According to Garner (2011), margin and leverage are “perhaps the most important features that separate Forex from other financial markets.” Due to their intertwined relation, before discussing margin, let’s briefly explore both terms. Leverage allows traders to control a substantial market position with a relatively modest capital outlay. Margin in Forex, or FX margin, on the other hand, is the required deposit for opening and maintaining a leveraged account, which typically range from 1-2% of the value of the position. In other words, the margin acts as a security deposit to cover potential losses and maintain open positions.

While employing margin and leverage carries inevitable advantages and risks, optimizing their use necessitates a thorough understanding of these mechanisms. Therefore, in this article, we’ll comprehensively elaborate on margin in forex, how it works, and how it can work for your benefit or against you. Choosing a reliable forex trading broker is also crucial to making the most of these tools and mitigating potential downsides.
The difference Between Leverage and Margin in Forex
Sometimes, traders might not have the funds to achieve satisfying profits. Brokerage firms offer a solution in the form of leverage. Simply put, leverage is the enhanced trading power that allows traders to control a larger amount of capital.
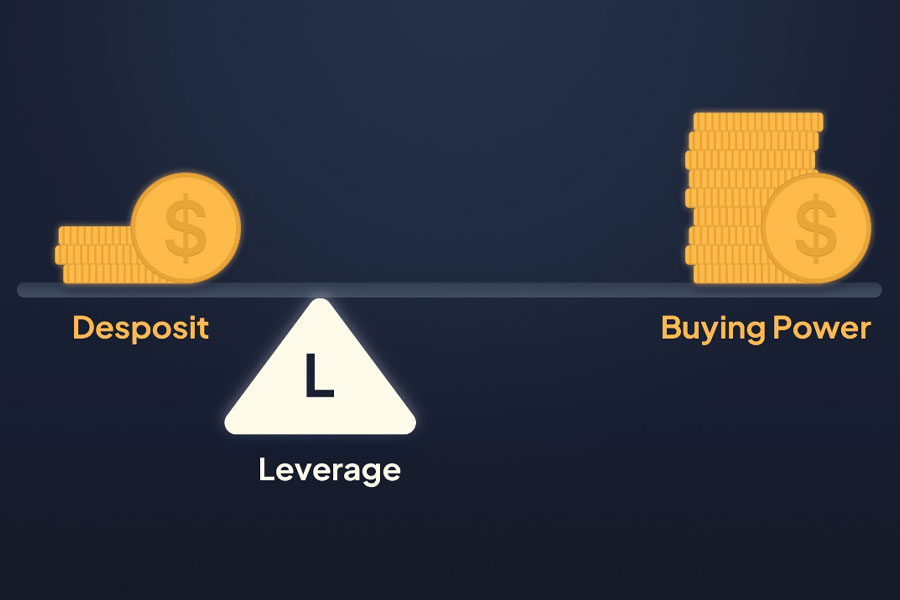
What is the role of margin in leveraged trading accounts? It’s straightforward. You use margin to create leverage. Margin is the fraction of the trade’s value you need to deposit.
Leverage is represented as a ratio, typically in the format “X:1.” For example, to trade 1 standard lot of USD/JPY without margin, you would need $100,000 in your account. However, with a margin requirement of just 1%, you only need to deposit $1,000. This means the provided leverage is 100:1.
Types of Margin in Forex
Initial Margin
The margin we’ve been referring to is actually the initial margin, which is the amount required to open a position. According to Carley Garner (2011), initial margin is “a single yet dynamic figure that constantly fluctuates” depending on the broker and the currency pair being traded.
Maintenance Margin
Maintenance margin is the minimum amount of capital required to keep a position open. If your account balance falls below this limit, you’ll receive a margin call from the broker, informing you to add additional funds. If you do not, the position will be automatically closed.
Read More: What is the 1% rule in forex trading ?
Required Margin
Required Margin, also known as:
– Entry Margin
– Initial Margin
– Initial Entry Margin
– Maintenance Margin Required (MMR),
is the amount of money that is locked up when you open a position. For example, if you open a $20,000 (mini lot) position with a Required Margin of 5% (or 20:1 leverage), $1,000 will be “locked up” for the duration of the trade.
Forex Margin Calculator

1- If the base currency and your account’s currency are the same:
Required margin= national value x margin requirement
2- If the base currency and your account’s currency are different:
Required margin= national value x margin requirement x exchange rate between the base currency and account currency
Margin Requirement
Margin Requirement is the amount of margin required for opening a position. It is presented as a percentage (%) of the total position size or the “Notional Value” of the position you plan to open.
Read More: Risk management principles for both novice and advanced traders
How Forex Brokers Determine Margin Requirements
Margin requirements are set by forex brokers based on several factors in order to assist traders with more realistic risk management circumstances. These factors include the type of currency pair, its market volatility, offered leverage, and the broker’s regulatory guidelines.
Forex brokers determine margin requirements based on several key factors, aiming to balance trader accessibility with risk management. These factors include market volatility, currency pair characteristics, leverage offered, regulatory guidelines, and the broker’s risk appetite.
Market Volatility
Margin requirements for volatile markets are more strict and larger in terms of volume since market fluctuations raise the risk of capital loss. For instance, to trade exotic pairs that have lower market share and whose prices can oscillate more easily, traders are asked for more margin to open positions.
Currency Pair Characteristics
Liquidity levels of different currency pairs vary, causing distinct margin requirements for each pair. For instance, EUR/USD is a major pair with high liquidity and hence lower margin requirements.
Leverage Offered
As mentioned earlier in this article, leverage increases a trader’s potential profit because they have control over larger capital. However, since it increases the risks of potential losses, brokers determine higher margin requirements for higher leverage.
Regulations
Credible brokers operate under the supervision of financial authorities and their regulations. A regulated broker must consider the maximum and minimum leverage ratios and margin requirements determined by these authorities.
How to Trade Forex Using Margin More Effectively
How to Handle Margin Calls
As previously explained, if your balance falls below the required margin, you’ll receive a margin call from the broker, requesting you to add funds to your account or risk having your position closed. Although this can be a frustrating situation, there are several steps you can take to manage it effectively.
Firstly, try not to panic. Even though it seems like an irritating situation, see it as an opportunity to reassess your strategy and analyze it in order to find its weaknesses.
Next, review the margin requirements. Ideally, this should be done before engaging in margin trading; however, upon receiving a margin call, it’s crucial to reexamine the broker’s terms and minimum margin levels to fully understand your options.
Lastly, take decisive action. If the appropriate response is to close some positions or add funds to your account, do so confidently. Additionally, consider seeking advice from an expert to ensure you are making informed decisions.
Monitor Your Margin Level
Margin calls occur when a trader fails to monitor their positions and, more importantly, their margin levels. Your account balance, equity, and margin levels are three key metrics you should constantly track to adjust your trading promptly. Monitoring these metrics does not require continuous presence behind a laptop or phone. You can simply set up alerts or use trading platforms with real-time margin level information.
Risk Management Strategies
Before opening a position, it is crucial to identify and implement effective risk management strategies. For instance, setting a stop-loss order is essential. Diversifying your trades, rather than investing all your capital in a single currency pair, is also vital. Additionally, comprehending the risk-reward ratio, which entails understanding the potential gains relative to the risks undertaken, is necessary. Lastly, maintaining control over your emotions is significant. Impulsive trading decisions can be detrimental to your success.
Read More: What Is the Spread in Forex and How do you Calculate It?
Avoid Over-Funding
According to the book Currency Trading in the Forex and Futures Market, “over-funding a trading account will cut down on the adrenaline rush but it might also prevent the inevitable rush to account-depleting trading.” The author continues to explain, “More margin and less leverage immediately provide traders with more room for error, and simultaneously shift the odds of success in the desired direction.” In other words, having more money and using less borrowed funds (leverage) gives traders more flexibility and increases their chances of success.

Results of a Survey of FX Margin Traders in Japan
A survey conducted in 2018 by Bernd Hayo 1 and Kentaro Iwatsubo on Forex margin traders considering their sociodemographic and economic circumstances, investment strategies, trading behavior, and financial literacy. The results may provide insights into the factors you should prioritize to enhance your success rate in margin trading within the forex market.
First, the survey revealed that traders lacking a specific strategy tended to perform worse, while those who employed fundamental analysis achieved greater profits.
Additionally, the survey indicated that the most successful traders possessed a profound understanding of FX trading and adhered to professional advice.
To sum up, although the use of margin and leverage entails risks alongside the potential for higher gains, a comprehensive knowledge of the forex market’s complexities, the application of fundamental analysis, and adherence to expert analysis and advice are crucial for improving your trading results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, forex brokers offer their clients various levels of leverage based on multiple factors, including regulatory guidelines and market volatility. Leverage allows traders to control larger amounts of capital than they have invested. To use leverage, traders must deposit a specific amount of money called margin. The required margin varies depending on the currency pair and the brokerage’s policies. If your account balance falls below a certain threshold, known as the maintenance margin, you will receive a margin call from the broker. This means you must either add funds to your account or the broker will close your positions. While there are strategies to avoid margin calls, it is crucial to be aware of the risks associated with margin trading in forex, as well as its benefits.
References: +
What is the difference between the used margin and the free margin?
When you open positions, the amount of money that is being locked up as collateral to hold your positions open is the used margin. The remaining amount of funds in your account that can be used to open new positions is the free margin.
How does market volatility affect margin trading?
One of the effects of market volatility is rapid changes in equity and margin levels. Therefore, it is vital to monitor your positions during volatile periods, such as the release of economic news, to avoid margin calls and forced liquidations.







