Volatility index trading strategies have gained significant traction among savvy investors aiming to benefit from market fluctuations. The Volatility Index, or VIX, commonly referred to as the market’s “fear gauge,” offers unique opportunities for traders to profit from both increasing and decreasing volatility. This comprehensive guide delves into various volatility index trading strategies, including volatility index 100 trading strategies and volatility index 75 trading strategies, to assist you in mastering the intricate dynamics of VIX trading and potentially enhancing your returns. For those exploring forex broker options, understanding these strategies can complement your trading toolkit effectively.

Volatility index trading strategies involve using derivatives and other financial instruments to profit from changes in market volatility as measured by the VIX. These strategies can range from simple directional bets on volatility to more complex options spreads and volatility arbitrage techniques. By understanding and implementing these strategies, traders can potentially enhance their portfolio performance and manage risk more effectively.
The world of volatility trading is dynamic and ever-evolving, with new techniques and instruments constantly emerging. As markets become increasingly interconnected and influenced by global events, the ability to trade volatility effectively has become a valuable skill for both professional and retail traders alike.
Read More: strategies for trading volatility indices
Understanding the Volatility Index (VIX)
Before diving into specific trading strategies, it’s crucial to understand what the VIX is and how it works.
What is the VIX?
The VIX, created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), measures the market’s expectation of 30-day volatility implied by S&P 500 index options. It’s calculated using a complex formula that takes into account the prices of various S&P 500 options.
The VIX is often called the “fear index” because it tends to spike during periods of market uncertainty or turmoil. However, it’s important to note that the VIX doesn’t measure current volatility, but rather the market’s expectation of future volatility.
How does the VIX work?
The VIX typically moves inversely to the S&P 500 index. When market fear increases, the VIX tends to rise, and when markets are calm, the VIX usually falls. This relationship makes the VIX a valuable tool for traders looking to hedge their portfolios or speculate on market volatility.
The calculation of the VIX is based on the implied volatilities of a wide range of S&P 500 options. Specifically, it uses near-term and next-term out-of-the-money options, with more than 23 days and less than 37 days to expiration. The formula is designed to yield a constant, 30-day measure of expected volatility.
Understanding the mechanics of the VIX is crucial for implementing effective volatility index trading strategies. It’s not just about knowing the current VIX level, but also understanding how it’s derived and what factors influence its movements.
Read More: carry trading strategies
Top 7 Volatility Index Trading Strategies
Now, let’s explore seven powerful volatility index trading strategies that can help you capitalize on market movements:

1. Direct VIX Futures Trading
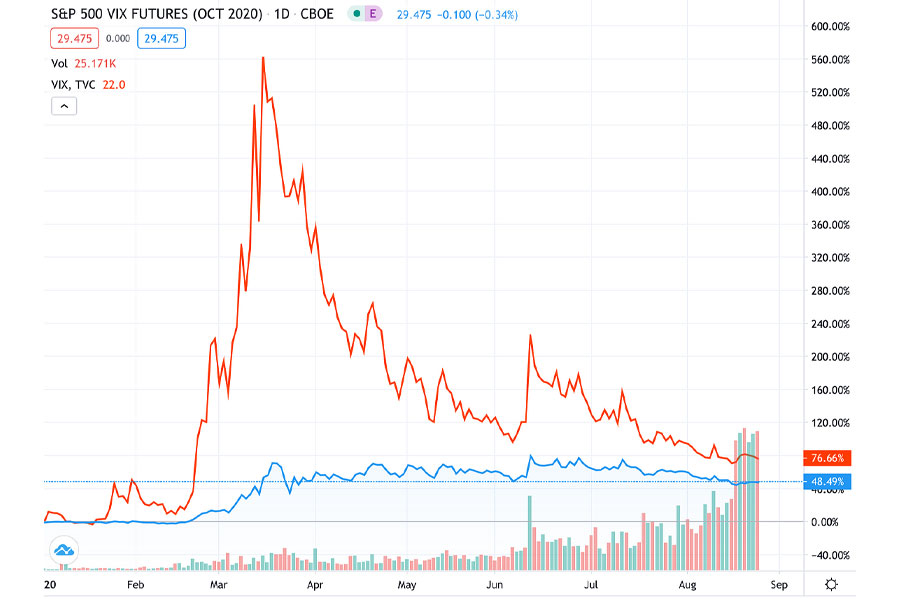
One of the most straightforward volatility index trading strategies is trading VIX futures directly. This approach allows traders to take a position on future volatility levels.
Pros:
- Direct exposure to volatility
- Potential for significant profits in volatile markets
- Ability to go long or short volatility
Cons:
- High risk due to leverage
- Requires careful timing and market analysis
- Contango and backwardation can affect returns
Implementation: To trade VIX futures, you’ll need a futures trading account with a broker that offers VIX products. It’s crucial to understand the contract specifications, including tick size, expiration dates, and margin requirements. Traders often focus on the front-month or near-term contracts for better liquidity.
When implementing this strategy, pay close attention to the term structure of VIX futures. The relationship between different contract months can provide valuable insights into market expectations and potential trading opportunities.
Read More: 4 hour forex trading strategy
2. VIX Options Trading
Trading VIX options offers more flexibility than futures trading and can be used to create various strategies.
Pros:
- Limited downside risk when buying options
- Ability to profit from both rising and falling volatility
- Flexibility to create complex strategies
Cons:
- Options can expire worthless
- Requires understanding of complex options strategies
- Implied volatility of VIX options can be high
Implementation: VIX options can be traded through most options-approved brokerage accounts. Popular strategies include buying calls or puts for directional bets, or creating spreads for more defined risk-reward profiles.
For example, a long straddle (buying both a call and a put at the same strike price) can be profitable if the VIX makes a significant move in either direction. Alternatively, a short strangle (selling an out-of-the-money call and put) can profit from range-bound VIX movements.
Remember to account for the unique characteristics of VIX options, such as European-style expiration and settlement based on the Special Opening Quotation (SOQ) of the VIX on expiration day.
3. Volatility ETFs and ETNs
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and Exchange-Traded Notes (ETNs) that track the VIX provide an accessible way to trade volatility.
Pros:
- Easy to trade through standard brokerage accounts
- No need to trade futures or options directly
- Some products offer leveraged exposure
Cons:
- Some products may not accurately track the VIX long-term
- Potential for significant losses in trending markets
- Daily rebalancing can lead to decay in leveraged products
Implementation: Popular VIX-based ETPs include the ProShares VIX Short-Term Futures ETF (VIXY) and the iPath Series B S&P 500 VIX Short-Term Futures ETN (VXX). These products typically track short-term VIX futures rather than the spot VIX index.
When trading these products, it’s crucial to understand their underlying methodology and how they may deviate from the spot VIX over time. Many traders use these products for short-term trades or hedging rather than long-term holdings due to the potential for decay in value over time.
4. Volatility Arbitrage
This advanced strategy involves exploiting pricing discrepancies between VIX derivatives and the underlying S&P 500 options.
Pros:
- Potential for consistent profits regardless of market direction
- Lower risk when executed correctly
- Can benefit from market inefficiencies
Cons:
- Requires sophisticated analysis and execution
- Opportunities may be limited and short-lived
- Can be capital intensive
Implementation: Volatility arbitrage often involves simultaneously trading VIX derivatives and S&P 500 options to capitalize on mispricing. For example, if VIX futures appear overpriced relative to the implied volatility of S&P 500 options, a trader might short VIX futures while buying S&P 500 options.
This strategy requires advanced modeling techniques to identify opportunities and precise execution to capture small pricing discrepancies. It’s typically employed by institutional traders or sophisticated individual investors with access to high-speed trading systems.
5. Mean Reversion Trading
This strategy is based on the principle that volatility tends to return to its average level over time.
Pros:
- Can be profitable in both high and low volatility environments
- Based on a well-established market tendency
- Can be applied to various volatility products
Cons:
- Timing can be challenging
- Requires patience and discipline
- Risk of significant losses if volatility trends persist
Implementation: To implement a mean reversion strategy, traders first establish a “normal” range for the VIX based on historical data. This might involve calculating moving averages or other statistical measures.
When the VIX moves significantly above this range, traders might consider short volatility positions, expecting it to decrease. Conversely, when the VIX is unusually low, they might take long volatility positions.
It’s crucial to use appropriate position sizing and stop-loss orders, as volatility can sometimes trend for extended periods before reverting to the mean.
6. Volatility Spreads
Spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling different VIX derivatives to create a specific risk-reward profile.
Pros:
- Can limit risk while still providing profit potential
- Allows for customized strategies based on market outlook
- Can profit from changes in the volatility term structure
Cons:
- More complex than outright directional trades
- Requires careful management of multiple positions
- May have higher transaction costs
Implementation: Common volatility spreads include calendar spreads (trading two different expiration months) and vertical spreads (trading two different strike prices in the same expiration month).
For example, a bullish calendar spread might involve selling a near-term VIX future and buying a longer-dated one. This strategy can profit if the term structure of VIX futures flattens or inverts.
When implementing spreads, pay close attention to the risk-reward ratio and potential maximum loss. Use options analytics tools to visualize how the spread will perform under different market scenarios.
7. Correlation Trading
This strategy involves trading the relationship between the VIX and other market indices or assets.
Pros:
- Can provide diversification benefits
- Offers unique trading opportunities
- Can exploit temporary breakdowns in typical correlations
Cons:
- Correlations can break down unexpectedly
- Requires monitoring multiple markets simultaneously
- May involve cross-asset risk management challenges
Implementation: Correlation trading might involve taking positions in both the VIX and related assets, such as the S&P 500 index or individual stocks known for their sensitivity to volatility.
For instance, if the typical inverse relationship between the VIX and S&P 500 appears to be weakening, a trader might simultaneously buy VIX calls and S&P 500 calls, anticipating a potential market dislocation.
This strategy requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and the ability to identify when typical relationships are breaking down. It often involves using correlation coefficients or other statistical measures to quantify relationships between assets.
Implementing Volatility Index Trading Strategies
To successfully implement these volatility index trading strategies, consider the following steps:
- Educate Yourself: Thoroughly understand the VIX, its components, and how it relates to market movements. This includes studying the VIX calculation methodology, historical behavior, and its relationship with other market indicators.
- Develop a Trading Plan: Create a detailed plan that outlines your entry and exit points, risk management rules, and overall strategy. Your plan should be tailored to your risk tolerance, capital availability, and trading goals.
- Start Small: Begin with small positions to gain experience and refine your approach. This allows you to learn from real market conditions without risking significant capital.
- Use Proper Risk Management: Always use stop-loss orders and position sizing to protect your capital. Consider implementing a maximum drawdown limit for your overall volatility trading activities.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with market news and events that could impact volatility. This includes monitoring economic releases, geopolitical events, and company-specific news that might affect the broader market.
- Backtest Your Strategies: Use historical data to test your strategies before risking real money. This can help you understand how your strategy would have performed in various market conditions.
- Continuously Evaluate and Adjust: Regularly review your performance and make necessary adjustments to your strategies. Markets evolve, and successful traders adapt their approaches accordingly.
Risk Management in Volatility Trading
Effective risk management is crucial when implementing volatility index trading strategies. Consider these key principles:
- Position Sizing: Never risk more than a small percentage of your trading capital on any single trade. A common rule of thumb is to risk no more than 1-2% of your account on a single position.
- Diversification: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Spread your risk across different strategies and markets. This can help mitigate the impact of unexpected market moves on your overall portfolio.
- Use of Stops: Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. For volatile products, consider using options or spread positions to define your maximum risk.
- Hedging: Consider using hedging techniques to protect against adverse market movements. This might involve using options to protect directional positions or employing cross-asset hedges.
- Stress Testing: Regularly stress test your strategies to ensure they can withstand extreme market conditions. This involves simulating various market scenarios to understand how your positions might perform.
- Monitoring VIX-Related Indicators: Keep an eye on additional volatility indicators such as the VVIX (volatility of VIX) and the put-call ratio to gain a more comprehensive view of market sentiment and potential volatility trends.
- Liquidity Management: Be aware of the liquidity characteristics of the VIX products you’re trading. During market stress, liquidity can dry up quickly, potentially leading to wider spreads and slippage.
OpoFinance Services: Your Partner in Volatility Trading
At OpoFinance, we understand the intricacies of volatility index trading strategies and are committed to helping our clients succeed in this dynamic market. Our comprehensive suite of services includes:
- Advanced trading platforms with real-time VIX data and analytics
- Expert guidance from seasoned volatility traders
- Educational resources to help you master volatility trading techniques
- Customized risk management solutions tailored to your trading style
- Access to a wide range of VIX-related products, including futures, options, and ETFs
With OpoFinance, you’ll have the tools and support you need to navigate the complex world of volatility trading with confidence. Our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve your financial goals through sophisticated volatility index trading strategies. Join us today and take your trading to the next level!
Conclusion
Volatility index trading strategies offer exciting opportunities for traders to profit from market fluctuations and enhance their overall portfolio performance. By understanding the VIX and implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can potentially improve your trading results and better manage market risks.
Remember that successful volatility trading requires continuous learning, careful risk management, and adaptability to changing market conditions. Start with a solid foundation of knowledge, practice with small positions, and gradually refine your approach as you gain experience.
Whether you’re exploring volatility index 100 trading strategies or volatility index 75 trading strategies, the key to success lies in developing a well-rounded understanding of the market and consistently applying sound trading principles. With dedication and the right approach, you can master the art of volatility trading and potentially unlock new avenues for financial success.
As you embark on your volatility trading journey, remember that the market is constantly evolving. Stay curious, remain open to new ideas, and always be prepared to adapt your strategies as market conditions change. With persistence and a commitment to ongoing education, you can develop the skills needed to thrive in the exciting world of volatility trading.
How does volatility seasonality affect VIX trading strategies?
Volatility seasonality refers to the tendency for market volatility to exhibit patterns at certain times of the year. This phenomenon can significantly impact VIX trading strategies. For example, volatility often increases in September and October, while it tends to be lower during summer months. Traders can incorporate this seasonality into their strategies by adjusting their positioning or risk exposure based on historical volatility patterns. However, it’s important to note that seasonality is not a guarantee, and other factors can override these tendencies in any given year.
What role do market makers play in VIX derivatives markets?
Market makers play a crucial role in VIX derivatives markets by providing liquidity and facilitating trades. They continuously quote bid and ask prices for VIX futures and options, ensuring that traders can enter and exit positions efficiently. Market makers also help to keep prices in line with fair value by arbitraging between related products. Their presence is essential for the smooth functioning of VIX markets, particularly during times of stress when liquidity can become scarce. However, traders should be aware that market makers are also profit-seeking entities, and their activities can sometimes lead to short-term price distortions
How can machine learning be applied to improve volatility trading strategies?
Machine learning techniques are increasingly being applied to enhance volatility trading strategies. These advanced algorithms can analyze vast amounts of historical and real-time data to identify patterns and relationships that might not be apparent to human traders. For example, machine learning models can be used to predict short-term VIX movements, optimize trade entry and exit points, or detect regime changes in volatility behavior. Some traders use neural networks to forecast volatility surfaces or employ reinforcement learning algorithms to dynamically adjust trading strategies. While machine learning offers powerful tools for volatility trading, it’s important to combine these techniques with fundamental market understanding and robust risk management practices.







