Fair Value Gap (FVG) scalping is a powerful trading strategy that leverages short-term price imbalances in the forex market. This technique focuses on identifying gaps in price action where the market has moved rapidly, providing opportunities for quick profits. By mastering and executing FVG scalping with precision, traders can potentially boost their trading performance and maximize their profitability in the dynamic environment of forex. For traders seeking a reliable forex broker, having the right platform is essential to implement such strategies effectively.

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of Fair Value Gap scalping, providing you with the knowledge and tools to implement this strategy successfully. From understanding what Fair Value Gaps are and how to identify them, to executing trades with precision and managing risk, we’ll cover everything you need to know to master this technique.
2. Understanding Fair Value Gaps
2.1 What are Fair Value Gaps?
Fair Value Gaps, often referred to as FVGs, are areas on a price chart where there is a significant imbalance between supply and demand. These gaps occur when price moves rapidly in one direction, leaving behind a void or “gap” in the price action. This phenomenon is particularly common during periods of high volatility, such as during news releases or at the opening of major trading sessions.
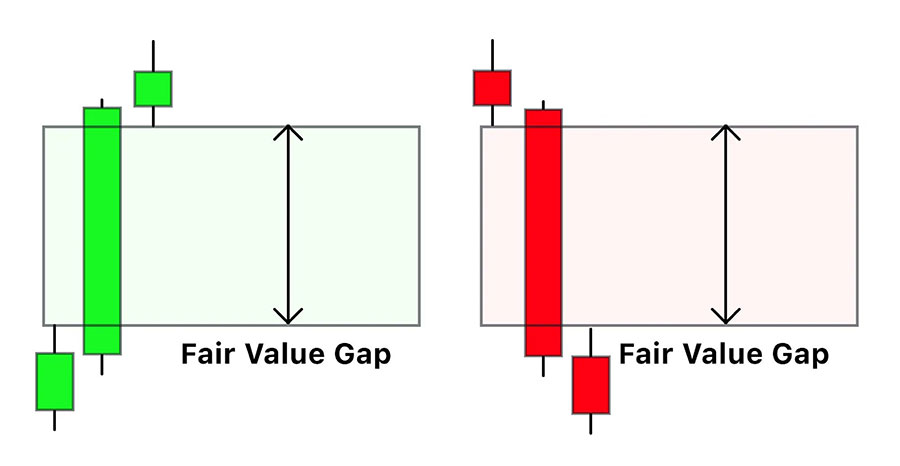
Key characteristics of Fair Value Gaps include:
- Rapid price movement: FVGs form when price moves quickly, often within a single candle or a series of consecutive candles moving in the same direction.
- Lack of trading activity: The gap represents an area where little to no trading has taken place, creating a potential imbalance in the market.
- Tendency to fill: Markets generally seek equilibrium, which means there’s often a tendency for price to return to the gap area, “filling” the void left behind.
- Short-term nature: FVGs are typically short-lived, making them ideal for scalping strategies that aim to profit from quick price movements.
2.2 Identifying Fair Value Gaps (Manual & Indicator Methods)
2.2.1 Manual Method
To identify Fair Value Gaps manually, traders need to develop a keen eye for price action and chart patterns. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Analyze candlestick patterns: Look for a series of candles moving strongly in one direction, particularly those with long bodies and short or no wicks.
- Identify the gap: The gap is typically formed between the high of one candle and the low of the next non-overlapping candle in the opposite direction.
- Confirm the gap size: A significant FVG should be larger than the average candle size for the timeframe you’re trading.
- Consider market context: FVGs are more significant when they occur at key support or resistance levels or during major trend reversals.
2.2.2 Indicator Method
For traders who prefer a more automated approach, several indicators can help identify Fair Value Gaps:
- Fair Value Gap Indicator: This custom indicator automatically marks FVGs on your chart, often color-coding them based on whether they’re bullish or bearish gaps.
- Volume Profile: While not specifically designed for FVGs, this tool can help identify areas of low trading activity, which often correspond to Fair Value Gaps.
- Market Profile: Similar to the Volume Profile, the Market Profile can highlight areas of price acceptance and rejection, helping to identify potential FVGs.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Rapid changes in the MACD histogram can sometimes indicate the formation of an FVG.
3. Trading the Fair Value Gap Scalping Strategy

3.1 Key Conditions for a Valid Fair Value Gap
Not all gaps in price action qualify as tradeable Fair Value Gaps. To increase the probability of successful trades, consider the following conditions:
- Gap Size: The gap should be significant enough to warrant a trade. A common rule of thumb is that the gap should be at least 1.5 times the average true range (ATR) for the timeframe you’re trading.
- Market Structure: The FVG should align with the overall market structure. For example, a bearish FVG is more significant if it occurs during a downtrend or at a key resistance level.
- Time of Formation: FVGs that form during high-liquidity periods (such as London or New York session opens) are often more reliable.
- Absence of Conflicting Signals: There should be no significant support or resistance levels, trendlines, or other technical indicators conflicting with the potential trade direction.
- Volatility: The market should be sufficiently volatile to support quick price movements, but not so volatile that it becomes unpredictable.
3.2 Entry Points: Targeting the Gap Area
When trading Fair Value Gaps (FVGs), entering at the optimal point is crucial for maximizing profit potential while minimizing risk. Below are several strategies for entering FVG trades:
3.2.1 Retracement Entry
This method involves waiting for the price to retrace to the FVG area before entering the trade.
Steps:
- Identify the FVG on your chart.
- Wait for price to retrace to the gap area.
- Look for confirmation signals such as candlestick patterns, momentum indicator divergence, or support/resistance levels within the gap.
- Enter the trade when confirmation signals align with the FVG setup.
3.2.2 Breakout Entry
This strategy involves placing a pending order at the edge of the FVG, entering the trade if price breaks through this level with momentum.
Steps:
- Identify the FVG on your chart.
- Place a pending order (buy stop for bullish FVG, sell stop for bearish FVG) at the edge of the gap.
- Set a stop-loss just beyond the opposite side of the gap.
- Enter the trade if price breaks through the gap edge with strong momentum.
3.2.3 Multi-Level Entry
This approach involves entering the trade at multiple levels within the FVG, allowing for a more nuanced entry strategy.
Steps:
- Identify the FVG on your chart.
- Divide the gap into 2-3 levels.
- Enter partial positions at each level as price moves through the gap.
- Adjust stop-loss and take-profit levels for each entry point.
Read More: Fair Value Gap And Order Block Strategy
3.3 Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Proper placement of stop-loss and take-profit orders is crucial for managing risk and maximizing potential returns in FVG scalping:
Stop-Loss Placement:
- Beyond the FVG: Place the stop-loss just beyond the opposite side of the Fair Value Gap.
- Volatility-Based: Use a multiple of the Average True Range (ATR) to set a dynamic stop-loss.
- Structure-Based: Place the stop-loss beyond the nearest significant support or resistance level.
Take-Profit Strategies:
- Fixed Risk-Reward Ratio: Set a take-profit at a predetermined risk-reward ratio (e.g., 1:2 or 1:3).
- Partial Profits: Take partial profits at key levels and move the stop-loss to breakeven.
- Trailing Stop: Implement a trailing stop to capture extended moves while protecting profits.
- Indicator-Based Exit: Use technical indicators like RSI or MACD to signal exit points.
Additional Considerations
4.1 Market Context and Trend Analysis
While Fair Value Gaps can provide excellent trading opportunities, it’s crucial to consider the broader market context:
- Trend Identification: Determine the overall market trend using higher timeframes and trend indicators like moving averages or the ADX (Average Directional Index).
- Support and Resistance: Identify key support and resistance levels that may influence price action around the FVG.
- Market Sentiment: Consider fundamental factors and market sentiment that may impact currency pair movements.
- Correlation Analysis: Be aware of correlations between different currency pairs and how they might affect your FVG trades.
- Economic Calendar: Keep an eye on upcoming economic releases that could create volatility and new Fair Value Gaps.
Read More: Silver Bullet Forex Strategy
4.2 Risk Management for Scalping Strategies
Effective risk management is paramount in any trading strategy, but it’s especially crucial in fast-paced scalping:
- Position Sizing: Limit each trade to a small percentage of your total account (typically 1-2% maximum).
- Risk per Trade: Maintain a consistent risk per trade, adjusting position size based on stop-loss distance.
- Daily Loss Limit: Implement a daily loss limit (e.g., 3-5% of account balance) to prevent overtrading and emotional decisions.
- Profit Targets: Set realistic profit targets based on market conditions and your risk tolerance.
- Drawdown Management: Have a plan for managing extended periods of drawdown, including when to pause trading and reevaluate your strategy.
4.3 Backtesting and Optimization
To refine your Fair Value Gap scalping strategy, consider the following:
- Historical Data Analysis: Backtest your strategy using historical data to assess its performance over different market conditions.
- Parameter Optimization: Experiment with different parameters (e.g., gap size, entry criteria) to optimize your strategy.
- Forward Testing: After backtesting, forward test your strategy on a demo account before risking real capital.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and refine your strategy based on performance metrics and changing market conditions.
4.4 Technology and Tools
Leverage technology to enhance your FVG scalping strategy:
- Advanced Charting Software: Use professional-grade charting platforms with customizable indicators and alert functions.
- Automated Trading Systems: Consider implementing automated or semi-automated trading systems to execute your FVG strategy.
- Market Scanner: Utilize market scanners to quickly identify potential FVG setups across multiple currency pairs.
- Trading Journals: Use digital trading journals to track and analyze your trades, helping you identify areas for improvement.
Read More: Scalping Techniques In Forex
Conclusion
Fair Value Gap scalping is a powerful technique that allows traders to capitalize on short-term price imbalances in the forex market. By identifying these gaps, entering trades strategically, and managing risk effectively, traders can potentially achieve consistent profits in fast-moving market conditions.

Key points to remember:
- FVGs represent areas of price imbalance caused by rapid market movements.
- Successful FVG scalping requires accurate identification, strategic entry, and precise exit planning.
- Risk management is crucial, including proper position sizing and stop-loss placement.
- Consider market context, trend analysis, and broader economic factors when implementing the strategy.
While FVG scalping can be profitable, it’s essential to develop your skills gradually, starting with demo trading before risking real capital. Stay informed about market conditions, refine your technique consistently, and always prioritize risk management to build a sustainable trading career.
How does Fair Value Gap scalping differ from other scalping strategies?
Fair Value Gap scalping focuses specifically on exploiting price imbalances created by rapid market movements, whereas other scalping strategies may rely on different market inefficiencies or patterns. FVG scalping typically involves longer holding periods compared to traditional scalping, as traders wait for the gap to fill. This strategy also often requires a deeper understanding of market structure and price action analysis.
Can Fair Value Gap scalping be combined with other trading strategies?
Yes, Fair Value Gap scalping can be effectively combined with other trading strategies to enhance overall performance. For example, traders might use trend analysis to determine the broader market direction and then apply FVG scalping within that trend. Additionally, some traders incorporate order flow analysis or market depth information to confirm FVG trades. The key is to ensure that any combined strategies complement each other and don’t introduce conflicting signals.
How does liquidity affect Fair Value Gap trading, and are there specific currency pairs that work best with this strategy?
Liquidity plays a crucial role in Fair Value Gap trading. Highly liquid currency pairs tend to produce cleaner and more tradeable FVGs due to their smooth price action and tight spreads. Major pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY are often favored for FVG scalping. However, some traders also find success with certain minor pairs that exhibit good liquidity during specific market sessions. It’s important to note that less liquid pairs may have wider spreads and more erratic price movements, which can make FVG trading more challenging and potentially increase trading costs.







