The Smart Money Concept (SMC) is a sophisticated trading strategy centered on analyzing the actions of institutional investors, commonly known as “smart money,” within the forex market. This method uses technical analysis to decode the supply and demand dynamics that influence price movements. By identifying these patterns, traders can make better-informed decisions, enhancing their potential for profitability. Many traders rely on platforms offered by a forex trading broker to implement SMC strategies effectively. This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental principles, essential concepts, trading methodologies, and critical considerations involved in SMC trading.

Definition and Core Principles
Definition of the Smart Money Concept (SMC)
The Smart Money Concept (SMC) in forex trading is a technical analysis strategy that centers on tracking and responding to the trading actions of institutional investors in the market. These institutions, which include banks, hedge funds, and large financial entities, wield substantial capital and influence that often drive significant market movements. By identifying and interpreting the trading patterns and zones created by these institutions, retail traders can align their strategies with the dominant market forces, enhancing their trading accuracy and profitability.

Core Principles of SMC Trading
Supply and Demand Dynamics
SMC revolves around understanding where imbalances between supply and demand occur. These imbalances, driven by institutional trading activities, create zones of high buying or selling pressure on price charts.
Institutional Activity
The focus is on recognizing and analyzing the behaviors of institutional investors, whose large trades have a notable impact on market direction.
Market Imbalances
SMC identifies how institutional orders, due to their size, create imbalances that propel price movements in specific directions.
By adhering to these principles, traders can pinpoint high-probability trading opportunities and refine their decision-making processes effectively.
Comparison to Price Action Trading
While SMC shares some similarities with price action trading—such as analyzing market patterns and behaviors—it differs in its specific focus and terminology. Price action trading predominantly involves interpreting candlestick patterns and market trends, often emphasizing the psychological aspects of market participants.
In contrast, SMC specifically targets institutional trading footprints. It concentrates on understanding how these entities influence price movements through their strategic trading activities. By focusing on institutional order zones, SMC provides traders with a more nuanced understanding of market dynamics compared to traditional price action trading approaches.
History and Evolution of the Smart Money Concept
Origins of SMC
The Smart Money Concept has its roots in early market theories that emphasized the importance of institutional activity. Pioneers of market analysis, such as Richard Wyckoff, recognized that understanding the behavior of large financial players could provide significant trading advantages. Wyckoff’s methods focused on identifying the accumulation and distribution phases of market cycles, which are often driven by institutional activities.
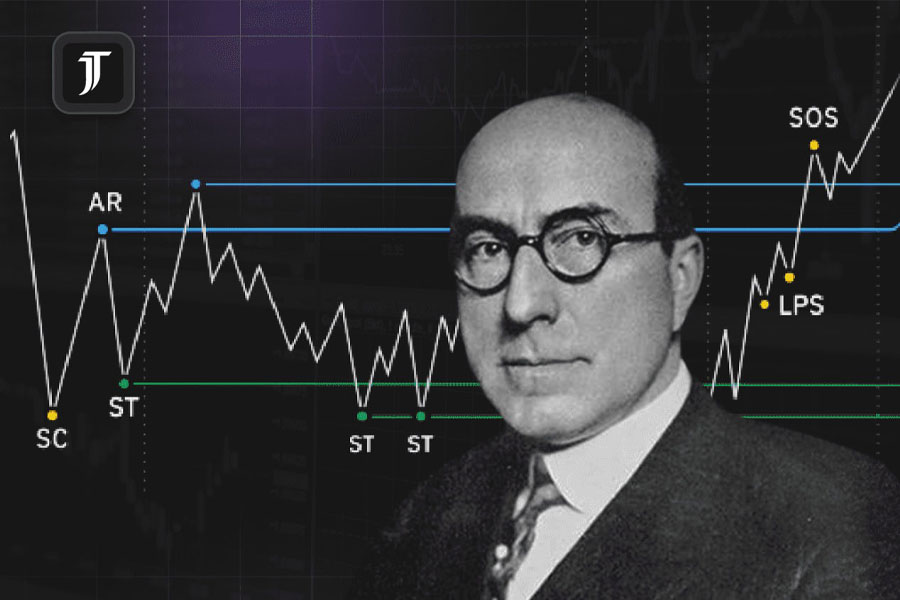
Over time, the foundational ideas of Smart Money Concept (SMC) trading have evolved into sophisticated techniques used in modern markets. This evolution has been driven by the development of technical analysis tools and the increased availability of market data, enabling traders to refine concepts and apply them more effectively.
Influence of Technology on SMC
The integration of advanced trading platforms and algorithmic trading has profoundly influenced the Smart Money Concept. Technological advancements have facilitated the analysis of extensive market data, enhancing the ability to detect institutional activity and optimize trading strategies.
Key Technological Advancements
- Advanced Charting Tools Modern platforms provide robust charting tools that aid in precise identification of SMC zones on price charts.
- Algorithmic Trading Algorithms automate the identification of SMC patterns and execute trades based on predefined criteria, improving efficiency and accuracy.
- Real-Time Data Analysis Access to real-time market data enables traders to promptly respond to institutional activity and market developments.
These technological innovations have democratized high-level market analysis, empowering retail traders to implement SMC strategies effectively.
Key SMC Concepts
The Smart Money Concept (SMC) comprises fundamental concepts that are pivotal for traders aiming to discern and track institutional activities within the forex market. These concepts encompass order blocks, fair value gaps, liquidity grabs, breaker blocks, and mitigation blocks. Each plays a crucial role in understanding market dynamics and making informed trading decisions.
Order Blocks
Order blocks are specific zones on a price chart where significant buying or selling activity has occurred, typically driven by institutional traders. These areas are characterized by clusters of candlesticks exhibiting substantial volume, indicating robust price action in either an upward or downward direction. Identifying order blocks is essential as they signify areas of high-volume transactions that often dictate future price movements.
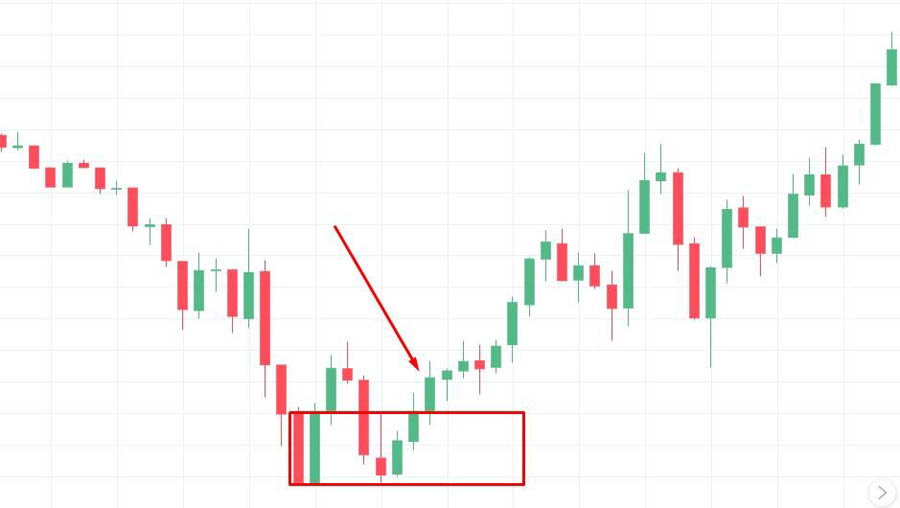
Identifying Order Blocks
To identify order blocks, traders look for:
- Clusters of Candlesticks: A series of candlesticks with consistent high volume.
- Volume Spikes: Unusually high trading volume in a specific area.
- Price Consolidation: A period where the price moves sideways within a tight range before a breakout.
Order blocks can act as strong support or resistance levels. When the price revisits these zones, it often reacts strongly, providing potential entry or exit points for traders.
Fair Value Gaps
Fair value gaps (FVGs) are price gaps that occur due to an imbalance between supply and demand. These gaps represent areas where the price has not traded, suggesting a rapid shift in market sentiment. FVGs can provide valuable clues about potential price reversals or continuations.
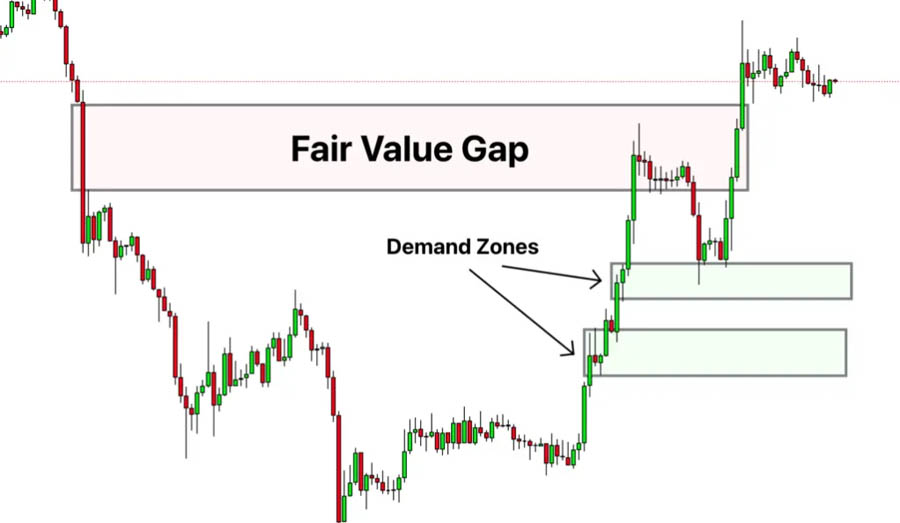
Identifying Fair Value Gaps
Fair value gaps can be identified by:
- Price Gaps: Visible gaps on the chart where the price jumps from one level to another without any trading in between.
- Candlestick Patterns: Gaps between the high of one candlestick and the low of the next in an uptrend, or between the low of one candlestick and the high of the next in a downtrend.
Fair value gaps often occur during periods of high volatility and can signal strong market moves. Traders use these gaps to predict where the price might retrace to fill the gap before continuing in the original direction.
Liquidity Grabs
Liquidity grabs are deliberate price movements designed to attract additional market participants and trigger stop-loss orders. These movements create volatility, allowing institutional traders to accumulate or distribute positions at more favorable prices.
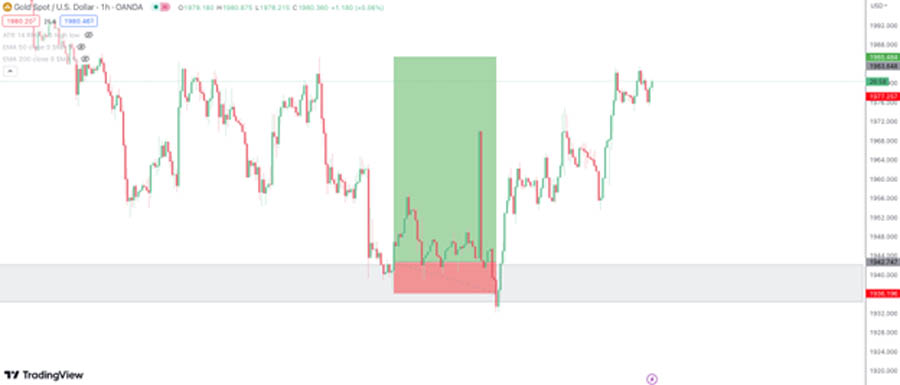
Identifying Liquidity Grabs
Liquidity grabs can be identified by:
- Stop-Loss Hunts: Sharp moves that trigger stop-loss orders placed by retail traders.
- False Breakouts: Price breaks through a support or resistance level but quickly reverses direction.
- Wicks and Shadows: Long wicks on candlesticks indicating sudden price reversals.
Liquidity grabs are often seen near key support and resistance levels where many traders place their stop-loss orders. Identifying these moves can help traders avoid being caught in false breakouts and capitalize on the subsequent price action.
Read More: Sentiment Analysis in Forex
Breaker Blocks
Breaker blocks are areas on the chart where the price breaks through a significant support or resistance level and then reverses direction. These blocks are crucial for identifying potential trend changes or continuations.
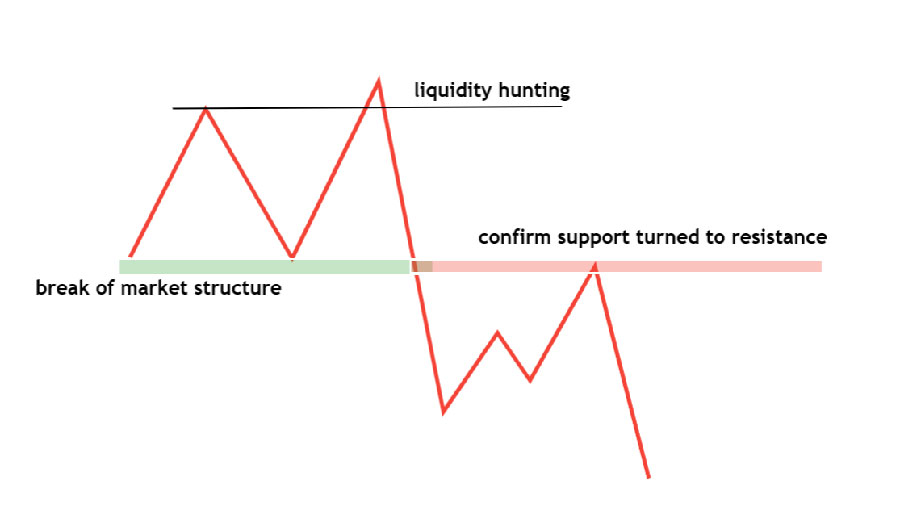
Identifying Breaker Blocks
Breaker blocks can be identified by:
- Breakout and Retest: Price breaks through a support/resistance level, then retests the same level.
- Volume Confirmation: High volume on the breakout and retest, indicating strong market interest.
- Candlestick Patterns: Engulfing patterns or strong reversal candlesticks at the retest.
Breaker blocks serve as confirmation zones. When the price revisits these blocks and holds, it can indicate a continuation of the new trend.
Mitigation Blocks
Mitigation blocks are zones where the price retests a previous breakout, providing potential entry points. These blocks help traders confirm the validity of a breakout and the strength of the ongoing trend.
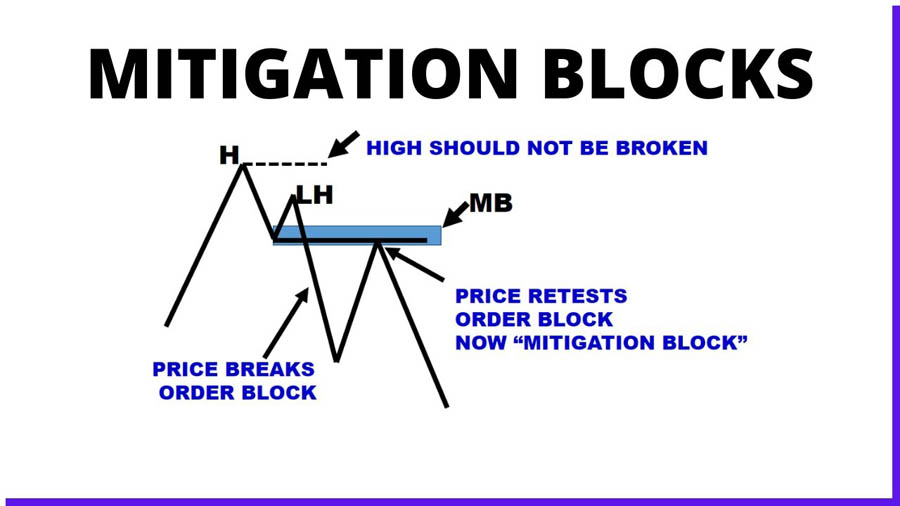
Identifying Mitigation Blocks
Mitigation blocks can be identified by:
- Retest of Breakout Levels: Price returns to the breakout point and consolidates.
- Reduced Volatility: Lower volatility during the retest compared to the breakout.
- Support/Resistance Confirmation: The breakout level acts as new support or resistance during the retest.
Mitigation blocks offer traders opportunities to enter the market at more favorable prices after the initial breakout.
Advanced SMC Techniques
Expanding upon the foundational principles of the Smart Money Concept (SMC), advanced techniques offer traders deeper insights and more sophisticated methods for maximizing trading effectiveness. These advanced SMC techniques include combining SMC with order flow analysis, understanding market microstructure, and implementing SMC strategies algorithmically.
Combining SMC with Order Flow Analysis
Order flow analysis is a technique that examines the flow of buy and sell orders in the market to understand the underlying supply and demand dynamics. By combining SMC with order flow analysis, traders can gain a more comprehensive view of market movements and institutional activity.
Understanding Order Flow Analysis
Order flow analysis focuses on:
- Order Book Data: The total number of buy and sell orders at different price levels.
- Trade Volume: The actual number of transactions executed at various price points.
- Bid-Ask Spread: The difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept.
Read More: Geopolitical Impact on Forex Trading
Practical Applications
- Enhancing SMC Zones: By analyzing order flow data, traders can better identify and confirm SMC zones such as order blocks and fair value gaps. High volume and significant order flow at these levels can validate the presence of institutional activity.
- Predicting Market Moves: Order flow analysis helps traders anticipate market moves by revealing where large orders are clustered, indicating potential support or resistance levels.
SMC and Market Microstructure
Market microstructure refers to the detailed study of the processes and mechanisms that underlie trading in financial markets. It examines how various market participants’ interactions lead to price formation and liquidity. Understanding market microstructure can significantly enhance SMC trading strategies.
Key Elements of Market Microstructure
- Order Types: Different types of orders (e.g., market orders, limit orders) and their impact on price.
- Liquidity Providers and Takers: The roles of market makers and takers in providing and consuming liquidity.
- Transaction Costs: The costs associated with trading, including bid-ask spreads, slippage, and fees.
Integrating Market Microstructure with SMC
- Identifying Institutional Behavior: By understanding how large institutions operate and influence market microstructure, traders can better identify institutional activity within SMC frameworks.
- Improving Entry and Exit Points: Insights into market microstructure can help traders optimize their entry and exit points by understanding the likely behavior of liquidity and order flow around SMC zones.
Algorithmic Implementation of SMC
Algorithmic trading involves using computer programs to execute trades based on predefined criteria. Implementing SMC strategies algorithmically can enhance efficiency, accuracy, and the ability to manage multiple trades simultaneously.
Steps to Implement SMC Algorithmically
- Define SMC Criteria: Clearly outline the criteria for identifying SMC zones, such as order blocks, fair value gaps, and liquidity grabs.
- Develop Algorithms: Write algorithms that scan price charts for these criteria using historical and real-time data.
- Backtesting: Test the algorithms on historical data to evaluate their performance and refine parameters.
- Optimization: Continuously optimize the algorithms based on backtesting results and market changes.
- Execution: Use the algorithms to execute trades in real-time, with automated order placement and management.
Benefits of Algorithmic SMC Trading
- Speed and Efficiency: Algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data quickly and execute trades at optimal times.
- Consistency: Automated strategies remove emotional bias, ensuring consistent application of SMC principles.
- Scalability: Algorithms can manage multiple trades across different markets and timeframes simultaneously.
Community and Support for SMC Traders
As the popularity of Smart Money Concepts (SMC) trading continues to grow, so does the need for robust community support and resources. A thriving community can provide traders with invaluable insights, guidance, and a sense of belonging, which is crucial for navigating the complexities of SMC trading.
Online Trading Communities and Forums
Online communities and forums are essential resources for SMC traders, providing platforms to share strategies, discuss market conditions, and learn from each other.
Key Benefits:
- Knowledge Sharing: Experienced traders offer insights and trade setups.
- Strategy Discussion: Discussions help refine SMC strategies and gain diverse perspectives.
- Real-time Feedback: Immediate feedback aids in informed decision-making.
- Emotional Support: Community support helps manage emotional challenges.
Popular Communities:
- Reddit: Subreddits like r/Forex and r/DayTrading.
- Trade2Win: Forum for various trading strategies, including SMC.
- Forex Factory: Active forums for market analysis and strategy discussion.
Social Media and Influencer Insights
Social media platforms like Twitter, YouTube, and LinkedIn are vital for SMC traders, offering real-time analysis, trading tips, and educational content.
Twitter: Follow professional traders and analysts for market insights and trade setups. YouTube: Channels like “Trader Tom” and “The Trading Channel” offer tutorials and market analysis. LinkedIn: Groups and networks for connecting with industry experts and accessing professional resources.
Educational Resources and Training Programs
Comprehensive education is crucial for mastering SMC trading. Numerous free and paid resources help traders deepen their understanding and refine their skills.
Online Courses: Platforms like Udemy and Coursera offer courses on SMC trading. Webinars and Workshops: Many trading educators host sessions on SMC principles with live Q&A. Books and E-books: Titles like “Trading in the Zone” by Mark Douglas provide valuable market psychology insights. Mentorship and Coaching: Personalized guidance helps develop and refine SMC strategies.
Finding a Mentor:
- Professional Organizations: Offer mentorship programs with experienced traders.
- Trading Academies: Institutions like Online Trading Academy provide structured programs.
- Networking: Engage in forums, social media, and local trading groups to find mentors.
Local Trading Groups and Meetups
Local groups and meetups provide face-to-face interactions, where traders can discuss strategies, share experiences, and participate in group trading sessions.
Benefits:
- Networking: Building relationships with local traders for learning opportunities.
- Live Discussion: In-person discussions offer detailed insights.
- Workshops and Events: Hands-on learning experiences through organized events.
Professional Trading Networks
Joining professional trading networks grants access to exclusive resources, advanced analytical tools, proprietary strategies, and educational content.
Conclusion
The Smart Money Concept (SMC) offers a robust framework for identifying and following the activities of institutional investors in the forex market. By understanding key concepts such as order blocks, fair value gaps, and liquidity grabs, traders can make more informed decisions and improve their trading performance. Combining SMC with other technical analysis tools, practicing disciplined risk management, and continuously learning and adapting are crucial for success.
What is the primary advantage of using the Smart Money Concept in trading?
The primary advantage of using the Smart Money Concept (SMC) in trading is its focus on identifying and following the activities of institutional investors. By recognizing the zones where these large entities are buying or selling, traders can align their strategies with the market’s underlying forces, potentially increasing their profitability.
How can traders effectively practice and refine their SMC skills?
Traders can effectively practice and refine their SMC skills by using demo accounts provided by forex brokers. These accounts allow traders to apply SMC strategies in real-time market conditions without risking actual capital. Additionally, participating in online forums and trading communities can provide valuable feedback and insights.
Are there any specific indicators or tools that complement SMC?
Yes, several indicators and tools complement SMC, including moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). These indicators can help confirm SMC signals and provide additional insights into market trends and potential entry or exit points.








One Response
Appreciate it for this post, I am a big fan of this web site would like to go on updated.