In the dynamic world of financial markets, Contract for Difference (CFD) trading has gained significant popularity among investors looking to profit from price movements without owning the underlying assets. Choosing the right online forex broker plays a crucial role in ensuring a seamless trading experience. The best strategy for CFD trading combines in-depth market analysis, effective risk management, and disciplined execution. This comprehensive guide explores the most effective CFD trading strategies, offering both novice and experienced traders valuable insights to enhance their performance.

CFD trading strategies encompass a wide range of approaches, from technical analysis and fundamental research to momentum trading and swing trading. The key to success lies in finding a strategy that aligns with your trading style, risk tolerance, and financial goals. Whether you’re interested in CFD trading strategies for beginners or looking to refine your approach to CFD indices trading, this article will equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the markets with confidence.
Understanding the Basics of CFD Trading
Before diving into specific strategies, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of CFD trading:

- Definition: CFDs are financial derivatives that allow traders to speculate on price movements of various assets without owning them.
- Leverage: CFDs offer the ability to trade with leverage, potentially amplifying both profits and losses.
- Margin: Traders only need to deposit a small percentage of the total trade value as margin.
- Long and Short Positions: CFDs enable traders to profit from both rising (long) and falling (short) markets.
- Diverse Markets: CFDs cover a wide range of financial instruments, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies.
Read More: best trading strategies for volatile markets
Difference Between CFDs and Other Financial Derivatives
While CFDs share some similarities with other financial derivatives, they have unique characteristics that set them apart:
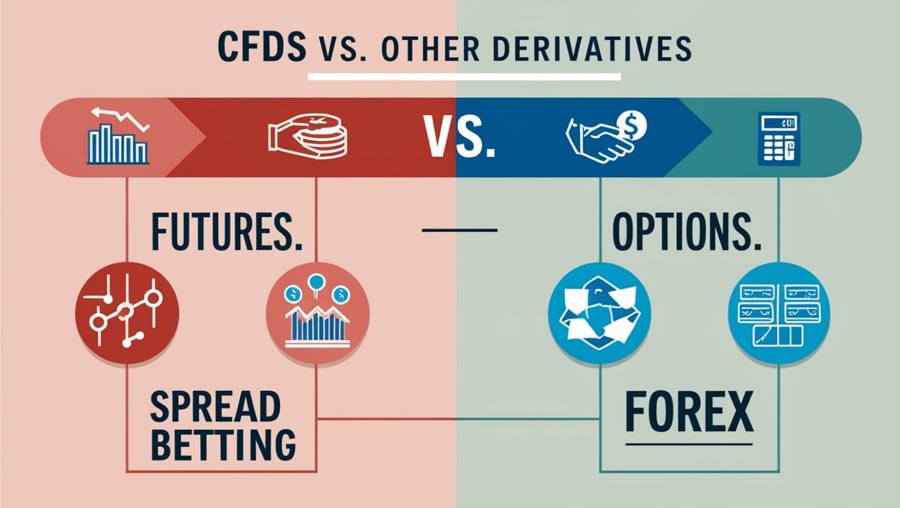
- CFDs vs. Futures Contracts:
- Expiration: CFDs don’t have expiration dates, while futures contracts do.
- Standardization: Futures contracts are standardized, whereas CFDs can be more flexible.
- Settlement: CFDs are settled in cash, while futures may involve physical delivery.
- CFDs vs. Options:
- Obligation: CFD traders are obligated to honor the contract, while options buyers have the right but not the obligation to exercise.
- Time Decay: Options are affected by time decay, whereas CFDs are not.
- Pricing: CFD pricing directly mirrors the underlying asset, while options pricing is more complex.
- CFDs vs. Spread Betting:
- Tax Treatment: In some jurisdictions, spread betting profits may be tax-free, while CFD profits are typically taxable.
- Product Range: CFDs often offer a wider range of tradable assets compared to spread betting.
- Global Availability: CFDs are more widely available globally, while spread betting is predominantly a UK and Ireland phenomenon.
- CFDs vs. Forex Trading:
- Asset Range: CFDs cover a broader range of assets, while forex focuses solely on currency pairs.
- Market Hours: Forex markets operate 24/5, while CFD trading hours depend on the underlying asset’s market.
- Unique Aspects of CFDs:
- Direct Price Tracking: CFDs more closely mirror the price of the underlying asset compared to many other derivatives.
- No Ownership: Unlike stocks or commodities, CFD traders never own the underlying asset.
- Flexibility: CFDs offer greater flexibility in trade size and duration compared to many other derivatives.
Understanding these differences can help traders choose the most suitable financial instrument for their trading goals and risk tolerance. CFDs offer unique advantages in terms of flexibility and market access, but they also come with their own set of risks and considerations.
Considerations
While CFDs offer unique advantages, they also come with significant risks, especially due to leverage. Traders should carefully consider their risk tolerance and investment goals when choosing between CFDs and other financial derivatives. It’s also crucial to be aware of the regulatory environment in your jurisdiction, as CFD trading is restricted or banned in some countries.
Read More: hedging strategies in forex trading
Key Elements of a Successful CFD Trading Strategy

1. Thorough Market Analysis
Effective CFD trading relies heavily on comprehensive market analysis. This involves:
- Technical Analysis: Studying price charts, patterns, and indicators to identify potential entry and exit points.
- Fundamental Analysis: Evaluating economic factors, company financials, and news events that may impact asset prices.
- Sentiment Analysis: Gauging market sentiment through various indicators and social media trends.
2. Risk Management
Implementing robust risk management techniques is crucial for long-term success in CFD trading:
- Position Sizing: Determining the appropriate trade size based on your account balance and risk tolerance.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Setting automatic exit points to limit potential losses.
- Take-Profit Orders: Defining profit targets to secure gains.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Aiming for trades with a favorable risk-reward ratio, typically 1:2 or higher.
3. Emotional Control
Maintaining emotional discipline is essential in CFD trading:
- Stick to Your Plan: Avoid impulsive decisions by adhering to your pre-defined trading strategy.
- Manage Stress: Develop techniques to handle the psychological pressures of trading.
- Learn from Mistakes: Analyze losing trades objectively and use them as learning opportunities.
4. Continuous Education
The financial markets are constantly evolving, making ongoing education crucial:
- Stay Informed: Keep up with market news, economic events, and industry developments.
- Attend Webinars: Participate in educational webinars and workshops offered by reputable brokers and analysts.
- Read Trading Literature: Expand your knowledge through books, articles, and research papers on CFD trading.
Top CFD Trading Strategies for Success
1. Trend Following Strategy
Trend following is a popular approach in CFD trading, based on the principle that markets tend to move in sustained directions:
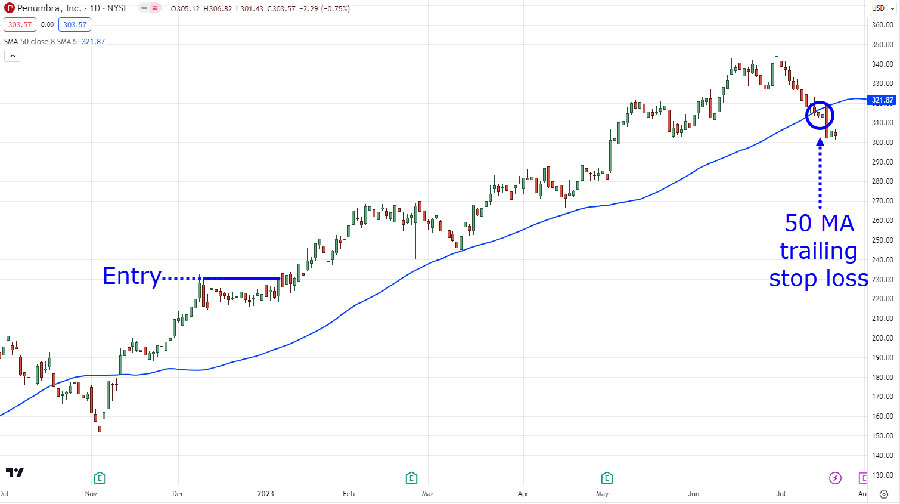
- Identifying Trends: Use moving averages, trendlines, and other technical indicators to spot prevailing trends.
- Entry Points: Look for pullbacks or consolidations within the trend for potential entry opportunities.
- Exit Strategy: Set trailing stop-losses to lock in profits as the trend progresses.
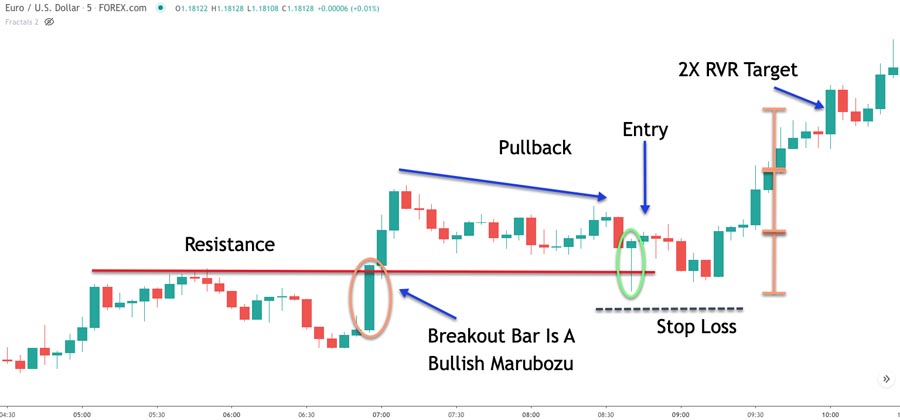
2. Breakout Trading Strategy
Breakout trading aims to capitalize on significant price movements that occur when an asset breaks through a key support or resistance level:
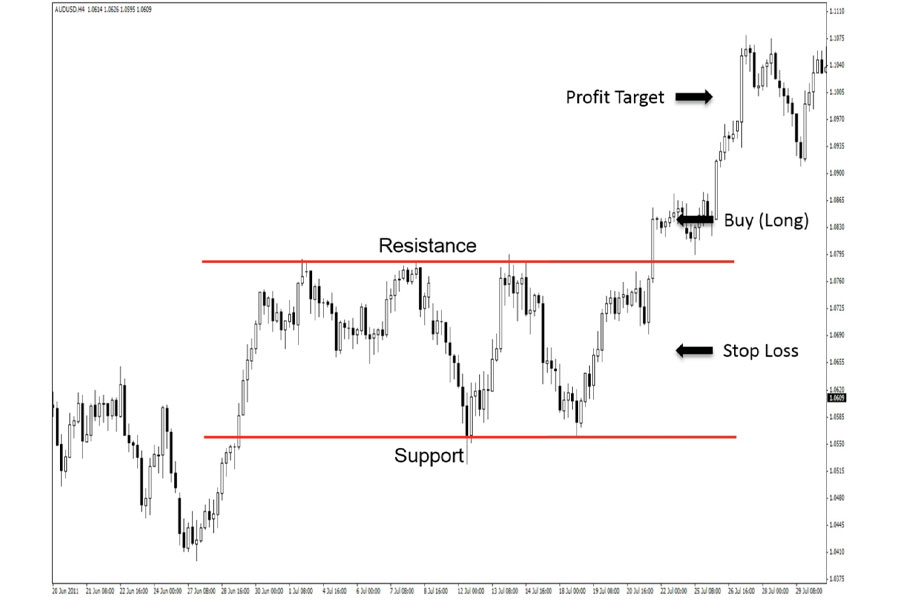
- Identify Key Levels: Use chart patterns and previous price action to determine important support and resistance zones.
- Volume Confirmation: Look for increased trading volume to confirm the validity of a breakout.
- False Breakouts: Be aware of the possibility of false breakouts and use appropriate stop-loss orders.
3. Range Trading Strategy
Range trading involves identifying and trading within established price ranges:
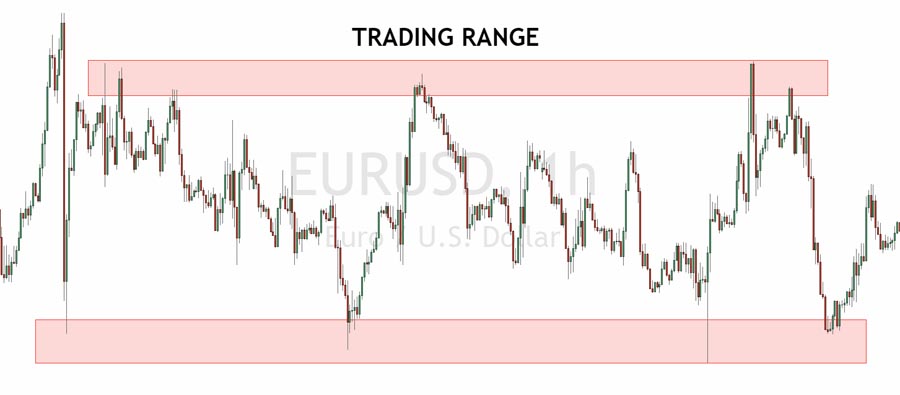
- Identify the Range: Look for assets that are trading sideways between clear support and resistance levels.
- Entry Points: Buy near support and sell near resistance.
- Risk Management: Place stop-losses just outside the range to protect against breakouts.
4. News Trading Strategy
News trading involves taking positions based on significant economic or company-specific news events:
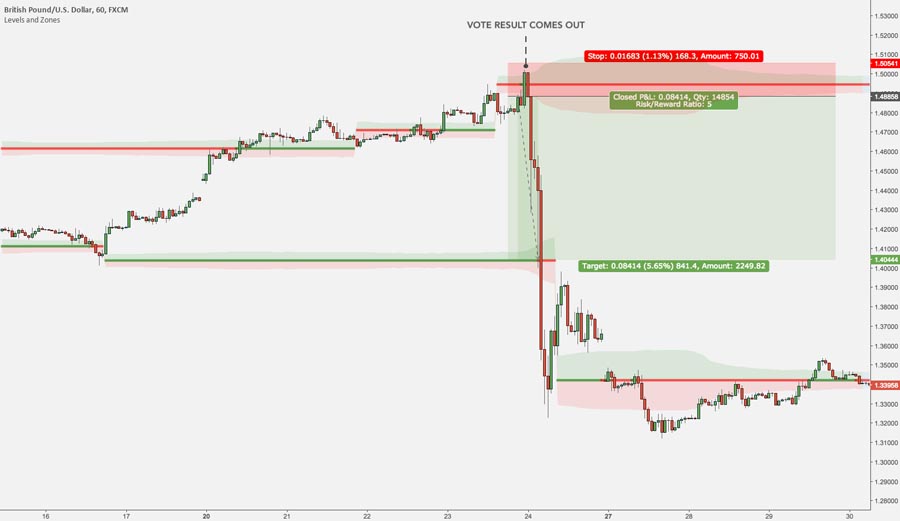
- Economic Calendar: Stay informed about upcoming economic releases and their potential market impact.
- Quick Execution: Be prepared to act swiftly as markets can move rapidly during news events.
- Risk Control: Use wider stop-losses to account for increased volatility during news releases.
5. Scalping Strategy
Scalping is a high-frequency trading approach that aims to profit from small price movements:
- Short Time Frames: Focus on very short-term charts, typically 1-minute or 5-minute timeframes.
- High Liquidity: Trade highly liquid assets to ensure quick execution of trades.
- Tight Spreads: Look for CFD brokers offering competitive spreads to minimize trading costs.
6. Swing Trading Strategy
Swing trading aims to capture medium-term price movements, typically over a few days to weeks:
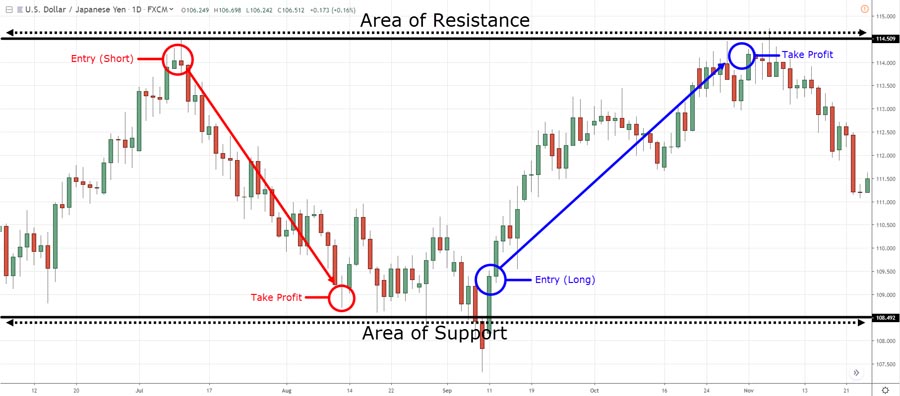
- Identify Swings: Use technical indicators and chart patterns to spot potential swing trading opportunities.
- Multiple Time Frame Analysis: Combine higher time frame trends with lower time frame entry points.
- Patience: Be prepared to hold positions for longer periods compared to day trading strategies.
Read More : forex fundamental trading strategies
Advanced CFD Trading Techniques
1. Pair Trading Strategy
Pair trading involves simultaneously taking long and short positions in two correlated assets:
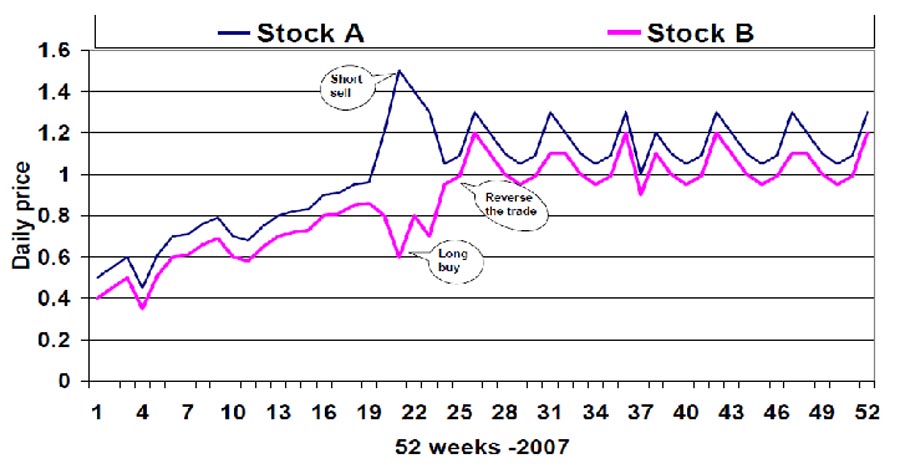
- Correlation Analysis: Identify pairs of assets with a strong historical correlation.
- Divergence Opportunities: Look for temporary divergences in the correlation to initiate trades.
- Risk Neutrality: Aim for market-neutral positions to reduce overall portfolio risk.
2. Multi-Time Frame Analysis
Combining multiple time frames can provide a more comprehensive view of market dynamics:
- Higher Time Frames: Use longer-term charts to identify overall trends and key levels.
- Lower Time Frames: Zoom in to shorter time frames for precise entry and exit points.
- Confluence: Look for setups where multiple time frames align for stronger trade signals.
3. Algorithmic Trading
Implementing automated trading systems can help execute strategies with precision and consistency:
- Backtesting: Rigorously test your algorithms using historical data before live trading.
- Risk Parameters: Set appropriate risk controls within your algorithmic trading system.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly review and adjust your algorithms to adapt to changing market conditions.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in CFD Trading
- Overtrading: Avoid excessive trading, which can lead to increased costs and emotional fatigue.
- Overleveraging: Use leverage responsibly to prevent outsized losses that can quickly deplete your trading capital.
- Ignoring Risk Management: Always use stop-loss orders and maintain proper position sizing.
- Chasing Losses: Resist the urge to increase position sizes or take unnecessary risks to recover losses.
- Lack of Patience: Avoid jumping into trades without proper analysis or exiting profitable positions too early.
Oppofinance Services
Oppofinance, regulated by ASIC Australia and classified as an onshore broker, is committed to protecting your investments. With ultra-competitive spreads close to zero pips, you can enhance your trading power. By joining us and taking advantage of our comprehensive rewards program, you can experience the potential for passive income. At Oppofinance, we believe our reputation in the market is our greatest asset, and we are always striving to meet the needs of our clients.
Conclusion
Developing the best strategy for CFD trading requires a combination of knowledge, skill, and discipline. By understanding the various strategies available and continuously refining your approach, you can improve your chances of success in the competitive world of CFD trading. Remember that no single strategy is perfect for all market conditions or traders. The key is to find an approach that aligns with your personal goals, risk tolerance, and trading style.
As you progress in your CFD trading journey, focus on continuous learning, rigorous risk management, and emotional discipline. Stay informed about market developments, regularly review and adjust your strategies, and always trade within your means. With dedication and practice, you can develop a robust CFD trading strategy that helps you navigate the markets with confidence and profitability.
How much capital should I start with when trading CFDs?
The amount of capital you should start with when trading CFDs depends on various factors, including your financial situation, risk tolerance, and trading goals. Generally, it’s recommended to start with an amount you can afford to lose without significantly impacting your lifestyle. Many brokers offer mini or micro accounts that allow you to start with as little as $100-$500. However, a more substantial starting capital of $5,000-$10,000 can provide better risk management options and potential for growth. Remember, it’s crucial to only invest money you can afford to lose and to start with smaller position sizes as you gain experience.
Can I use fundamental analysis for short-term CFD trading?
erm CFD trading as well. Fundamental factors like economic data releases, company earnings reports, and geopolitical events can cause significant short-term price movements. Traders can incorporate fundamental analysis into their short-term strategies by:
Monitoring economic calendars for important data releases
Following company news and earnings announcements
Staying informed about geopolitical events that may impact markets
Combining fundamental insights with technical analysis for a more comprehensive approach
By incorporating fundamental analysis, short-term CFD traders can gain a deeper understanding of potential market catalysts and make more informed trading decisions.
How do I handle overnight positions in CFD trading?
are some key points to keep in mind:
Funding charges: Many CFD brokers charge or credit overnight funding fees for positions held beyond the daily cut-off time. Be aware of these costs and factor them into your trading decisions.
Gap risk: Markets can gap up or down at the open, potentially leading to significant losses or gains. Use appropriate stop-loss orders to manage this risk.
Extended market hours: Some CFD providers offer extended trading hours, allowing you to manage positions outside regular market hours.
News monitoring: Stay informed about potential news events that could impact your positions overnight.
Position sizing: Consider reducing position sizes for trades held overnight to manage risk exposure.
Use of guaranteed stops: Some brokers offer guaranteed stop-loss orders, which can protect against slippage during volatile market opens.
By carefully managing these factors, you can effectively handle overnight positions in CFD trading while minimizing potential risks.







