Hedging strategies in forex trading are crucial risk management techniques that safeguard traders’ investments against unfavorable market movements. These strategies involve taking offsetting positions to reduce potential losses while still allowing for profit opportunities. Utilizing a broker for forex trading, traders can implement effective hedging methods to minimize exposure to currency fluctuations and market volatility, providing a reliable safety net during uncertain periods.

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore seven powerful hedging strategies in forex trading, their benefits, and how to implement them effectively. Whether you’re a novice trader or an experienced professional, understanding these techniques can significantly enhance your trading performance and help safeguard your portfolio.
The forex market, with its daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion, offers tremendous opportunities for profit but also comes with significant risks. Currency values can fluctuate rapidly due to various factors, including economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. This volatility makes hedging an indispensable tool in a forex trader’s arsenal.
The Importance of Hedging in Forex Trading
Before diving into specific strategies, it’s crucial to understand why hedging is vital in the forex market:
- Risk mitigation: Hedging helps protect your trading positions from unexpected market movements, reducing the impact of adverse price changes on your overall portfolio.
- Portfolio protection: By implementing hedging strategies, you can safeguard your investments against systemic risks that may affect multiple currency pairs simultaneously.
- Market volatility management: Hedging allows traders to navigate through periods of high market volatility with greater confidence and reduced stress.
- Preservation of profits: Once you’ve made gains on a trade, hedging can help lock in those profits, ensuring that sudden market reversals don’t wipe out your hard-earned returns.
- Enhanced trading flexibility: With proper hedging in place, traders can maintain their long-term positions while still capitalizing on short-term market opportunities.
Hedging is not about eliminating risk entirely but rather about managing it effectively. By understanding and implementing various hedging strategies, traders can create a more balanced and resilient forex portfolio.
Now, let’s explore the seven most effective hedging strategies in forex trading..
Read More: best strategy for cfd trading
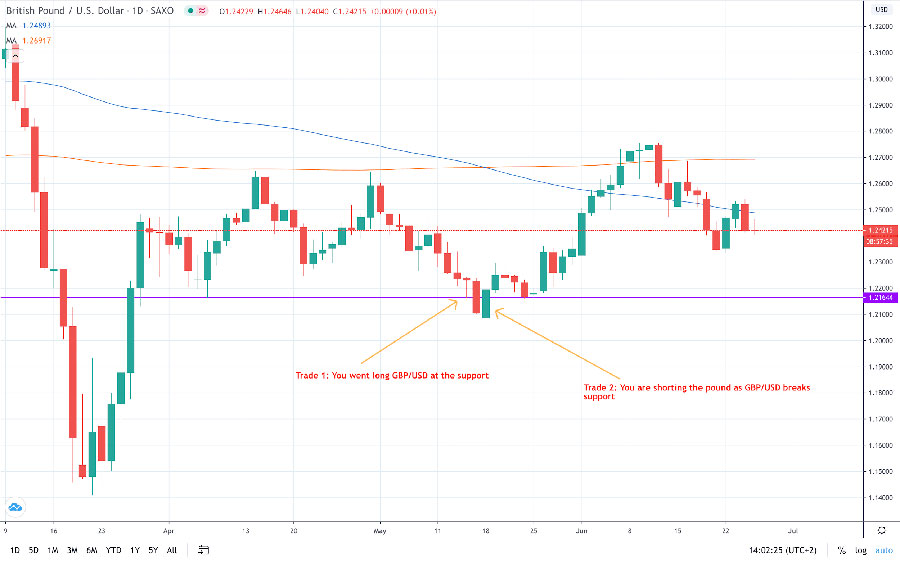
1. Direct Hedging: The Classic Approach
Direct hedging is the most straightforward strategy, involving opening opposite positions on the same currency pair.
How it works:
- Open a long position on EUR/USD
- Simultaneously open a short position on EUR/USD
For example, let’s say you’ve opened a long position of 100,000 EUR/USD at 1.2000. To implement a direct hedge, you would open a short position of 100,000 EUR/USD at the current market rate, say 1.2050.
Benefits:
- Locks in profits: If you’ve already made gains on your initial position, direct hedging ensures you retain those profits regardless of future price movements.
- Minimizes losses during market uncertainty: When major economic announcements or events are expected, direct hedging can protect your position from sudden adverse movements.
Drawbacks:
- May result in paying double spreads: Opening two positions means paying the spread twice, which can eat into potential profits.
- Limits potential gains: While direct hedging protects against losses, it also caps your potential profits from further favorable price movements.
Practical application:
Direct hedging is particularly useful when you have a long-term view on a currency pair but anticipate short-term volatility. For instance, if you believe the EUR will appreciate against the USD over the next few months, but you’re concerned about an upcoming European Central Bank announcement that might cause short-term euro weakness, you could use direct hedging to protect your position during this period of uncertainty.
Read More: best trading strategies for volatile markets
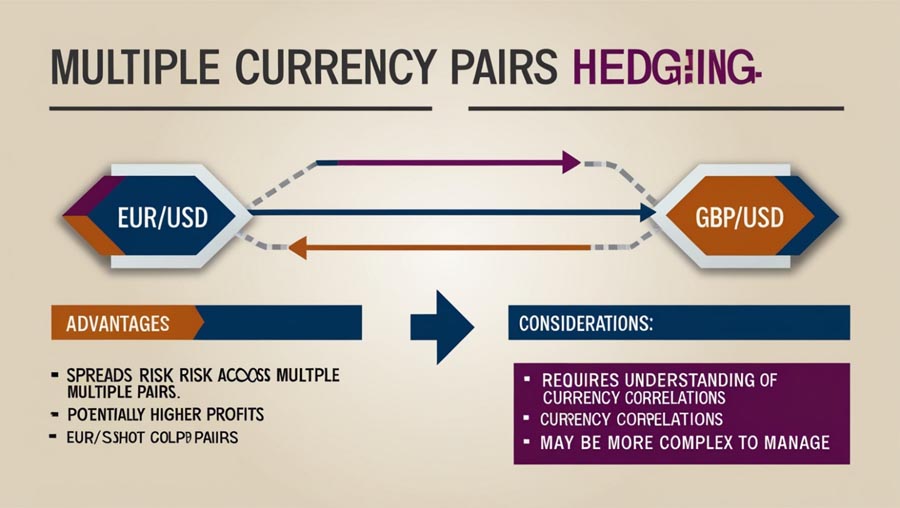
2. Multiple Currency Pairs Hedging: Diversification in Action
This strategy involves trading correlated currency pairs to offset potential losses.
Example:
- Long position on EUR/USD
- Short position on GBP/USD (negatively correlated with EUR/USD)
Let’s say you open a long position of 100,000 EUR/USD at 1.2000. To hedge this position, you might open a short position of 80,000 GBP/USD at 1.4000, assuming a correlation coefficient of -0.8 between the two pairs.
Advantages:
- Spreads risk across multiple pairs: By diversifying your hedging across different currency pairs, you’re not overly reliant on the performance of a single pair.
- Potentially higher profits compared to direct hedging: If managed correctly, this strategy can allow for some degree of profit from both positions.
Considerations:
- Requires understanding of currency correlations: Traders need to stay updated on how different currency pairs move in relation to each other.
- May be more complex to manage: Balancing multiple positions requires more attention and frequent adjustments.
Advanced application:
Experienced traders often use correlation matrices and heat maps to identify suitable pairs for multiple currency hedging. They might also incorporate other correlated assets, such as gold for AUD/USD trades or oil for CAD/USD trades, to create a more comprehensive hedging strategy.
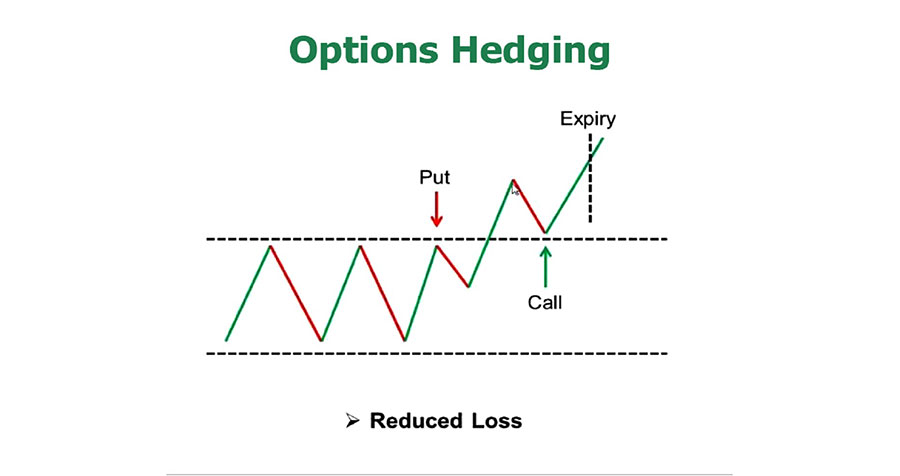
3. Options Hedging: Flexibility with a Price
Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency pair at a predetermined price.
Types of options:
- Call options (right to buy)
- Put options (right to sell)
For instance, if you hold a long position of 100,000 EUR/USD at 1.2000, you might purchase a put option with a strike price of 1.1900 to protect against downside risk.
Benefits:
- Limited downside risk: Options cap your potential losses while still allowing for unlimited profit potential.
- Potential for significant profits: If the market moves in your favor, you can let the option expire and benefit from the price movement of your underlying position.
Drawbacks:
- Requires payment of premium: The cost of purchasing options can be significant, especially for longer-dated contracts.
- Can be complex for beginners: Understanding option pricing, Greeks, and expiration dates requires a learning curve.
Strategic use:
Options are particularly useful for protecting positions around major economic events. For example, if you’re holding a significant USD position before a Federal Reserve interest rate decision, purchasing options can provide a safety net against unexpected policy changes while still allowing you to benefit if the announcement is favorable.
Read More: forex fundamental trading strategies
4. Forward Contracts: Locking in Future Rates
Forward contracts allow traders to agree on a future exchange rate for a specific amount of currency.

Key features:
- Set exchange rate
- Predetermined future date
- Obligation to execute the trade
For example, a trader might enter into a forward contract to buy 1 million euros in three months at a rate of 1.2000 USD per euro.
Advantages:
- Protects against unfavorable rate changes: Ideal for businesses or traders with known future currency needs.
- Provides certainty for budgeting and planning: Knowing the exact exchange rate in advance allows for more accurate financial forecasting.
Considerations:
- Less flexibility than options: Unlike options, forward contracts must be executed at maturity.
- May miss out on favorable rate movements: If the market moves in your favor, you’re still obligated to trade at the agreed-upon rate.
Business application:
Forward contracts are widely used by international businesses to manage currency risk. For instance, a European company expecting to receive a large payment in USD in six months might use a forward contract to lock in the current EUR/USD rate, protecting against potential euro appreciation that could reduce the value of the incoming payment.
5. Cross-Currency Hedging: Indirect Protection
This strategy involves using a third currency to hedge against fluctuations in the primary currency pair.
Example:
- Primary exposure: EUR/USD
- Hedge: Short USD/JPY
If you have a long position in EUR/USD and are concerned about USD strength, you might short USD/JPY as a hedge, assuming the yen’s relative stability.
Benefits:
- Useful when direct hedging is not available: Some forex brokers or regulatory environments may not allow direct hedging on the same pair.
- Can provide additional trading opportunities: Cross-currency hedging can open up new avenues for profit if managed skillfully.
Challenges:
- Requires understanding of currency relationships: Traders need to be aware of how different currencies interact and correlate.
- May introduce additional risk if not managed properly: Incorrect analysis of currency relationships can lead to increased rather than reduced risk.
Advanced strategy:
Sophisticated traders might use cross-currency hedging in combination with interest rate differentials to create complex carry trade strategies while minimizing currency risk.
6. Correlation Hedging: Leveraging Market Relationships
Correlation hedging takes advantage of the relationships between different financial instruments.
Examples:
- Long EUR/USD, short US stock index futures
- Long AUD/USD, short gold futures
A trader long on AUD/USD might short gold futures as a hedge, given the historical negative correlation between the Australian dollar and gold prices.
Advantages:
- Diversifies risk across asset classes: This approach can provide protection against broader market movements.
- Can provide protection during major economic events: Correlation hedging can be particularly effective during times of significant market stress or global economic shifts.
Considerations:
- Correlations can change over time: What worked as a hedge in the past may not be as effective in the future.
- Requires monitoring multiple markets: Traders need to stay informed about developments in various financial markets, not just forex.
Sophisticated application:
Some hedge funds and institutional traders use complex statistical models to identify and exploit temporary breakdowns in historical correlations, allowing them to implement more nuanced hedging strategies.
7. Algorithmic Hedging: Automation for Precision
Algorithmic hedging uses computer programs to execute trades based on predefined criteria.

Key features:
- Automated trade execution
- Real-time market analysis
- Customizable parameters
For instance, an algorithm might automatically hedge a portion of a currency position when certain technical indicators or news sentiment thresholds are met.
Benefits:
- Removes emotional decision-making: Algorithms execute trades based on pre-set rules, eliminating the impact of fear and greed.
- Can react quickly to market changes: Algorithmic systems can process and respond to market data much faster than human traders.
Drawbacks:
- Requires programming knowledge or specialized software: Developing effective hedging algorithms requires technical expertise.
- May have high initial setup costs: Sophisticated algorithmic trading systems can be expensive to develop and maintain.
Cutting-edge applications:
Advanced algorithmic hedging systems are incorporating machine learning and artificial intelligence to adapt their strategies in real-time based on changing market conditions. These systems can analyze vast amounts of data, including economic indicators, social media sentiment, and news flows, to make more informed hedging decisions.
Implementing Hedging Strategies: Best Practices
To effectively use hedging strategies in forex trading, consider the following tips:
- Understand your risk tolerance
- Start with simple strategies and gradually increase complexity
- Regularly review and adjust your hedging positions
- Keep track of transaction costs associated with hedging
- Use a combination of strategies for comprehensive protection
- Stay informed about economic events that may impact your hedged positions
- Practice with a demo account before using real money
Regulatory Considerations for Forex Hedging
It’s essential to be aware of the regulatory environment surrounding forex hedging:
- Different countries have varying regulations on hedging practices
- Some brokers may have restrictions on certain hedging strategies
- Ensure compliance with local laws and regulations before implementing hedging strategies
The Future of Hedging in Forex Trading
As the forex market evolves, so do hedging strategies:
- Integration of artificial intelligence for more sophisticated hedging
- Increased use of blockchain technology for transparency and efficiency
- Development of new financial instruments for hedging purposes
- Growing emphasis on sustainable and ethical hedging practices
Staying informed about these trends can help traders adapt their strategies and maintain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
Hedging strategies in forex trading are powerful tools for managing risk and protecting profits in the volatile currency markets. By understanding and implementing these seven strategies – direct hedging, multiple currency pairs hedging, options hedging, forward contracts, cross-currency hedging, correlation hedging, and algorithmic hedging – traders can significantly enhance their risk management capabilities.
Remember, successful hedging requires careful planning, continuous monitoring, and a deep understanding of market dynamics. As you explore these strategies, focus on developing a comprehensive risk management approach that aligns with your trading goals and risk tolerance.
Whether you’re a seasoned forex trader or just starting, incorporating hedging strategies into your trading toolkit can provide the safety net needed to navigate the unpredictable waters of the forex market. Stay informed, practice diligently, and always be prepared to adapt your strategies as market conditions change.
By mastering these hedging techniques and staying abreast of technological advancements and regulatory changes, you’ll be well-equipped to protect your forex investments and potentially enhance your trading performance. Remember that while hedging can significantly reduce risk, it’s not a guarantee against losses. Always trade responsibly and within your means.
How does hedging affect leverage in forex trading?
Hedging can impact leverage in forex trading by potentially reducing the overall exposure of your account. When you open a hedged position, it may not require additional margin, as the risk is offset by the opposing trade. However, it’s crucial to understand that while hedging can protect against losses, it can also limit potential gains. Always consider how hedging strategies interact with your broker’s leverage policies and margin requirements.
Can hedging strategies be combined with technical analysis in forex trading?
Absolutely! Combining hedging strategies with technical analysis can create a powerful approach to forex trading. Technical indicators can help identify potential entry and exit points for hedging positions. For example, you might use moving averages or support and resistance levels to determine when to implement a hedge. Remember that while technical analysis can enhance your hedging decisions, it’s essential to use it in conjunction with fundamental analysis and proper risk management techniques.
How do tax implications differ for hedged versus non-hedged forex trades?
Tax treatment of hedged forex trades can be more complex than non-hedged trades. In some jurisdictions, hedged positions may be treated as a single transaction for tax purposes, while in others, each leg of the hedge might be taxed separately. Additionally, the use of certain hedging instruments like options or futures contracts may have different tax implications compared to spot forex trades. It’s crucial to consult with a tax professional familiar with forex trading to understand the specific tax consequences of your hedging strategies in your jurisdiction.







