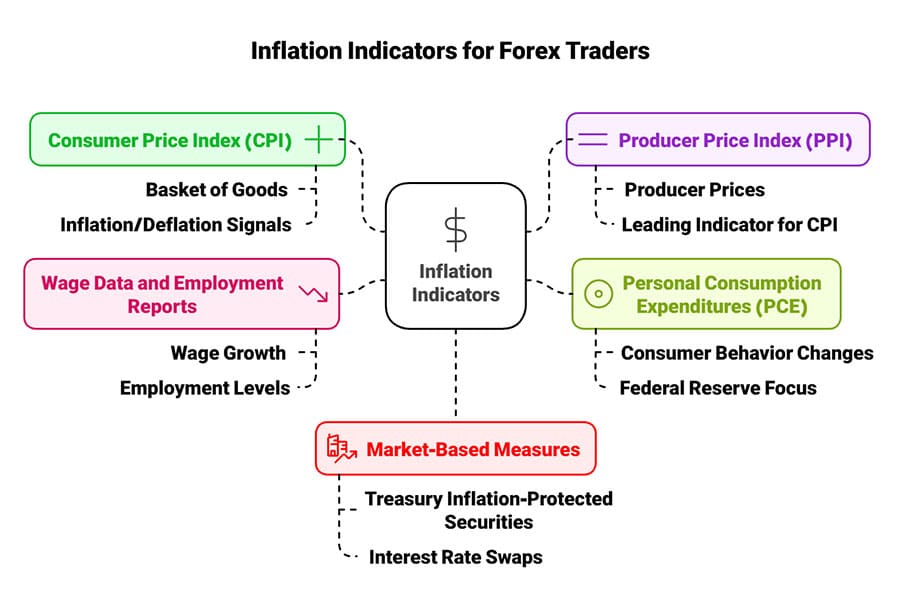
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The CPI measures the average change over time in the prices paid by consumers for a “basket” of goods and services. A rising CPI indicates inflation; a falling CPI signals deflation. Forex traders watch monthly or quarterly CPI releases closely, as an unexpected jump can spark speculation over imminent rate hikes.
Producer Price Index (PPI)
The PPI tracks the average changes in prices received by domestic producers for their output. Because producers often pass higher costs to consumers, the PPI can serve as a leading indicator of where CPI may head next. If the PPI climbs substantially, the market may anticipate future inflation hikes, influencing currency valuations.
Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE)
In the United States, the Federal Reserve pays particular attention to the PCE. It’s thought to be more comprehensive than the CPI because it accounts for changes in consumer behavior, such as substituting one product for another when prices rise. Traders focusing on the U.S. dollar often consider both CPI and PCE to get a complete picture of inflationary trends.
Wage Data and Employment Reports
Rising wages can bolster consumer purchasing power, potentially fueling inflation if supply remains limited. Similarly, low unemployment can push up wages. For this reason, monthly employment reports—like the U.S. Non-Farm Payroll—are pivotal. If wage growth spikes, inflation concerns may intensify, altering currency sentiment.
Market-Based Measures
Beyond official statistics, forex traders also look at market-based measures like breakeven inflation rates derived from Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) or interest rate swaps. These instruments reflect real-time market expectations of future inflation, offering another clue into where prices might be heading.
Incorporating these indicators into your trading strategy helps you anticipate central bank responses and investor sentiment shifts. You can better time your trades around data releases, or at least use them to confirm or refute the direction your technical analysis suggests.
Real-World Stories that Illustrate Inflation’s Power
To understand how quickly inflation can reshape the forex landscape, it’s helpful to glance at notable examples in economic history. While each scenario has unique political, social, and economic backdrops, they all demonstrate the profound inflation impact on forex market dynamics.

Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe (Late 1990s–2000s)
Zimbabwe’s currency crisis is one of the most extreme examples of hyperinflation in recent history. At its worst, inflation soared to astronomical levels, rendering the Zimbabwean dollar nearly worthless. People resorted to bartering for essentials, and foreign currencies like the U.S. dollar became the default medium of exchange. For forex traders observing from outside, the take-home lesson was the critical role of sound monetary policy. Without it, a currency can collapse beyond salvation.
The Oil Shock of the 1970s
A sudden cut in oil supplies led to sky-high energy prices in much of the Western world. Because energy underpins the cost of nearly every industry, inflation surged. Central banks responded with hefty interest rate increases, which triggered a wave of global economic turmoil. The U.S. dollar initially benefited from rate hikes, as investors sought higher yields. However, prolonged inflation and sluggish growth (stagflation) eventually undercut the dollar’s strength. This period highlighted how commodity-driven inflation can quickly disrupt traditional currency dynamics.
Post-2008 Quantitative Easing
Following the 2008 financial crisis, central banks like the Federal Reserve, the Bank of England, and the European Central Bank introduced quantitative easing (QE) to revitalize their economies. Some investors feared QE would immediately lead to severe inflation. While hyperinflation didn’t materialize, asset prices soared, and currencies wobbled as markets digested trillions of newly created money. Ultimately, central banks had to walk a tightrope between stimulating growth and preventing inflation from spiraling out of control.
Each case underscores a central theme: when inflation surges, all bets can be off in forex trading. Whether it’s political turmoil, spikes in crucial commodities, or large-scale money injections, inflation can swiftly alter how currencies are valued and perceived.
Strategies for Thriving in a High-Inflation Environment
Inflation doesn’t merely introduce risk; it also creates openings for the well-prepared trader. Spotting these opportunities starts with acknowledging that the inflation effect on foreign exchange market can tilt the odds in favor of those who anticipate policy changes, currency moves, and potential capital flows.
Trade Safe-Haven Currencies
In times of high inflation, investors often pivot to currencies deemed “safe havens,” such as the Swiss franc (CHF) or Japanese yen (JPY). Allocating a portion of your capital to these currencies can hedge against volatility in more inflation-exposed pairs. Even if their yields are lower, these currencies may stay relatively stable amid economic turbulence.
Consider Carry Trades Carefully
Carry trading involves borrowing in a low-interest-rate currency and investing in a higher-interest-rate currency to earn the interest rate differential. In inflationary climates, central banks that aim to combat inflation often raise rates, potentially making carry trades more attractive. However, the risk is that runaway inflation could erode the currency’s value if economic growth stalls. Prudent risk assessment is a must.
Monitor Central Bank Commentary
Statements from central banks can be as impactful as actual policy moves. Traders who actively monitor speeches, meeting minutes, and press releases often gain insight into possible interest rate changes. Quick responses to unexpected language shifts—like signs of aggressive hawkishness—can yield significant gains or prevent sharp losses.
Diversify Across Currency Pairs
Relying on a single currency pair when inflation is volatile can be risky. Instead, distribute positions across different currencies and economic blocs. If one region faces rampant inflation, others might still have stable growth or moderate price levels. Spreading out your trades reduces the impact of a single inflation-driven shock.
Use Technical and Fundamental Analysis Together
Inflation is fundamentally driven, but forex charts reveal how traders are reacting. Combining fundamental data (like CPI reports and rate announcements) with technical tools (like support-resistance lines, moving averages, and momentum indicators) offers a more holistic strategy. For instance, if fundamental analysis suggests an interest rate hike is imminent but the chart shows a currency pair hitting strong support, you might time your entry for a potential bullish breakout.
Trading in inflationary periods demands agility. By adopting these strategies, you not only mitigate the downsides but also position yourself to seize the market shifts that inflation inevitably triggers.
Risk Management Essentials During Inflationary Volatility
When inflation rises, unpredictability becomes the norm rather than the exception. As you execute trades based on the inflation effect on foreign exchange market, solid risk management isn’t merely a luxury—it’s a necessity.
Position Sizing and Leverage Restraint
Leverage can be a double-edged sword. While it magnifies profits, it also amplifies losses. In high-inflation conditions, where currency swings can be abrupt, it’s prudent to reduce leverage and keep position sizes manageable. This approach ensures that even if the market moves against you, you won’t wipe out your trading account in a single swoop.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders automatically close your position once the market hits a certain price. Inflation-driven volatility can produce sharp, sudden movements, so set your stop-loss levels carefully. Placing them too close could trigger premature exits, while placing them too far could increase your potential losses. Dynamic or trailing stop-loss orders can strike a balance by adjusting as the market moves in your favor.
Hedging Tactics
Some traders hedge currency exposure using options or futures. If you’re concerned that a particular currency might plunge due to rising inflation, a put option can offset potential losses on a long position. For those dealing with multiple currency pairs, cross-hedging—going long in one currency pair while shorting another correlated pair—can minimize net exposure.
Emotional Discipline
Rampant inflation often leads to a barrage of alarming headlines and nervous market chatter. Reacting impulsively to every news snippet can be dangerous. Instead, stick to your trading plan. If an economic indicator reveals higher-than-expected inflation, review your technicals and fundamentals before making a move. Rash decisions typically lead to suboptimal results, especially in high-volatility conditions.
Continuous Learning
No two inflationary periods are exactly alike. Keeping a trading journal to document your trades, rationale, and market conditions can help refine your approach over time. Reflect on what worked, what didn’t, and why. A well-documented trading history is a roadmap to improvement, especially when facing inflation-fueled turbulence again in the future.
Robust risk management transforms a high-inflation environment from a destabilizing threat to a navigable landscape. By minimizing downside exposure, you’ll remain in the game longer, accumulating knowledge and sharpening your strategies for the next surge or dip in inflation.
Pro Tips for Advanced Traders
If you already have a few notches on your forex trading belt, these strategies can give you an extra edge in an inflation-driven market.
Correlate Currency Pairs with Bond Yields
Forex markets often move in tandem with shifts in the bond market. When inflation rises, bond yields usually increase. Observing yield spreads between countries can forecast currency strength or weakness. For instance, if U.S. 10-year Treasury yields rise faster than German Bund yields, the U.S. dollar might appreciate against the euro.
Track Yield Curve Inversions
An inverted yield curve (where short-term rates exceed long-term rates) can signal an impending economic slowdown or recession. Inflation might still be climbing, but a slowing economy could pressure the central bank to pivot on rate hikes. If you anticipate this pivot early, you can trade currency pairs poised for a reversal.
Deploy Options Strategically
Advanced traders often use forex options for both directional plays and hedging. For instance, if you suspect a central bank will tighten monetary policy aggressively due to surging inflation, buying call options on that currency offers upside potential without fully exposing you to market whipsaws.
Multi-Timeframe Analysis
Zoom out to weekly or monthly charts to identify macro trends shaped by inflation data, then zoom in to daily or hourly charts to find precise entries. This multi-timeframe approach ensures you’re trading in the direction of the bigger trend, yet timing your moves with near-term fluctuations.
Stay Flexible and Adaptable
High inflation phases can evolve fast. A single press release or data point—like a sudden drop in unemployment—might drastically shift inflation expectations. Be ready to pivot. Adaptability is the hallmark of successful advanced traders, especially when markets are on edge about rising prices.
By integrating these pro tips into your strategy, you can better navigate the complexities of inflation cycles. Combining macroeconomic awareness with technical sophistication positions you to seize opportunities that others miss or fear.
Opofinance Services
If you’re looking to trade in a secure, cutting-edge environment while tackling the inflation impact on forex market, consider ASIC-regulated Opofinance. They provide a range of tools and features designed for both newcomers and experienced traders:
- Advanced Trading Platforms – Access MT4, MT5, cTrader, and OpoTrade for flexible and intuitive execution.
- Innovative AI Tools – Utilize AI Market Analyzer, AI Coach, and AI Support for smart, data-driven trading decisions.
- Social & Prop Trading – Learn from seasoned professionals or showcase your own expertise in an interactive community.
- Secure & Flexible Transactions – Enjoy safe and convenient deposits and withdrawals, including crypto payments, with zero fees from Opofinance.
Read More: How Interest Rates Affect Forex Market
Ready to enhance your trading journey?
Start Trading with Opofinance
Conclusion
The inflation impact on forex market runs deep. From altering consumer purchasing power to swaying central bank decisions, inflation exerts a powerful force on currency valuations worldwide. While high inflation can breed volatility, it can also create abundant opportunities for traders willing to adapt. By mastering the economic indicators that track inflation, understanding central bank moves, and implementing risk management tactics, you position yourself to navigate this challenging yet potentially rewarding terrain.
Whether you’re eyeing safe-haven currencies or exploiting interest rate differentials, staying informed is your greatest ally. Keep a sharp watch on evolving policy statements, pay attention to data releases, and remain mindful of broader economic contexts like commodity prices and geopolitical tensions. In a market where a single report or surprise central bank move can alter the course of currencies, knowledge truly translates to power.
Key Takeaways
- Inflation Matters: Shifting price levels directly affect currency strength and trading sentiment.
- Central Banks Set the Tone: Rate hikes and policy announcements can either stabilize or unsettle forex markets.
- Indicators are Crucial: Keep track of CPI, PPI, PCE, and wage growth to anticipate inflation-driven moves.
- Risk Management is Non-Negotiable: Use stop-loss orders, proper position sizing, and hedging tactics to safeguard capital.
- Pro Tips Boost Returns: Advanced traders can leverage bond yield correlations, options, and yield curve analysis to refine their edge.
What if a currency’s inflation is high but the central bank is reluctant to raise rates?
A scenario where a central bank hesitates to fight high inflation can trigger a downward spiral for that currency. Foreign investors may lose confidence, prompting capital flight and pushing the currency’s value even lower. In this situation, savvy traders often short the currency or move their capital to regions with more proactive monetary policies.
Is it beneficial to trade commodities when inflation is soaring?
Commodities like gold, oil, and agricultural products often rise in price when inflation accelerates, making them appealing hedges. However, commodity trading has its own nuances, and storing physical commodities isn’t always straightforward. Many forex brokers offer CFD trading on commodities, which can be a simpler way to diversify exposure without taking physical delivery.
Do government fiscal policies impact the inflation effect on foreign exchange market?
Absolutely. When a government runs large budget deficits and finances spending through borrowing, it can add inflationary pressure. This can influence how central banks set interest rates. If investors see a country piling up debt with no clear plan to manage inflation, they may demand higher yields or ditch that currency for safer alternatives.







