In the ever-changing landscape of financial markets, strategies for trading volatility indices have become essential tools for savvy investors seeking to capitalize on market fluctuations. Volatility indices, such as the VIX (CBOE Volatility Index), measure the market’s expectation of future volatility and provide unique opportunities for traders to profit from market uncertainty. This comprehensive guide will explore seven powerful strategies for trading volatility indices, equipping you with the knowledge and techniques to navigate turbulent markets with confidence.
Understanding Volatility Indices
Before diving into trading strategies, it’s crucial to understand what volatility indices are and how they function in the financial markets.
What are Volatility Indices?
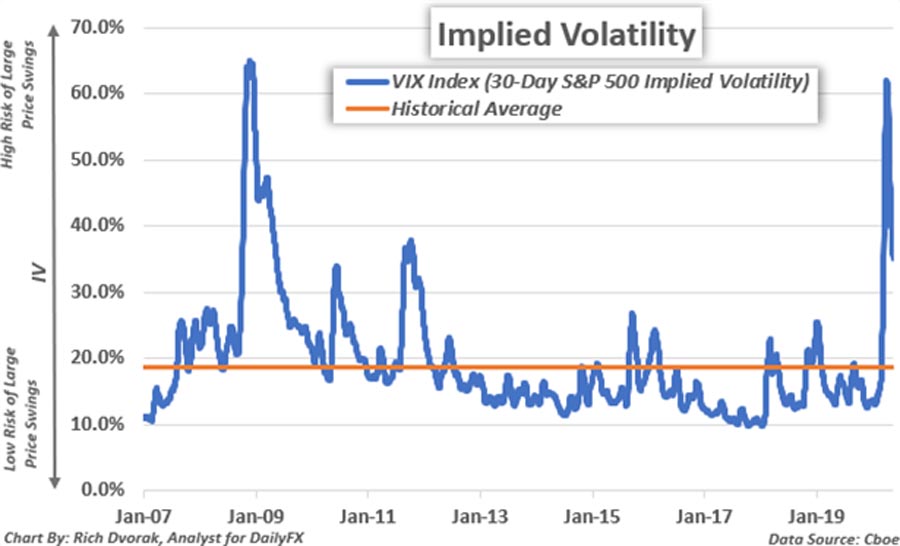
Volatility indices are financial instruments designed to measure the market’s expectation of future volatility. The most well-known volatility index is the VIX, often referred to as the “fear gauge” of the market. Other popular volatility indices include:
- VSTOXX (Euro STOXX 50 Volatility Index)
- VKOSPI (Korea Stock Exchange Volatility Index)
- India VIX (National Stock Exchange of India Volatility Index)
These indices are calculated using complex mathematical formulas that take into account the prices of various options on their respective underlying stock indices.
How Volatility Indices Work
Volatility indices typically have an inverse relationship with the stock market. When stock prices fall sharply, volatility indices tend to rise, reflecting increased investor fear and uncertainty. Conversely, when stock markets are calm and trending upwards, volatility indices often decline.
Key characteristics of volatility indices include:
- Mean-reverting nature: Volatility tends to spike during market stress but usually returns to its long-term average over time.
- Forward-looking: These indices reflect expectations of future volatility, not past performance.
- Non-tradable: The indices themselves cannot be directly traded, but various derivative products based on them are available.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of volatility indices is crucial for implementing effective trading strategies.
Benefits of Trading Volatility Indices
Trading volatility indices offers several advantages that make them attractive to both novice and experienced traders:
1. Diversification
Volatility indices often have a low or negative correlation with traditional asset classes like stocks and bonds. This makes them excellent tools for portfolio diversification, potentially reducing overall portfolio risk.
2. Hedging Opportunities
Investors can use volatility products to hedge against market downturns. Since volatility typically increases when stock prices fall, long positions in volatility indices can offset losses in equity portfolios during market crashes.
3. Profit from Both Bull and Bear Markets
Unlike traditional stock investing, volatility trading allows investors to profit from both rising and falling markets. Traders can go long when they expect increased volatility or short when they anticipate market calm.
4. Leverage
Many volatility products offer leveraged exposure, allowing traders to control a larger position with a smaller capital outlay. However, it’s important to note that leverage amplifies both gains and losses.
5. Market Sentiment Indicator
Volatility indices serve as excellent indicators of market sentiment. Traders can use these indices to gauge fear and greed levels in the market, informing their decisions across various asset classes.
6. Liquidity
Popular volatility products, such as VIX futures and options, are highly liquid, allowing for easy entry and exit of positions even in turbulent market conditions.
7. 24-Hour Trading
Some volatility products offer extended trading hours, providing opportunities to react to global events and news that occur outside regular market hours.
By understanding these benefits, traders can make informed decisions about incorporating volatility indices into their trading strategies.
1. Long Volatility Strategy: Capitalizing on Market Fear
One of the most straightforward strategies for trading volatility indices is the long volatility approach. This strategy involves buying volatility index futures or call options when you anticipate an increase in market uncertainty.
Key points:
- Best implemented during periods of low volatility
- Profit potential increases as market fear rises
- Requires careful timing and risk management
To execute this strategy effectively:
- Monitor market sentiment and potential catalysts for volatility spikes
- Use technical indicators to identify oversold conditions in volatility indices
- Consider implementing stop-loss orders to protect against sudden reversals
Advanced considerations:
- Analyze the volatility term structure to identify optimal entry points
- Combine with options strategies to create more defined risk-reward profiles
- Consider the impact of volatility of volatility (VOL of VOL) on your positions
2. Short Volatility Strategy: Profiting from Market Calm
The short volatility strategy is the opposite of going long and can be highly profitable during periods of market stability.

Key considerations:
- Involves selling volatility index futures or put options
- Most effective when volatility is high and expected to decrease
- Carries significant risk due to potential for unlimited losses
To implement this strategy:
- Analyze historical volatility patterns to identify potential mean reversion opportunities
- Use options strategies like credit spreads to limit downside risk
- Be prepared to exit positions quickly if market conditions change
Risk management tips:
- Set strict stop-loss levels and adhere to them religiously
- Consider using portfolio insurance techniques to protect against black swan events
- Diversify short volatility exposure across different time frames and products
3. Mean Reversion Trading: Exploiting Volatility Overreactions
Mean reversion is a powerful concept in volatility trading, based on the principle that volatility tends to return to its average level over time.
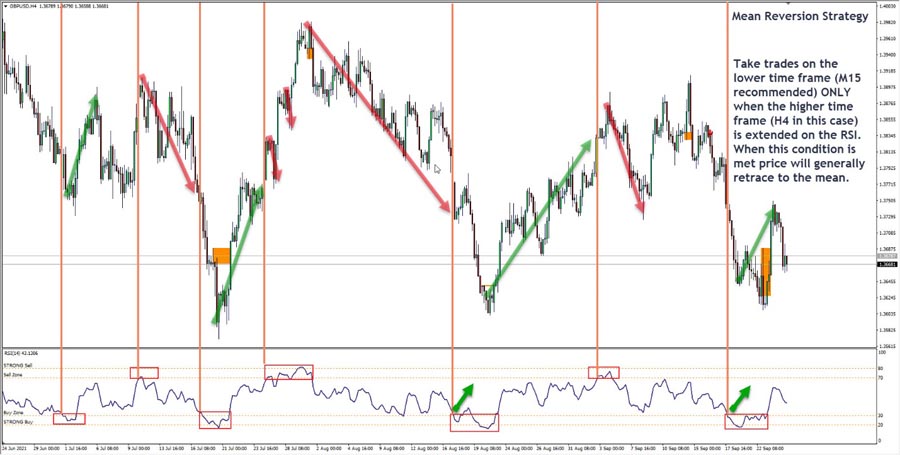
Key aspects:
- Involves buying low volatility and selling high volatility
- Requires patience and a strong understanding of historical volatility levels
- Can be combined with other strategies for enhanced effectiveness
Steps to implement:
- Calculate and track long-term average volatility levels
- Identify significant deviations from the mean
- Enter positions when volatility moves too far from its average, anticipating a return to normal levels
Advanced techniques:
- Develop quantitative models to identify statistically significant deviations
- Use rolling volatility measures to adapt to changing market regimes
- Incorporate fundamental analysis to validate mean reversion signals
4. Volatility Term Structure Trading: Leveraging the Futures Curve
The volatility term structure refers to the relationship between short-term and long-term volatility expectations.
Key points:
- Involves trading the spread between different volatility index futures contracts
- Profits from changes in the shape of the volatility curve
- Requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and futures pricing
Implementation tips:
- Monitor the slope of the volatility term structure
- Look for opportunities when the curve is unusually steep or inverted
- Use calendar spreads or butterfly strategies to exploit term structure anomalies
Advanced strategies:
- Develop models to forecast changes in the term structure based on market conditions
- Combine term structure trading with other volatility strategies for more robust returns
- Consider the impact of roll yield on long-term positions in volatility futures
5. Volatility Arbitrage: Exploiting Pricing Inefficiencies
Volatility arbitrage seeks to profit from discrepancies between implied and realized volatility.
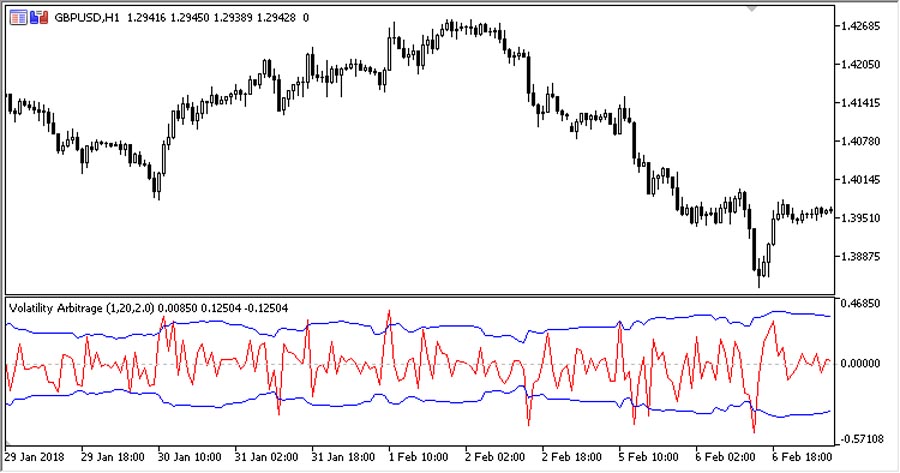
Key considerations:
- Involves simultaneously trading options and the underlying asset
- Requires sophisticated modeling and rapid execution
- Best suited for experienced traders with advanced analytical tools
To execute this strategy:
- Develop robust models to estimate future realized volatility
- Identify options that are mispriced relative to your volatility projections
- Implement delta-hedging techniques to isolate volatility exposure
Risk factors to consider:
- Transaction costs can significantly impact profitability
- Model risk: Your volatility forecasts may be inaccurate
- Execution risk: Prices may move against you before you can complete the trade
6. Correlation Trading: Capitalizing on Asset Relationships
Correlation trading involves exploiting the relationships between different asset classes and their impact on volatility indices.
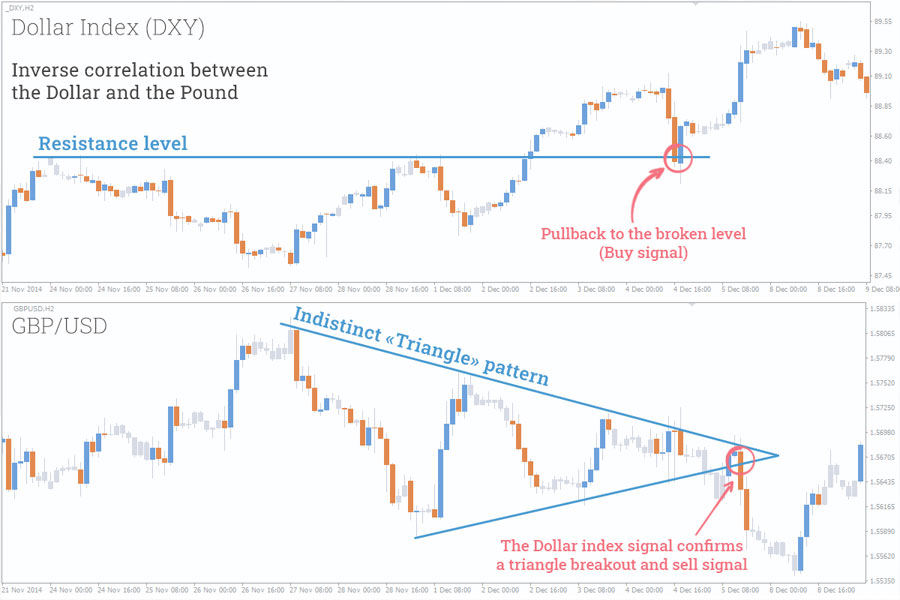
Key aspects:
- Focuses on how changes in one market affect volatility in another
- Requires a broad understanding of global market dynamics
- Can provide diversification benefits to a volatility trading portfolio
Implementation steps:
- Analyze historical correlations between major asset classes
- Identify potential correlation breakdowns or strengthening
- Use volatility index products to express views on changing market relationships
Advanced techniques:
- Develop multi-factor models to capture complex inter-market relationships
- Use machine learning algorithms to identify non-linear correlation patterns
- Implement dynamic hedging strategies to adapt to changing correlations
7. Event-Driven Volatility Trading: Profiting from Scheduled Announcements
Event-driven volatility trading capitalizes on the market’s reaction to scheduled economic releases, earnings reports, and other significant events.
Key points:
- Involves positioning ahead of known market-moving events
- Requires careful analysis of historical volatility patterns around similar events
- Can lead to quick profits but also carries substantial risk
To implement this strategy:
- Maintain a calendar of important economic and corporate events
- Study past volatility reactions to similar announcements
- Develop a playbook for different scenarios and be prepared to act quickly
Risk management considerations:
- Use options strategies to limit downside risk while maintaining upside potential
- Consider the impact of implied volatility crush after events
- Be prepared for unexpected outcomes and have contingency plans in place
Opofinance Services
Opofinance is a reputable and regulated financial brokerage that offers a variety of services to its clients. This brokerage is compatible with all operating systems and various tablets for traders. Whether you have a computer, laptop, tablet, or smartphone, you can easily and seamlessly access Opofinance and take advantage of the following services.
Stock and Securities Trading
Opofinance allows its users to buy and sell in various stock and securities markets. These services are provided online, enabling users to manage their trades with ease.
Portfolio Management
This brokerage offers tools and services for managing investment portfolios. These services help users make the best investment decisions based on their financial goals.
Market Analysis
Opofinance provides comprehensive market information and analysis to its users, enabling them to make more informed investment decisions. This analysis includes both technical and fundamental analysis.
Conclusion
Mastering strategies for trading volatility indices can significantly enhance your ability to navigate and profit from market turbulence. By understanding and implementing the seven powerful strategies outlined in this guide – long volatility, short volatility, mean reversion, term structure trading, volatility arbitrage, correlation trading, and event-driven volatility trading – you’ll be well-equipped to capitalize on market uncertainty.
Remember that successful volatility trading requires continuous learning, careful risk management, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions. Start by thoroughly researching each strategy, paper trading to gain experience, and gradually implementing these techniques in your real-world trading.
As you develop your skills in volatility trading, you’ll discover new opportunities to profit from market fluctuations and potentially enhance your overall investment performance. Stay informed, remain disciplined, and always be prepared to adjust your approach as market dynamics evolve. With dedication and practice, you can become a skilled volatility trader, ready to thrive in even the most turbulent market conditions.
By incorporating volatility indices into your trading arsenal, you’re opening up a world of new possibilities for portfolio management and profit generation. Whether you’re looking to hedge your existing positions, diversify your investment approach, or simply capitalize on market fear and greed, volatility trading offers a unique and powerful set of tools to achieve your financial goals.
As with any advanced trading strategy, it’s crucial to start small, continually educate yourself, and never risk more than you can afford to lose. With patience, discipline, and a deep understanding of the strategies outlined in this guide, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the art of trading volatility indices and turning market turbulence into opportunity.
How do volatility indices differ from traditional stock indices?
Volatility indices measure the market’s expectation of future volatility, typically over a 30-day period. Unlike stock indices, which track the performance of a basket of stocks, volatility indices reflect investor sentiment and fear levels. They often move inversely to the broader market, rising when stocks fall and vice versa.
What are the risks associated with trading volatility products?
Trading volatility products carries several unique risks:
High leverage: Many volatility products are highly leveraged, amplifying both gains and losses.
Contango and backwardation: The term structure of volatility futures can lead to significant losses for holders of long-term positions.
Complexity: Volatility products can be complex, making it difficult for inexperienced traders to fully understand their behavior.
Liquidity risk: Some volatility products may have limited liquidity, especially during market stress.
How can I incorporate volatility trading into my existing investment strategy?
Incorporating volatility trading into your investment strategy can provide diversification and new profit opportunities. Consider these approaches:
Use volatility products as a hedge against market downturns in your equity portfolio.
Allocate a small portion of your portfolio to volatility trading strategies to potentially enhance overall returns.
Use volatility analysis to inform your timing decisions in other asset classes.
Gradually increase your exposure to volatility trading as you gain experience and develop a track record of success.