Finding reliable areas on a price chart where significant reactions might occur is a common challenge for forex traders. Standard support and resistance lines offer some guidance, but often lack precision. This is where the concept of a point of interest in forex (POI) becomes useful. A POI is essentially a specific price zone identified as having potential importance due to past market activity or order flow dynamics. Selecting a suitable regulated forex broker is a prerequisite, but understanding where to anticipate market reactions is crucial for execution. This article provides a practical guide to the point of interest in forex, covering its definition, types, identification methods, and application in trading strategies.

Understanding POI in Forex Trading
Let’s clarify what a POI represents and its relevance in practical trading. It’s a designated area on the chart that signals potential significant price behavior, going beyond simple horizontal lines.
What Does POI Mean in Forex?
In the context of forex trading, a Point of Interest (POI) signifies a price level or zone where a meaningful market reaction is anticipated. This reaction could be a reversal, a pause in the current trend, or a continuation following a pullback. Using a poi in forex allows traders to prepare for potential moves and structure trades around these specific areas, improving strategic planning.
How POI Reflects Market Psychology and Order Flow
POIs often highlight zones where substantial transactions, particularly from institutional participants, previously took place. These large orders can leave behind unfilled portions or create a ‘memory’ in the market. When price revisits such a point of interest in forex, it may trigger these resting orders or attract new participants anticipating a similar reaction. This interaction between current price and the historical significance of the zone often leads to observable price responses. Identifying a key poi in forex helps in understanding these underlying dynamics.
Role of POI in Identifying Market Moves
The main function of a POI is to highlight areas with a higher probability of specific price actions. Traders use these zones to:
- Anticipate potential reversals: Price approaching a strong POI after a sustained move might suggest the trend is losing momentum.
- Identify breakout confirmations: A clear movement through a POI can validate the start or continuation of a trend.
- Locate pullback entry opportunities: Following a breakout, price often returns to test the breached point of interest in forex. This retest can offer a structured entry point.
Focusing analysis on these areas helps traders concentrate on more significant market structure points, making the use of a point of interest forex trading approach valuable.
Types of Points of Interest in Forex
Points of Interest manifest in various forms, each linked to different market mechanisms. Understanding these variations allows for a more nuanced interpretation of chart information. Each type represents a distinct point of interest in forex.
Read More: Identify Order Blocks in Forex
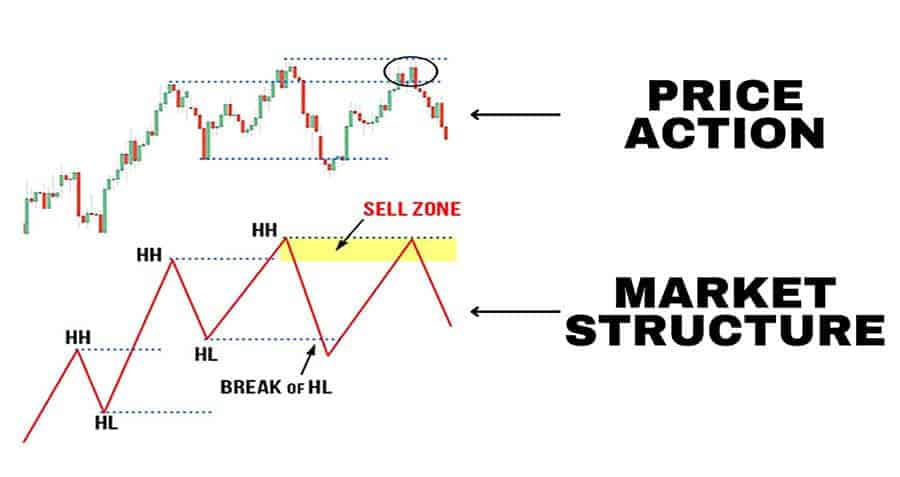
Liquidity Zones
These are specific price levels, typically just above recent swing highs or below recent swing lows, where stop-loss orders are likely concentrated. Larger market participants might target these areas to absorb the available orders (liquidity) before initiating a move. Recognizing these zones can help traders anticipate potential stop runs or false breakouts.
Order Blocks
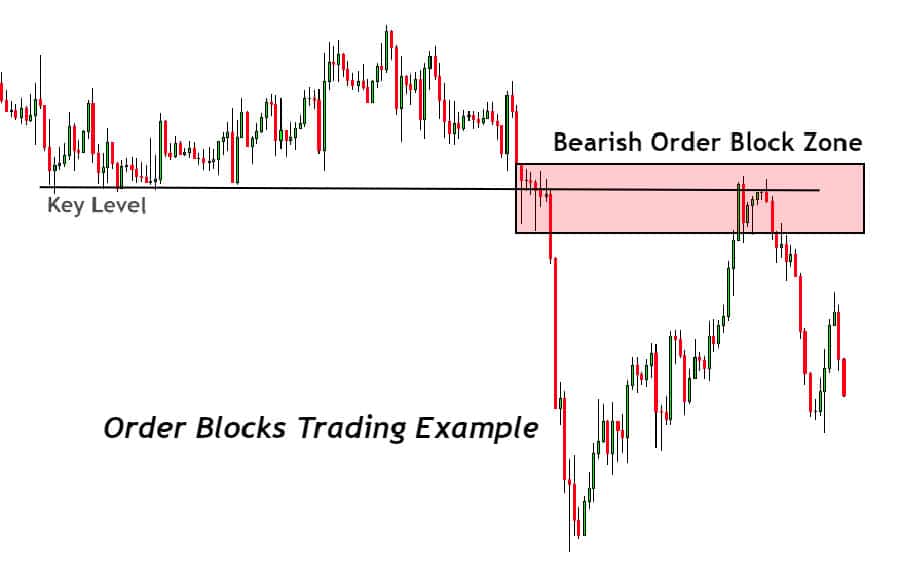
An order block is commonly defined as the last candlestick moving in the opposite direction before a strong, impulsive price move that breaks market structure (e.g., the last down-close candle before a sharp upward break). These blocks suggest where institutions may have initiated significant positions. Price frequently revisits these zones to ‘mitigate’ them (interact with any remaining orders), making them potent POIs for potential entries. A clear order block is a frequently sought-after point of interest in forex.
Imbalance Areas (Fair Value Gaps)
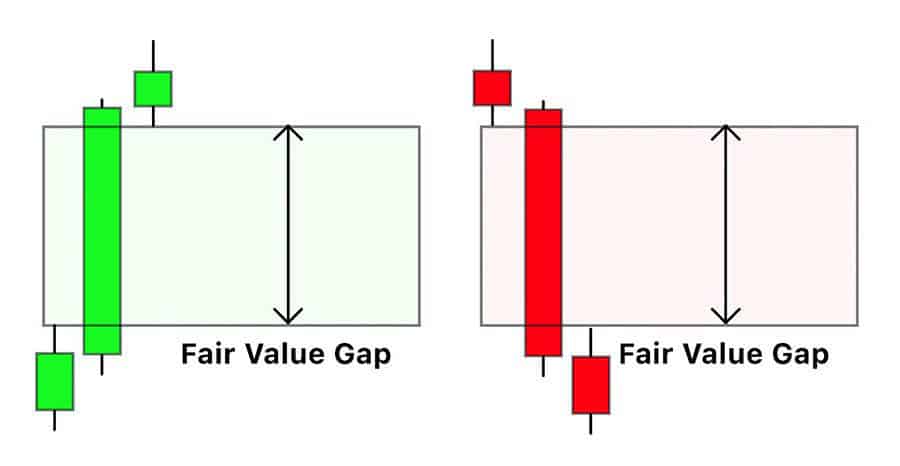
An imbalance, or Fair Value Gap (FVG), appears as a gap between the wicks of three consecutive candles following a rapid price movement. It indicates an inefficiency where buying or selling pressure was overwhelming. The market often tends to revisit these forex poi levels to ‘fill the gap’ or rebalance price delivery, making them areas to watch for reactions.
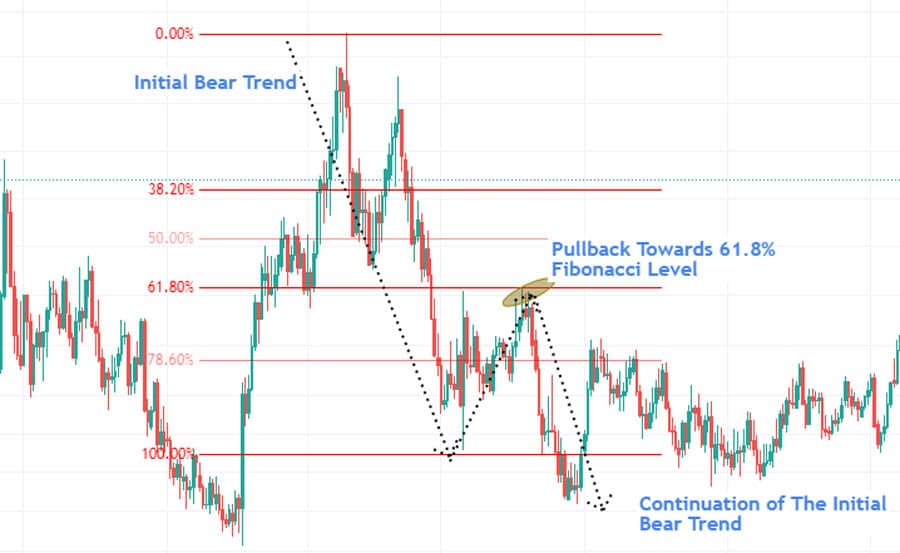
Fibonacci Retracement and Extension Levels
Applying Fibonacci tools to significant price swings identifies potential retracement levels (e.g., 50%, 61.8%) where a pullback might stall, and extension levels (e.g., 1.618, 2.618) where a trending move might reach. These mathematical ratios often align with other POI types, increasing their relevance as a point of interest in forex.
Psychological Price Levels
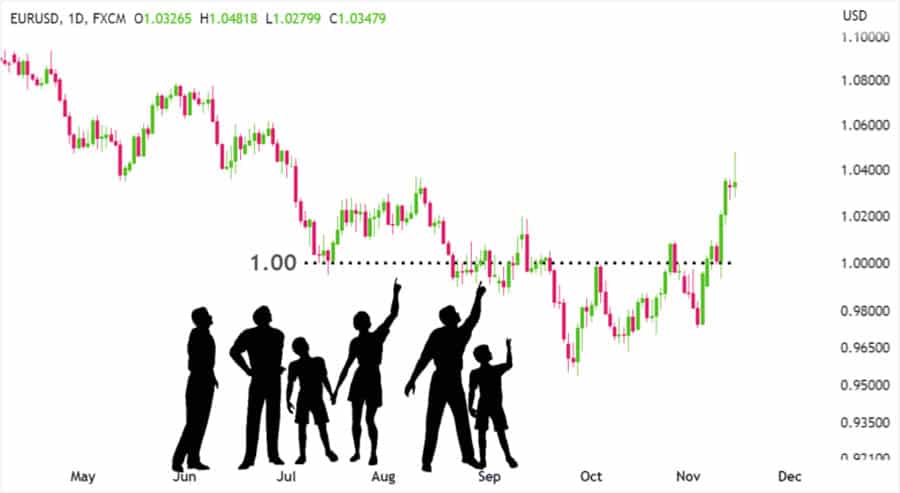
These refer to round numbers (e.g., 1.25000, 100.00) or major historical price points that attract attention due to their simplicity and memorability. Orders often cluster around these levels, making them function as psychological support or resistance and thus, a natural point of interest in forex.
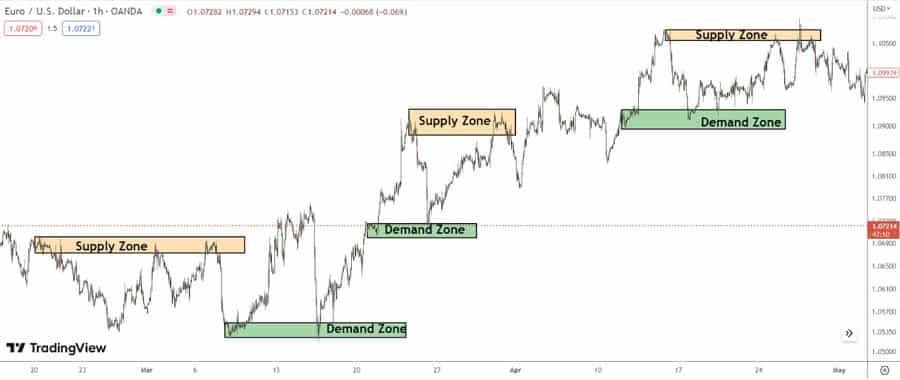
Support and Resistance as POIs
Classic horizontal support and resistance levels, identified by multiple previous price reversals, remain valid points of interest. While the overall POI concept incorporates more factors, these fundamental levels are important, especially when they coincide with other POI types like an imbalance or order block, reinforcing that specific point of interest in forex.
How to Identify POI on Price Charts
Identifying a potentially reliable point of interest forex trading zone involves combining technical analysis tools with careful observation of price action and market structure. It’s typically the confluence of several factors that highlights a high-probability area.
Read More: Liquidity Sweep Trading Strategy

Using Technical Analysis Tools
Common technical indicators can help locate potential POIs:
- Moving Averages: Key MAs (e.g., 50 EMA, 200 SMA) can act as dynamic support or resistance levels where price reactions may occur.
- Trend Lines: Properly drawn trend lines connecting significant swing points create diagonal levels; touches on these lines can be considered POIs.
- Fibonacci Levels: Plotting Fibonacci retracements on relevant price swings highlights potential pullback termination points (e.g., 61.8% level) which act as a point of interest in forex.
Recognizing POI through Price Action
Direct analysis of price movement is crucial:
- Chart Patterns: Formations like triangles, flags, head and shoulders, or double tops/bottoms inherently contain key levels (e.g., boundaries, necklines) that function as POIs.
- Candlestick Patterns: Specific reversal patterns (e.g., engulfing bars, pin bars, dojis) occurring at a pre-identified potential POI provide strong confirmation clues.
- Volume Analysis: A significant increase in trading volume as price interacts with a specific level suggests strong participation, marking it as a potentially more significant POI.
Identifying Liquidity Sweeps and CHoCH
More nuanced techniques focus on specific price behaviors:
- Liquidity Sweeps: Observe where price briefly extends beyond a previous swing high or low, likely triggering stops, before reversing strongly. The origin of the move that caused the sweep can then be identified as a POI.
- Change of Character (CHoCH): This occurs when price breaks the most recent minor structural point against the prevailing trend (e.g., breaks a minor low in an uptrend). This suggests a potential shift in order flow. The order block or imbalance associated with this break often becomes a high-probability point of interest in forex, especially for refining entries based on higher timeframe analysis.
Combining Multiple Indicators for Confirmation
The highest probability POIs are often found where multiple analytical signals converge. For instance, if a bearish order block aligns closely with a 61.8% Fibonacci retracement and a psychological round number, the likelihood of that zone acting as a significant point of interest in forex increases considerably.
Trading Strategies Using POI
Locating a point of interest in forex is useful, but integrating it into a practical trading strategy is essential. POIs provide context for trade entries, risk definition, and profit objectives.
Read More: Risk management principles for both novice and advanced traders
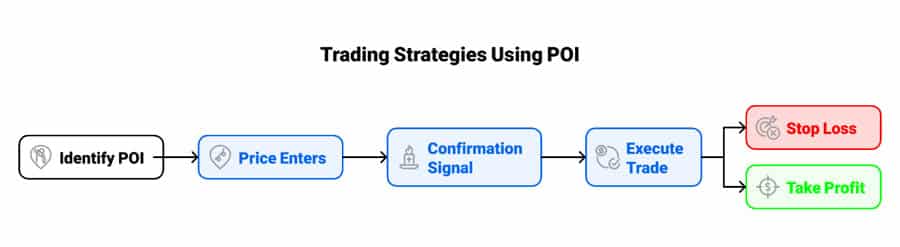
Entry and Exit Points Based on POI
Use POIs as reference points for trade execution:
- Entries: Avoid entering a trade solely because price has reached a POI. Wait for a specific confirmation signal. This could be a distinct candlestick reversal pattern, a break of a lower timeframe structure confirming the reaction, or divergence on an oscillator. For example, wait for a bullish engulfing pattern at a bullish poi in forex before considering a long entry.
- Exits (Take Profit): Other significant POIs located beyond your entry point serve as logical areas to consider taking profits. As price may react at the next poi in forex, planning partial or full profit-taking at such levels is a common practice.
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
POIs facilitate more structured risk management:
- Stop-Loss: Place the stop-loss logically beyond the identified POI zone. For a long entry at a bullish point of interest in forex, the stop would typically go slightly below the low of the zone. A clear break beyond the POI invalidates the immediate trade idea.
- Take-Profit: The next opposing POI often provides a reasonable initial target. Calculate the potential risk-to-reward ratio (distance to stop-loss vs. distance to target) before entering to ensure the trade meets your criteria (e.g., aiming for at least 1:2 R:R).
Using POI with Other Technical Indicators
Strengthen trade setups by combining POI analysis with other tools:
- Candlestick Patterns: A clear, well-formed reversal pattern directly at your point of interest in forex adds significant confirmation.
- Oscillators (RSI, Stochastics, MACD): Look for signs like divergence (price makes a new high/low, but the oscillator fails to) or overbought/oversold readings as price tests a POI, suggesting weakening momentum. Checking these conditions at specific forex poi levels can refine entry timing.
Adjusting POI Levels in Volatile Markets
During periods of high market volatility (e.g., around major economic news):
- Wider Zones Consideration: Price might exhibit larger swings, potentially requiring you to consider slightly wider POI zones or stop placements.
- Stricter Confirmation Criteria: Be more patient and demand clearer, more decisive confirmation signals before committing to a trade based on a poi in forex.
- Position Sizing Adjustment: Reduce your position size to manage the increased uncertainty and potential for wider price fluctuations.
Examples of Bullish and Bearish POI Scenarios
- Bullish Scenario: In an uptrend, price pulls back to a 4-hour bullish order block that aligns with the 61.8% Fibonacci level. On the 15-minute chart, a Change of Character occurs, followed by a bullish engulfing candle within the POI. A trader might enter long, placing a stop below the 4H order block’s low, targeting the next significant swing high or resistance POI.
- Bearish Scenario: After a downtrend, price retraces into a daily chart Fair Value Gap (imbalance) which also coincides with a broken prior support level. On the 1-hour chart, price forms a bearish engulfing pattern within this point of interest forex trading zone. A trader could initiate a short position, with a stop-loss placed just above the daily FVG’s high, aiming for the next major swing low or support POI.
Benefits of Using POI in Forex Trading
Incorporating point of interest forex trading analysis into your process offers several practical advantages, promoting a more systematic approach.
Reducing Emotional Trading Decisions
Trading based on pre-defined POIs introduces greater objectivity. Instead of reacting impulsively to price fluctuations, traders have specific zones to monitor for planned entries. This structure helps minimize decisions driven by fear or greed.
Enhancing Risk Management
POIs provide clear invalidation points for a trade idea. If price moves decisively through a point of interest in forex, the rationale for the trade at that level is nullified. This allows for more precise and logically placed stop-losses, contributing to better capital protection.
Improving Trade Accuracy and Confidence
Focusing on high-probability zones where significant reactions are anticipated helps filter out lower-quality trade setups. Executing trades at well-defined POIs, particularly when accompanied by confirmation signals, can potentially improve entry timing and success rates, which in turn builds confidence in one’s analytical process and use of the point of interest in forex.
Providing Strategic Reference Points
POIs serve as key reference levels on the chart, helping traders map out market structure and potential scenarios. They offer strategic locations for planning entries, exits, and overall trade management, adding clarity to market analysis beyond simple trend following. Understanding forex poi levels is integral to this.
Common Questions About POI in Forex
Practical application often raises questions. Here are answers to some common queries regarding the point of interest in forex concept.
What is the POI Rule?
There isn’t one single, standardized “POI rule.” Instead, strategies incorporate POIs based on certain principles. Common practices include: identifying significant POIs on higher timeframes for directional bias, waiting for price to enter the POI zone, seeking specific confirmation signals (like candlestick patterns or lower timeframe structure shifts) before entry, and setting stop-losses at logical points beyond the POI. The exact entry trigger and risk parameters define the trader’s specific rules for interacting with a point of interest in forex.
How Does POI Work?
The effectiveness of a POI stems from the idea that zones of previous significant order flow or imbalance tend to attract price in the future. Unfilled institutional orders might reside there, or the level might be recognized by many traders as historically important. When price returns to a point of interest in forex, this interaction can trigger resting orders, draw in new participants, or hit stop clusters, often causing a discernible price reaction. This mechanism is fundamental to point of interest forex trading.
How to Check and Monitor POI Effectively?
Effective monitoring involves:
- Multi-Timeframe Context: Identify major POIs on higher timeframes (e.g., Daily, 4H) to gauge the larger market structure. Then, observe price action on lower timeframes (e.g., 1H, 15M) as it approaches these zones to pinpoint potential entry signals or confirmations.
- Utilize Alerts: Set price alerts slightly ahead of your key POIs to be notified without needing constant screen time.
- Assess Context: Always consider the prevailing market trend and structure. A point of interest in forex aligning with the dominant trend generally offers a higher probability setup.
- Maintain Flexibility: Market conditions change. Regularly re-evaluate your identified POIs. Some may hold significance, while others get invalidated by subsequent price action. Adjust your analysis accordingly.
Tools and Resources for POI Analysis
Leveraging appropriate software and educational materials can significantly aid in effectively identifying and utilizing the point of interest in forex.
Charting Software and Indicators
Most capable charting platforms provide the necessary tools:
- Platforms (TradingView, MT4/MT5, cTrader): Offer essential drawing capabilities (rectangles for zones, Fibonacci tools, trendlines) and standard indicators (MAs, volume, oscillators).
- Volume Profile Tools: Indicators like Volume Profile Visible Range show volume distribution at price levels, helping identify high-volume nodes which can act as POIs.
- Specialized Indicators: Some custom indicators attempt to automatically highlight potential order blocks or imbalances. Use these cautiously as supplementary tools, always relying on your own analysis for confirmation.
- Session Range Indicators: Tools that highlight specific trading session highs and lows (e.g., Asian range) can help identify liquidity-based POIs.
Recommended Educational Resources
Seek out reputable sources focusing on:
- Price Action Analysis: Deep understanding of candlestick interpretation, market structure (swing points, breaks of structure), and order flow dynamics.
- Supply and Demand Methodologies: Learning these concepts provides a strong foundation as they overlap significantly with POI identification.
- Institutional Trading Concepts (SMC): Studying topics like order blocks, mitigation, liquidity engineering, and imbalances offers insights into the market mechanics often associated with identifying a high-probability point of interest in forex.
- Broker Educational Content: Many forex brokers provide articles, webinars, and courses covering technical analysis techniques that can be relevant.
Opofinance Services: Enhance Your Trading Edge
Successfully applying concepts like the point of interest in forex is supported by a robust trading infrastructure. Opofinance, an ASIC regulated broker, offers a comprehensive suite of tools and services for traders:
- Advanced Trading Platforms: Access markets via popular platforms including MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), cTrader, and the proprietary OpoTrade platform.
- Innovative AI Tools: Utilize AI-driven tools for market analysis (AI Market Analyzer), personalized coaching (AI Coach), and efficient customer support (AI Support).
- Social & Prop Trading: Explore community trading features or potential pathways through proprietary trading programs.
- Secure & Flexible Transactions: Benefit from reliable deposit and withdrawal processes, including options for cryptocurrency payments, with zero transaction fees applied by Opofinance.

Consider a broker that provides the technological edge and secure environment needed for today’s trading challenges.
Developing the skill to identify and utilize a point of interest in forex can significantly refine a trader’s methodology. It encourages a shift from reactive trading to proactively identifying specific, high-probability zones based on market structure and order flow evidence. Understanding concepts like order blocks, liquidity, and imbalances provides a clearer framework for anticipating potential price reactions. This structured approach aids objective analysis, improves risk definition through logical stop placement, and fosters more consistent decision-making. While no single concept guarantees success, integrating the point of interest in forex into analysis provides a valuable tool for navigating the complexities of the market.
- A Point of Interest (POI) in forex represents a specific price zone where a significant market reaction is expected based on past activity or order flow.
- Key types include order blocks, liquidity zones, imbalances (FVGs), Fibonacci confluence areas, and psychological levels. Recognizing the specific point of interest in forex matters.
- Identify POIs using technical tools (MAs, Fibs), price action (patterns, volume), and market structure analysis (liquidity sweeps, CHoCH).
- Use POIs to plan entries (requiring confirmation), set logical stop-losses just beyond the zone, and define potential take-profit targets at subsequent POIs.
- Applying POI analysis promotes disciplined trading, enhances risk management, can improve entry timing, and provides strategic market context. Forex poi levels are key reference points.
- Always use POIs in conjunction with broader market context, trend analysis, and confirmation signals for higher probability setups.
Are Points of Interest (POIs) guaranteed reversal points?
No, POIs should not be treated as guaranteed reversal points. They are zones where the probability of a reaction is higher based on historical data or structural significance. However, price can definitely break through any POI, especially with strong momentum. Always use confirmation signals before entering and implement proper risk management with stop-losses, as any point of interest in forex can fail.
How do different timeframes affect POI identification and significance?
POIs identified on higher timeframes (e.g., Weekly, Daily, 4-Hour) typically represent more significant structural levels and carry more weight. They provide the broader context. POIs on lower timeframes (e.g., 1-Hour, 15-Minute) are often used to refine entries or observe confirmation signals when price interacts with a higher timeframe point of interest in forex. The interplay between timeframes is crucial for effective analysis.
Can POI analysis be fully automated with indicators?
While certain indicators can automatically highlight potential POIs like order blocks or fair value gaps, fully automating the analysis effectively is challenging. Human analysis excels at interpreting context – the strength of the preceding trend, the freshness of the zone (number of times tested), overall market structure, and confluence with other factors. Indicators can be valuable assistants for scanning and highlighting potential areas, but discretionary judgment remains vital when evaluating a point of interest in forex.







