Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, involves buying and selling currencies to make a profit. The forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. Unlike other financial markets, forex operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, due to the global nature of currency trading. Traders often seek out an online forex broker to access the market and execute their trades efficiently.

In forex trading, currencies are traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen). Each pair represents the value of one currency against another. For example, if the EUR/USD pair is quoted at 1.2000, it means that one Euro is worth 1.2000 US Dollars. Traders aim to profit from the fluctuations in exchange rates by buying low and selling high or vice versa.
Trading Styles by Timeframe
Understanding the different trading styles by timeframe is crucial for forex traders. Each style has unique characteristics, advantages, and challenges. Traders should choose a style that aligns with their goals, risk tolerance, and availability for monitoring the markets. Here are the primary trading styles:

Scalping
Scalping is a highly active and fast-paced trading style that involves making numerous short-term trades throughout the day. Scalpers aim to capitalize on small price movements, often holding positions for just a few seconds to a few minutes. This method is popular among traders who prefer a high-energy trading environment and have the time to monitor the markets constantly.
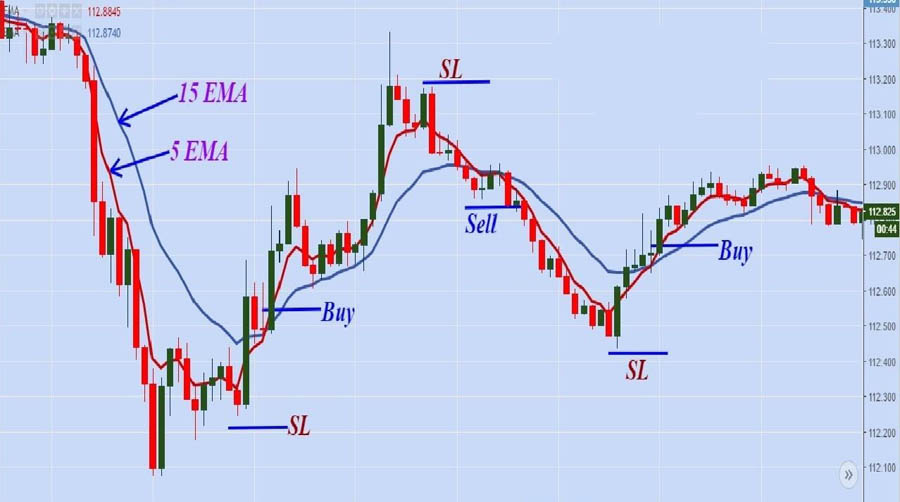
Characteristics of Scalping
- High Frequency: Scalpers may execute dozens or even hundreds of trades in a single day.
- Small Profits: Each trade aims for small profits, typically a few pips, but the cumulative gains can be significant.
- Quick Decision Making: Requires rapid analysis and execution, often relying on automated trading systems or high-speed trading platforms.
- Tight Spreads: Scalpers prefer currency pairs with tight spreads to minimize transaction costs.
Advantages of Scalping
- Reduced Exposure: Short holding periods mean less exposure to market risks and overnight news.
- Frequent Trading Opportunities: High trading frequency allows scalpers to take advantage of multiple opportunities in a single day.
Challenges of Scalping
- High Stress: The fast pace and constant monitoring can be stressful.
- Brokerage Costs: Frequent trading increases transaction costs, which can eat into profits if not managed properly.
Read More: What are scalping techniques in forex ?
Day Trading
Day trading involves opening and closing trades within the same trading day. Day traders aim to profit from intraday price movements and avoid overnight risk. This style suits traders who can dedicate a significant portion of their day to monitoring the markets.
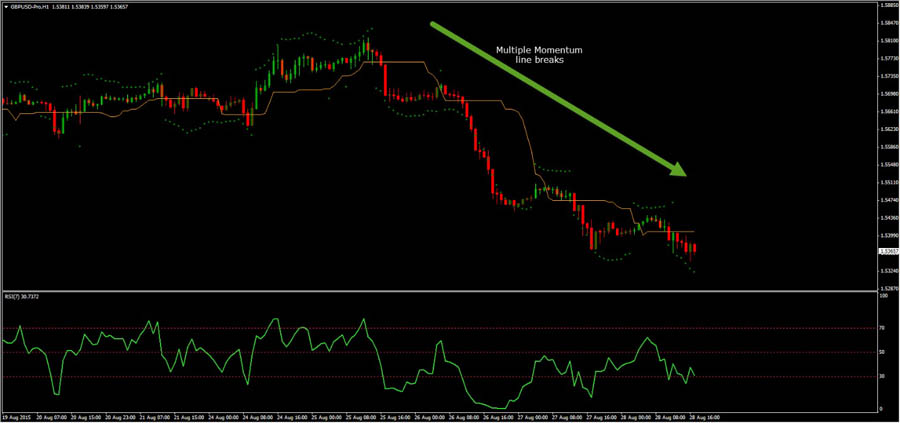
Characteristics of Day Trading
- Intraday Focus: All positions are closed by the end of the trading day, avoiding overnight exposure.
- Moderate Frequency: Day traders typically make fewer trades than scalpers but still engage in multiple trades per day.
- Technical Analysis: Relies heavily on technical analysis, chart patterns, and intraday indicators.
Advantages of Day Trading
- No Overnight Risk: By closing positions before the market closes, day traders avoid risks associated with overnight news and events.
- Clear Cutoff: Daily trading sessions provide a clear start and end to trading activities.
Challenges of Day Trading
- Time Intensive: Requires full-time attention and the ability to make quick decisions.
- Emotional Discipline: Traders need to manage emotions and stick to their trading plan to avoid impulsive decisions.
Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks, aiming to capture medium-term price movements. This style is suitable for traders who cannot monitor the markets constantly but can dedicate time to analyzing trends and market conditions.
Characteristics of Swing Trading
- Medium-Term Focus: Positions are held for days to weeks, allowing traders to capture more substantial price movements.
- Technical and Fundamental Analysis: Combines technical indicators to identify entry and exit points with fundamental analysis to understand market trends.
- Lower Frequency: Fewer trades are executed compared to day trading and scalping.
Advantages of Swing Trading
- Less Time Intensive: Requires less constant monitoring, making it suitable for part-time traders.
- Larger Price Movements: Aims to capture significant price swings, potentially leading to higher profits per trade.
Challenges of Swing Trading
- Overnight Risk: Holding positions overnight exposes traders to market gaps and unexpected news.
- Patience Required: Traders need to be patient and wait for the right opportunities to enter and exit trades.
Read More: Techniques for Timely Entry and Exit in Forex
Positional Trading
Positional trading is a long-term strategy where traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years. This style aims to capitalize on major market trends and is suited for traders who prefer a more passive approach.
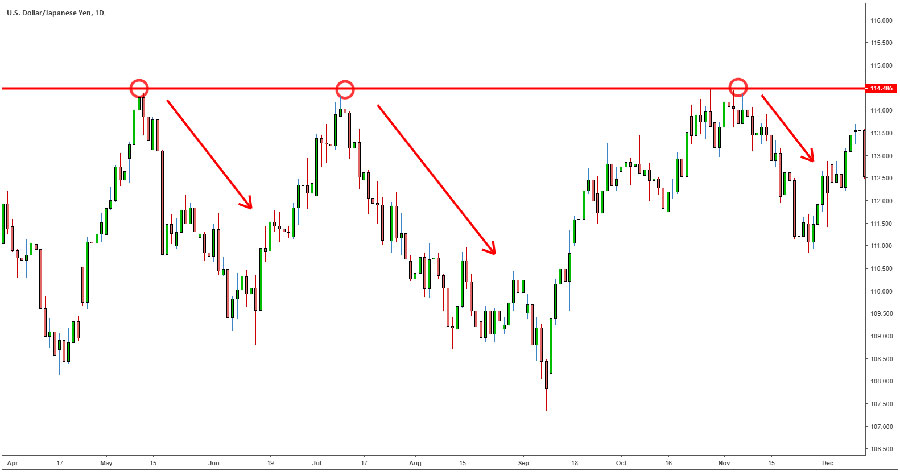
Characteristics of Positional Trading
- Long-Term Focus: Positions are held for extended periods, often based on fundamental economic trends.
- Fundamental Analysis: Relies heavily on analyzing economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events.
- Low Frequency: Fewer trades are made, with a focus on significant market movements.
Advantages of Positional Trading
- Reduced Transaction Costs: Fewer trades mean lower transaction costs and less stress from constant market monitoring.
- Potential for Significant Gains: Long-term trends can lead to substantial profits.
Challenges of Positional Trading
- Long-Term Commitment: Requires patience and the ability to withstand short-term market fluctuations.
- Capital Requirement: Larger capital is often needed to sustain long-term positions.
Technical Analysis vs. Fundamental Analysis
Understanding the methods of analysis is crucial in forex trading, where informed decisions can mean the difference between success and failure. The two primary approaches, Technical Analysis and Fundamental Analysis, offer distinct tools and insights to navigate the complexities of the forex market.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying price charts and using technical indicators to forecast price movements. Traders rely on historical price data to predict future trends and make trading decisions.
Key Elements of Technical Analysis
- Charts and Timeframes:
- Line Charts: Connect closing prices over a specific period to illustrate price trends.
- Bar Charts: Display open, high, low, and close prices for each period, offering more detailed information.
- Candlestick Charts: Provide a visual depiction of price movements, indicating bullish and bearish trends through candlestick patterns.
- Popular Technical Indicators:
- Moving Averages (MA): Smooth out price data to identify trends. Common types include Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures price momentum and indicates overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: Gauge market volatility by using a middle band (SMA) and two outer bands representing standard deviations.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Shows the relationship between two moving averages, revealing changes in a security’s price momentum.
- Chart Patterns and Trend Analysis:
- Head and Shoulders: Reversal pattern signaling a potential trend change.
- Double Tops and Bottoms: Patterns indicating a reversal in the prevailing trend.
- Triangles: Symmetrical, ascending, and descending triangles suggesting potential continuation or reversal of trends.
- New Trending Methods:
- Smart Money Concept: Focuses on understanding institutional traders’ behavior and liquidity flows, identifying significant institutional trades.
- Inner Circle Trader (ICT) Approach: Emphasizes market structure, liquidity pools, and institutional order flow to identify high-probability trading setups.
Advantages of Technical Analysis
- Visual Representation: Charts and indicators provide a clear visual depiction of price movements.
- Pattern Recognition: Helps identify recurring patterns and trends in the market.
- Timely Entries and Exits: Facilitates precise entry and exit points based on technical signals.
Challenges of Technical Analysis
- Subjectivity: Interpretation of charts and indicators can vary among traders.
- False Signals: Technical indicators may produce false signals, potentially leading to trading losses.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating economic data and events to assess the intrinsic value of a currency. Traders focus on economic indicators, central bank policies, and geopolitical events to make informed trading decisions.

Key Elements of Fundamental Analysis
- Economic Indicators:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Measures a country’s economic output. A growing GDP signals economic strength and can bolster the currency’s value.
- Interest Rates: Controlled by central banks, higher interest rates attract foreign capital, boosting the currency’s worth.
- Inflation Rates: Reflected by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), high inflation can diminish purchasing power and influence currency value.
- Employment Data: Indicators like the Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) report gauge labor market health and economic stability.
- Geopolitical Events and News:
- Political Stability: Countries with stable political climates often boast stronger currencies.
- Trade Agreements: Positive agreements can stimulate economic growth and currency appreciation.
- Major News Events: Elections, conflicts, and natural disasters can trigger significant market volatility.
Advantages of Fundamental Analysis
- Long-Term Insights: Provides a broad view of economic health and potential currency movements over time.
- Economic Context: Helps traders grasp the underlying drivers influencing currency prices.
- Predictive Power: Economic indicators and events often forecast future currency movements.
Challenges of Fundamental Analysis
- Complexity: Requires a deep understanding of economic data and geopolitical dynamics.
- Time-Consuming: Keeping abreast of relevant economic indicators and news demands significant time and effort.
- Short-Term Unpredictability: Immediate market reactions to economic news can be erratic and difficult to forecast.
Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Many traders combine technical analysis with fundamental analysis to refine their trading strategies. By using technical tools to time trades and fundamental insights to understand market context, traders aim to enhance decision-making and improve trading outcomes.
Read More: How to Make Consistent Profits in Forex Trading
Popular Forex Trading Methods
Forex trading offers diverse methods catering to different trading styles, risk appetites, and market conditions. Understanding these methods helps traders choose strategies aligned with their goals. Here are some of the most popular forex trading methods:
- Trend Following
- Characteristics: Utilizes technical indicators like moving averages and trendlines to identify and capitalize on established price trends.
- Advantages: Clear rules for entering and exiting trades based on trend confirmation signals like MACD and RSI.
- Challenges: Vulnerable to false signals during market volatility; late entries can reduce profit potential.
- Range Trading
- Characteristics: Involves buying at support and selling at resistance within a defined price range.
- Advantages: Predictable price movements within the range; multiple trading opportunities.
- Challenges: Breakouts beyond support or resistance levels can result in losses; less effective in trending markets.
- Carry Trade
- Characteristics: Capitalizes on interest rate differentials by borrowing a currency with a low-interest rate and investing in a currency with a higher interest rate.
- Advantages: Generates steady income from interest rate differentials; potential as a long-term strategy.
- Challenges: Exposed to exchange rate risk; vulnerable to market volatility.
- Breakout Trading
- Characteristics: Enters trades when prices breach established support or resistance levels.
- Advantages: Potential for significant price movements and profits; defined entry points.
- Challenges: Risk of false breakouts; requires quick execution and tight risk management.
- News Trading
- Characteristics: Reacts to economic data releases and major news events impacting currency prices.
- Advantages: High-profit potential from volatile market reactions to news; frequent trading opportunities.
- Challenges: High risk due to unpredictable market reactions; uncertainty about news impact.
- Smart Money Concept
- Characteristics: Focuses on understanding institutional traders’ behavior and their influence on the market.
- Advantages: Insight into market dynamics and higher probability trades aligned with institutional actions.
- Challenges: Complex analysis of market structure and institutional behavior; requires patience for confirmation.
- Inner Circle Trader (ICT) Methods
- Characteristics: Uses price action and market structure analysis to identify high-probability trading setups.
- Advantages: Precise entry and exit points based on market structure; deep understanding of market operations.
- Challenges: Steep learning curve; subjectivity in interpreting price action and market structure.
Understanding and applying these forex trading methods empower traders to navigate various market conditions effectively, enhancing their trading success.
Risk Management and Trading Psychology
Risk management and trading psychology are critical components of successful forex trading. They help traders protect their capital, make rational decisions, and maintain consistency in their trading practices. Without effective risk management and a strong psychological approach, even the best trading strategies can fail.
Importance of Setting Stop-Loss Orders and Managing Risk
Setting stop-loss orders is pivotal in limiting losses and protecting trading capital. These orders automatically close positions at predetermined levels to prevent further losses, ensuring traders adhere to their risk tolerance.
Position Sizing
Position sizing determines the appropriate allocation of capital per trade based on risk tolerance and account size. It ensures that no single trade significantly impacts overall portfolio performance, promoting sustainable trading practices.
Diversification
Diversifying trades across various instruments or asset classes reduces overall risk exposure. By spreading investments, traders mitigate the impact of potential losses on their overall portfolio, enhancing long-term stability.
Developing a Disciplined Trading Plan
A disciplined trading plan outlines a trader’s strategy, risk management rules, and objectives. It serves as a roadmap to guide trading decisions, maintain focus, and avoid impulsive actions influenced by emotions or market fluctuations.
Components of a Trading Plan
- Trading Strategy: Clearly define entry and exit criteria, indicators used, and preferred timeframes for trading decisions.
- Risk Management Rules: Establish stop-loss levels, position sizing guidelines, and diversification strategies to manage risk effectively.
- Trading Goals: Set achievable goals such as monthly profit targets or percentage returns to measure trading success.
- Record Keeping: Maintain a trading journal to track trades, review performance, and identify areas for improvement based on factual data.
Controlling Emotions and Avoiding Common Trading Mistakes
Emotional discipline is critical in avoiding common trading errors that can undermine profitability and consistency in trading performance.
Common Trading Mistakes
- Overtrading: Entering excessive trades driven by impatience or the desire for quick profits.
- Revenge Trading: Making impulsive trades to recover losses incurred from previous trades, often leading to further losses.
- Abandoning the Plan: Deviating from the trading plan due to emotional reactions or market volatility, compromising strategy effectiveness.
Strategies for Controlling Emotions
- Set Realistic Expectations: Acknowledge that losses are part of trading and set achievable profit targets aligned with risk tolerance.
- Take Breaks: Step away from trading after significant market events or losses to maintain emotional balance and avoid reactionary decisions.
- Practice Mindfulness: Techniques such as meditation and deep breathing help manage stress and enhance focus during trading sessions.
- Use a Demo Account: Practice trading strategies in a risk-free environment to refine skills, build confidence, and test new approaches before implementing them live.
Conclusion
Forex trading offers numerous opportunities for profit, but it requires a solid understanding of the market, effective trading strategies, and disciplined risk management. By exploring various trading methods and developing a comprehensive trading plan, traders can enhance their chances of success in the dynamic world of forex.
What are the best times to trade forex?
The best times to trade forex are during the major trading sessions: the London session (8 AM to 4 PM GMT), the New York session (1 PM to 9 PM GMT), and the overlap between these two sessions. These periods offer higher liquidity and volatility, providing more trading opportunities.
How can I improve my forex trading skills?
Improving forex trading skills involves continuous learning and practice. Traders should study market fundamentals, technical analysis, and trading strategies. Utilizing demo accounts, keeping a trading journal, and learning from successful traders can also enhance trading skills.
What is the role of a forex broker?
A forex broker acts as an intermediary between the trader and the forex market. Brokers provide trading platforms, market access, and leverage. They may also offer educational resources, market analysis, and customer support to assist traders in making informed decisions.







