In the competitive world of forex trading, understanding key strategies such as the ICT Breaker Block and ICT Mitigation Block can give traders a significant edge. These two advanced trading concepts are essential for identifying potential market reversals and shifts in market structure, enabling traders to make informed decisions and maximize their profits. By mastering these strategies, traders can better navigate the forex market’s complexities, whether they are working with a regulated forex broker or any other trading platform.
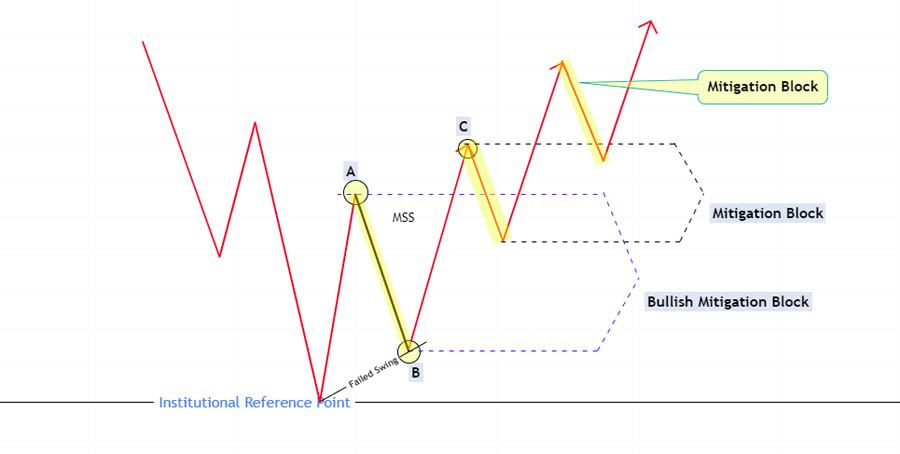
The ICT Mitigation Block is a pattern that emerges when the market fails to make a new high or low at a critical institutional reference point, such as an order block, breaker block, or imbalance. This failure often signals a shift in market direction, making it a powerful tool for traders who want to capitalize on short-term price movements within the broader market trend.
On the other hand, the ICT Breaker Block occurs after a liquidity sweep or a market structure shift, indicating a strong reversal point. Unlike the mitigation block, which is more focused on short-term corrections within a trend, the breaker block often signals a more significant change in market direction, providing traders with opportunities to enter the market at the beginning of a new trend.
This article will delve into the differences between ICT Breaker Blocks and ICT Mitigation Blocks, how to identify and trade them, and why these concepts are vital for traders working with a reliable broker for forex trading. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of these strategies and how to apply them in your trading routine.
What is an ICT Mitigation Block?
An ICT Mitigation Block is a reversal pattern observed when the market fails to swing higher or lower at a critical institutional reference point, such as an order block, breaker block, or imbalance. This failure indicates a potential shift in market direction, making the mitigation block a powerful signal for traders to consider.

The core concept behind the ICT Mitigation Block is simple: sell short-term rallies in a bearish trend and buy short-term declines in a bullish trend. This approach allows traders to align their strategies with the market’s overall direction while capitalizing on short-term price movements.
How to Identify an ICT Mitigation Block
Identifying an ICT Mitigation Block requires recognizing specific patterns at the end of a trend, whether bullish or bearish. These patterns are categorized into two types: Bearish ICT Mitigation Block and Bullish ICT Mitigation Block.
1. Bearish ICT Mitigation Block
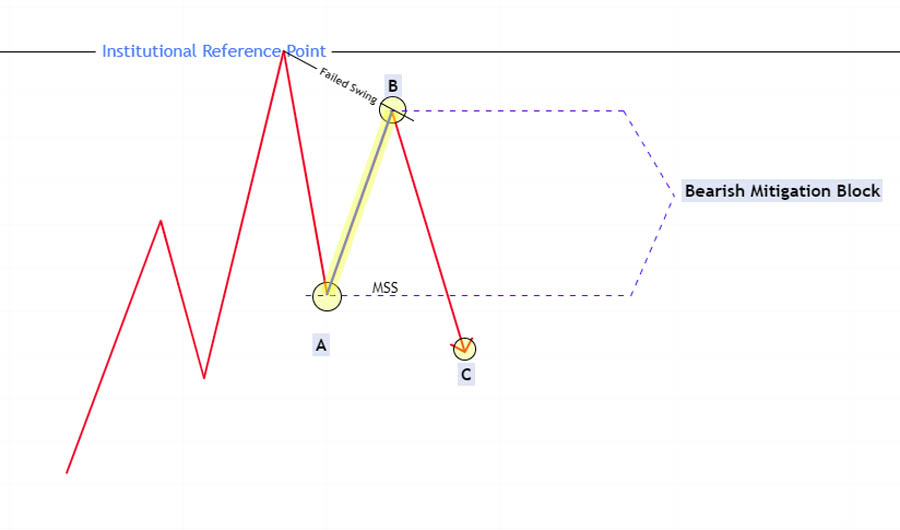
A Bearish ICT Mitigation Block forms at the end of a bullish trend when the price reaches a strong bearish institutional reference point, such as a bearish order block, breaker block, or after taking higher timeframe buy-side liquidity.
Key Characteristics:
- Bearish Reference Point: The price encounters a bearish order block, breaker block, or takes higher timeframe buy-side liquidity.
- Failure to Swing Higher: Instead of making a new higher high, the price forms a lower high.
- Market Structure Shift: The price then declines and breaks the previous higher low, indicating a shift towards a bearish market structure.
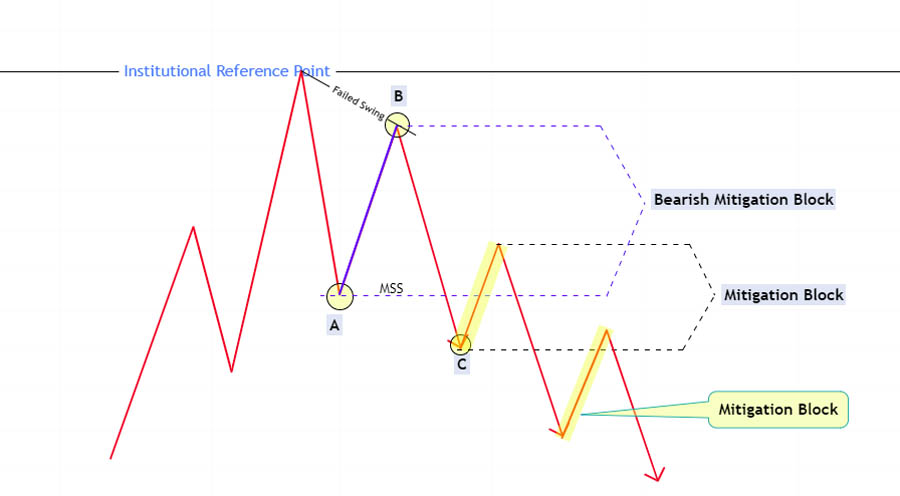
The area between the broken swing low (point A) and the newly formed lower swing high (point B) is termed the “Bearish Mitigation Block.” Traders can anticipate selling opportunities from this area as smart money looks to sell, expecting further downward movement.
2. Bullish ICT Mitigation Block
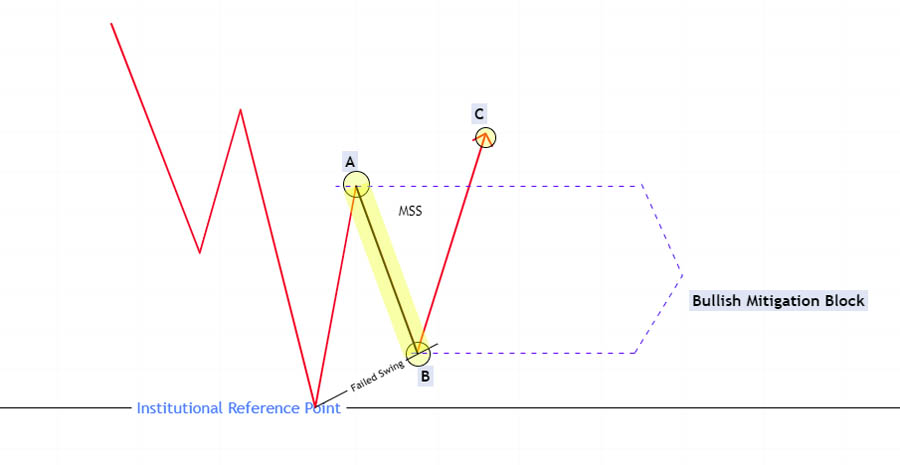
A Bullish ICT Mitigation Block forms at the end of a bearish trend when the price reaches a strong bullish institutional reference point, such as a bullish order block, breaker block, or after taking higher timeframe sell-side liquidity.
Read More: Mastering The ICT 30 Second Model
Key Characteristics:
- Bullish Reference Point: The price encounters a bullish order block, breaker block, or takes higher timeframe sell-side liquidity.
- Failure to Swing Lower: Instead of making a new lower low, the price forms a higher low.
- Market Structure Shift: The price then rises and breaks the previous lower high, indicating a shift towards a bullish market structure.
The area between the broken swing high (point A) and the newly formed higher swing low (point B) is termed the “Bullish Mitigation Block.” Traders can look for buying opportunities from this area, as smart money looks to buy, anticipating further upward movement.
What is an ICT Breaker Block?
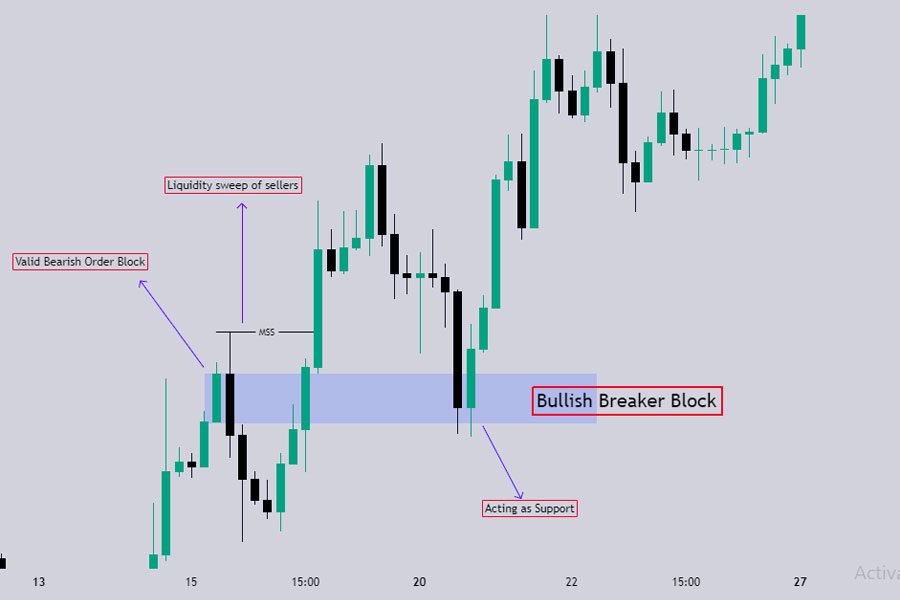
An ICT Breaker Block is another critical reversal pattern in forex trading, closely related to the ICT Mitigation Block but with distinct differences. The ICT Breaker Block forms after a liquidity sweep or market structure shift, often indicating a strong reversal point.
ICT Breaker Block vs. ICT Mitigation Block: Key Differences
- ICT Breaker Block: This pattern forms after the market sweeps a significant high or low and then shifts its structure. The last up or down closed candle before the sweep is marked as the breaker block, signaling a potential reversal.
- ICT Mitigation Block: Unlike the breaker block, the ICT Mitigation Block forms without a liquidity sweep. It occurs when the price fails to swing higher or lower and then shifts its structure, focusing on short-term price rallies or declines.
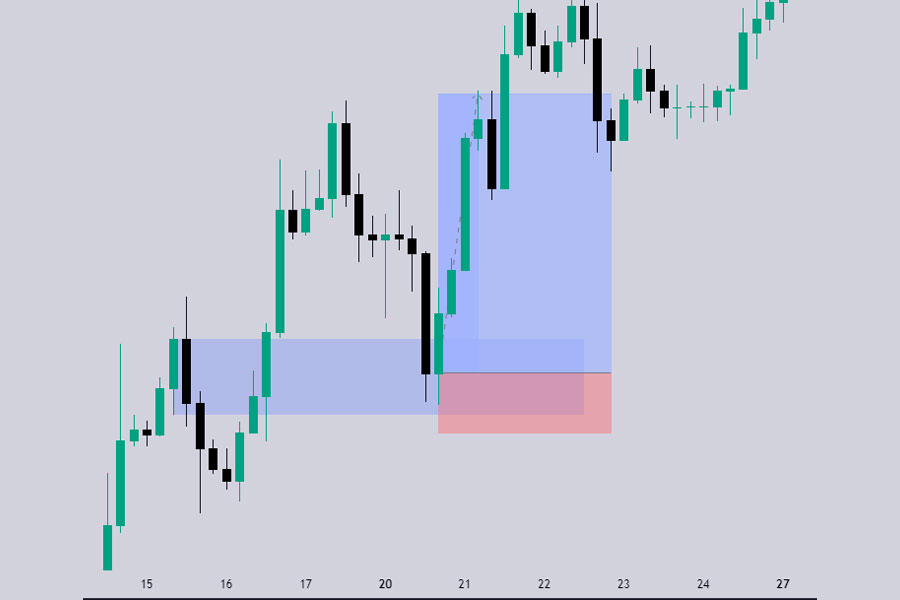
How to Identify an ICT Breaker Block
Identifying an ICT Breaker Block involves looking for specific market behaviors that indicate a failed order block and a subsequent market structure shift. This identification process can be divided into two main types: Bullish Breaker Block and Bearish Breaker Block.
1. Bullish Breaker Block
A Bullish Breaker Block forms when a bearish order block fails. After a liquidity sweep and market structure shift, the price closes above the high of the bearish order block, turning it into a bullish breaker block.
Key Identification Points:
- Valid Bearish Order Block: The initial bearish order block that the market fails to respect.
- Liquidity Sweep: The market takes out the previous lows, sweeping liquidity.
- Market Structure Shift: The price then breaks above the bearish order block, indicating a shift to a bullish trend.
- Breaker Block Formation: The last up-closed candle before the swing high (that swept liquidity and later broke it) is considered the breaker block.
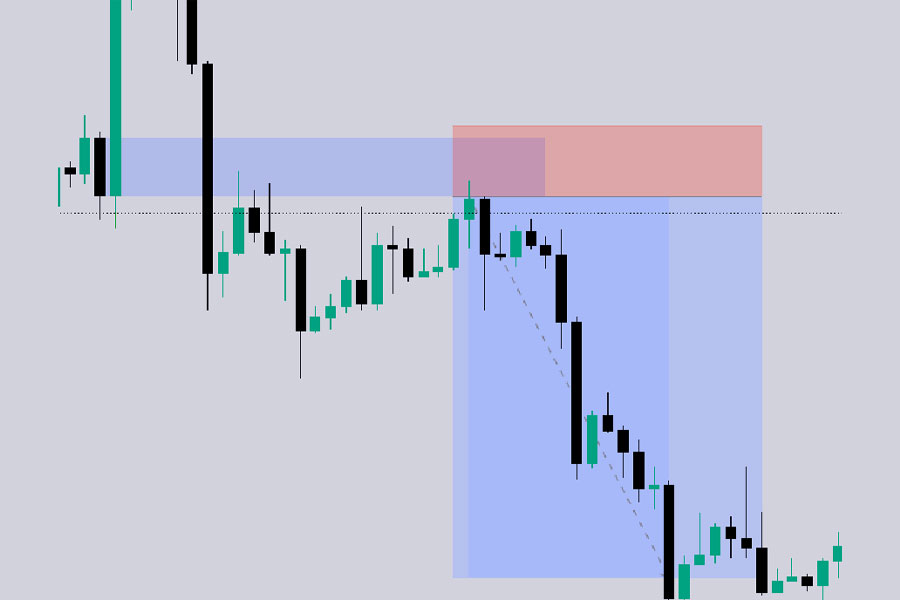
2. Bearish Breaker Block
A Bearish Breaker Block forms when a bullish order block fails. After a liquidity sweep and market structure shift, the price closes below the low of the bullish order block, turning it into a bearish breaker block.
Key Identification Points:
- Valid Bullish Order Block: The initial bullish order block that the market fails to respect.
- Liquidity Sweep: The market takes out the previous highs, sweeping liquidity.
- Market Structure Shift: The price then breaks below the bullish order block, indicating a shift to a bearish trend.
- Breaker Block Formation: The last down-closed candle before the swing low (that swept liquidity and later broke it) is considered the breaker block.
Read More: Understanding And Trading With ICT Breaker Blocks In Forex
How to Trade ICT Mitigation Blocks and Breaker Blocks: A Step-by-Step Guide
Trading these blocks effectively requires a clear understanding of their formation and the market conditions in which they appear. Below is a step-by-step guide to trading using ICT Mitigation Blocks and Breaker Blocks.
Step 1: Identify the Market Context
Determine whether the market is trending or ranging. Identify the key institutional reference points, such as order blocks, breaker blocks, or liquidity areas. Recognize whether the market is in a bullish or bearish phase.
Step 2: Spot the Reversal Patterns
- For Mitigation Blocks:
- In a bearish trend, look for a Bearish ICT Mitigation Block at the end of a bullish rally where the price fails to swing higher.
- In a bullish trend, look for a Bullish ICT Mitigation Block at the end of a bearish decline where the price fails to swing lower.
- For Breaker Blocks:
- Identify a Bullish Breaker Block after a bearish order block is broken and the price closes above its high.
- Identify a Bearish Breaker Block after a bullish order block is broken and the price closes below its low.
Step 3: Wait for Confirmation
Before entering a trade, wait for confirmation:
- Mitigation Blocks: Look for the price to revisit the mitigation block area, indicating potential selling or buying pressure.
- Breaker Blocks: Wait for the price to test the breaker block area and observe if it holds as a new support or resistance level.
Step 4: Execute the Trade
Once the price confirms the block as a significant reversal area:
- For Bearish ICT Mitigation Block: Enter a sell trade when the price revisits the bearish mitigation block.
- For Bullish ICT Mitigation Block: Enter a buy trade when the price revisits the bullish mitigation block.
- For Bullish Breaker Block: Enter a buy trade when the price tests the bullish breaker block area.
- For Bearish Breaker Block: Enter a sell trade when the price tests the bearish breaker block area.
Step 5: Set Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels
- Stop Loss: Place your stop loss a few pips above the high of the bearish breaker block or below the low of the bullish breaker block.
- Take Profit: Identify key levels of support or resistance where the price might reverse or consolidate and set your take profit accordingly.
Read More: Mastering ICT Change In State Of Delivery: Your Comprehensive Guide
Why Choose OpoFinance as Your Forex Trading Broker?
When it comes to selecting a reliable and regulated forex trading broker, OpoFinance stands out as an excellent choice. As an ASIC-regulated broker, OpoFinance provides a secure trading environment, ensuring that your investments are protected under stringent regulatory standards.
OpoFinance’s commitment to transparency and excellence makes it a preferred choice for both novice and experienced traders. The platform offers a wide range of services, including access to over 50 currency pairs, competitive spreads, and advanced trading tools designed to enhance your trading experience.

Exclusive Features of OpoFinance
- Regulated Environment: With ASIC regulation, you can trade with confidence, knowing that your funds are held in segregated accounts and that the broker adheres to strict compliance standards.
- Social Trading Service: OpoFinance offers an innovative social trading service that allows you to follow and copy the strategies of successful traders. This feature is ideal for beginners who want to learn from the best while still actively participating in the market.
- Educational Resources: OpoFinance provides a wealth of educational materials, including webinars, eBooks, and tutorials, helping you stay informed and up-to-date with the latest trading strategies and market trends.
Join OpoFinance today and take advantage of their cutting-edge trading platform, professional support, and the peace of mind that comes with trading with a regulated broker.
Conclusion
Mastering the ICT Breaker Block and ICT Mitigation Block strategies can greatly enhance a trader’s ability to navigate the complex and dynamic forex market. These advanced trading concepts provide invaluable insights into potential market reversals and shifts, enabling traders to make more informed and profitable decisions. Understanding the nuances between these two patterns—where the mitigation block focuses on short-term corrections and the breaker block signals more significant market reversals—can be the key to unlocking more consistent trading success.
For traders seeking to leverage these strategies effectively, partnering with a regulated forex broker is crucial. A reliable broker not only provides the necessary tools and resources but also ensures that traders operate within a secure and compliant environment. By combining these sophisticated trading strategies with the support of a trustworthy broker, traders can significantly improve their chances of success in the highly competitive forex market.
Incorporating the ICT Mitigation Block and ICT Breaker Block into your trading toolkit is not just about learning new techniques; it’s about evolving as a trader, enhancing your ability to predict market movements, and ultimately, achieving your financial goals. As you continue to refine your trading strategies, these concepts will serve as powerful assets, guiding you toward more strategic and successful trading decisions.
What is the main difference between an ICT Mitigation Block and an ICT Breaker Block?
The main difference lies in how they are formed. An ICT Mitigation Block forms when the market fails to swing higher or lower at a critical reference point, while an ICT Breaker Block forms after a liquidity sweep or market structure shift, leading to a significant reversal.
Can ICT Mitigation Blocks and Breaker Blocks be used in all market conditions?
While these blocks can be powerful tools in both trending and ranging markets, they are most effective in trending markets where reversals are more predictable.
How do I set stop-loss levels when trading using these blocks?
For Mitigation Blocks, set your stop loss just beyond the swing high or low of the block. For Breaker Blocks, place your stop loss a few pips above or below the breaker block’s extreme point.