Forex trading is legal in most countries around the world, including major financial hubs like the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, and Japan. However, the legality and regulatory landscape can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. As the largest and most liquid financial market globally, the foreign exchange (forex) market attracts millions of traders seeking to profit from currency fluctuations. For this purpose, selecting the right broker for forex trading is crucial. In fact, the average daily trading volume in the forex market reached a staggering $6.6 trillion in 2022, according to the Bank for International Settlements.

Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a curious newcomer considering forex as an investment opportunity, understanding the legal aspects of this market is crucial. The question “Is forex trading legal?” is more complex than it might seem at first glance, and the answer can have significant implications for your financial future.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the legality of forex trading, delve into the regulatory frameworks governing the market, and address common concerns for traders. We’ll also discuss the role of forex brokers, including regulated online forex brokers, in ensuring a safe and compliant trading environment. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of whether forex trading is a legal and viable option for you.
The Legal Status of Forex Trading Worldwide
Global Acceptance and Regulation

Forex trading is legally recognized and regulated in most developed countries. The global nature of currency markets necessitates international cooperation to maintain stability and protect traders. Here’s an overview of the legal status in key regions:
- United States: Forex trading is legal and regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the National Futures Association (NFA). The U.S. accounts for about 16.5% of global forex trading volume.
- European Union: The Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II) provides a harmonized regulatory regime for forex trading across EU member states. The EU collectively represents about 25% of global forex trading activity.
- United Kingdom: The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) oversees forex trading activities in the UK. London remains the world’s largest forex trading center, accounting for approximately 43% of global forex turnover.
- Australia: The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) regulates forex trading. Australia has seen significant growth in forex trading, with a daily turnover of about $166 billion.
- Japan: The Financial Services Agency (FSA) and the Japanese Financial Services Association (JFSA) govern forex trading. Japan is the third-largest forex market globally, with about 4.5% of total forex trading volume.
- Singapore: The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) supervises forex trading operations. Singapore has become a major forex hub in Asia, handling about 7.6% of global forex trading.
Variations in Legal Frameworks
While forex trading is broadly legal, the specific rules and regulations can differ significantly:
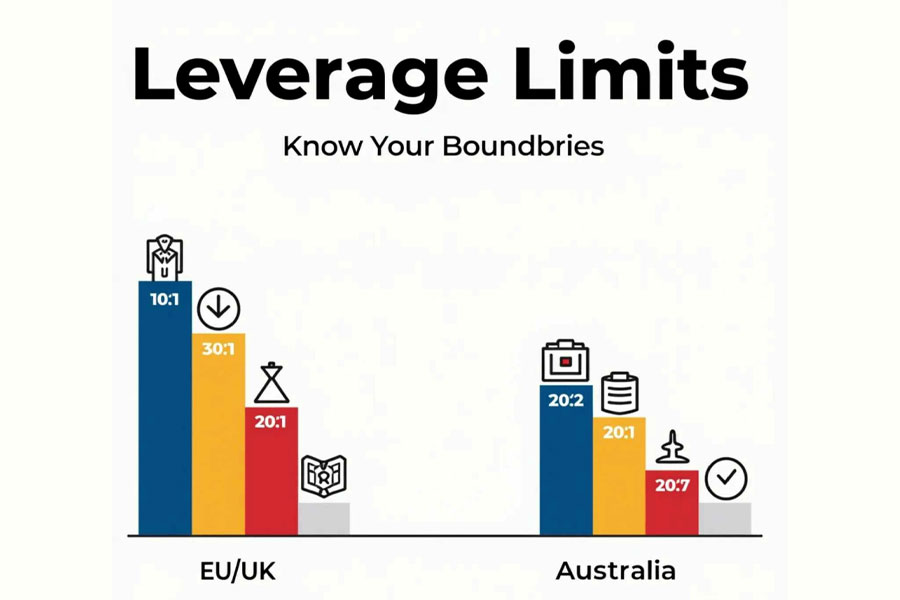
- Leverage limits: Some countries impose strict limits on the amount of leverage forex brokers can offer to retail traders. For example, in the EU and UK, retail traders are limited to 30:1 leverage for major currency pairs, while in Australia, the limit is 20:1.
- Licensing requirements: Brokers must obtain proper licenses to operate in different jurisdictions. This process can be rigorous and may involve substantial capital requirements and ongoing compliance obligations.
- Tax implications: The tax treatment of forex trading profits varies by country. In some nations, forex trading may be subject to capital gains tax, while in others, it might be treated as regular income.
- Investor protection: Many regulators require brokers to participate in investor compensation schemes. For instance, in the UK, the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS) protects traders up to £85,000 in case of broker insolvency.
Read more: Is forex trading haram?
Understanding Forex Regulation

The Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory authorities play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity of the forex market:
- Market oversight: They monitor trading activities to detect and prevent market manipulation. In 2022, global regulators imposed over $3 billion in fines related to forex market misconduct.
- Consumer protection: Regulators establish rules to safeguard traders’ interests and funds. This includes measures like negative balance protection, which prevents traders from losing more than their account balance.
- Licensing: They issue licenses to forex brokers and other market participants. As of 2023, there are over 3,000 licensed forex brokers worldwide.
- Enforcement: Regulatory bodies have the power to investigate and penalize non-compliant entities. In recent years, several high-profile cases have resulted in multi-million-dollar fines for major banks involved in forex manipulation.
Read more: Forex Market vs Other Markets
Key Regulatory Measures
To maintain a fair and transparent forex market, regulators implement various measures:
- Capital requirements: Brokers must maintain minimum capital levels to ensure financial stability. For example, in the U.S., forex brokers must maintain at least $20 million in adjusted net capital.
- Segregation of client funds: Traders’ money must be kept separate from the broker’s operational funds. This protects client assets in case of broker bankruptcy.
- Reporting obligations: Brokers are required to submit regular financial reports and audits. This transparency helps regulators identify potential issues before they escalate.
- Risk disclosures: Traders must be informed about the risks associated with forex trading. Many jurisdictions require brokers to display prominent risk warnings, stating that a high percentage of retail trader accounts lose money.
Choosing a Legal and Regulated Forex Broker

Importance of Broker Selection
Selecting a reputable, regulated forex broker is crucial for ensuring the legality and safety of your trading activities. Here are key factors to consider:
- Regulatory compliance: Verify that the broker is registered with the appropriate regulatory authorities in your jurisdiction. You can usually check this information on the regulator’s website.
- Transparency: Look for brokers that provide clear information about their services, fees, and trading conditions. Hidden fees or vague terms should be red flags.
- Fund security: Ensure the broker offers robust measures to protect your deposited funds. This may include segregated accounts, insurance coverage, and regular audits.
- Trading platform: Choose a broker with a reliable and user-friendly trading platform. Many top brokers offer the popular MetaTrader 4 or 5 platforms, known for their stability and advanced features.
- Customer support: Opt for brokers with responsive and knowledgeable customer service. 24/7 support can be crucial in the fast-paced forex market.
Red Flags to Watch Out For
Be wary of brokers exhibiting these warning signs:
- Promises of guaranteed profits or unrealistic returns (remember, about 70-80% of retail forex traders lose money)
- Pressure to deposit funds quickly
- Lack of proper licensing or regulation
- Poor online reviews or a history of regulatory infractions
- Reluctance to provide clear information about their company structure or location
Legal Considerations for Forex Traders

Compliance with Local Laws
As a forex trader, it’s your responsibility to ensure compliance with local laws and regulations:
- Tax obligations: Report your forex trading profits accurately and pay any applicable taxes. In many countries, forex trading profits are subject to capital gains tax or income tax.
- Anti-money laundering (AML) rules: Be prepared to provide necessary documentation for identity verification and fund sources. This is part of the global effort to combat financial crime.
- Trading limits: Adhere to any trading restrictions or limits imposed by your local regulatory authority. Some countries may limit the amount of foreign currency citizens can purchase or trade.
Read more: Tax Implications of Forex Trading
Protecting Your Legal Rights
To safeguard your interests as a forex trader:
- Read and understand broker agreements: Carefully review all terms and conditions before opening an account. Pay special attention to clauses about account closures, withdrawals, and dispute resolution.
- Keep detailed records: Maintain comprehensive records of all your trading activities and communications with your broker. This can be crucial in case of disputes or tax audits.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date with changes in forex regulations that may affect your trading. Regulatory environments can change rapidly, especially in emerging markets.
The Future of Forex Trading Regulation
Emerging Trends
The regulatory landscape for forex trading continues to evolve:
- Increased scrutiny: Regulators are likely to implement stricter oversight measures to protect retail traders. This may include more stringent reporting requirements and tighter controls on marketing practices.
- Technological advancements: The rise of algorithmic trading and artificial intelligence may lead to new regulatory challenges. Regulators are already grappling with issues like high-frequency trading and its impact on market stability.
- Cross-border cooperation: Expect greater collaboration between international regulatory bodies to address global market risks. Initiatives like the Global Foreign Exchange Committee (GFXC) are working to establish consistent standards across jurisdictions.
Potential Impact on Traders
These regulatory trends may affect forex traders in several ways:
- Enhanced trader protection: Stricter regulations could lead to improved safety measures for retail traders, potentially reducing the risk of fraud and market manipulation.
- Possible restrictions: Some jurisdictions may impose tighter controls on leverage or introduce new trading limits. While this may reduce potential profits, it also helps manage risk for retail traders.
- Increased transparency: Traders may benefit from more transparent pricing and execution practices. This could lead to fairer trading conditions and more accurate price discovery.
OpoFinance Services: A Regulated Forex Broker You Can Trust
When it comes to choosing a reliable and regulated forex broker, OpoFinance stands out as an excellent option for traders seeking a secure and compliant trading environment. As an ASIC-regulated broker, OpoFinance adheres to strict regulatory standards, ensuring the highest level of protection for its clients.

OpoFinance offers a comprehensive suite of trading services, including:
- Advanced trading platforms: Access state-of-the-art trading technology for seamless execution of trades. OpoFinance provides both MetaTrader 4 and 5, catering to traders of all experience levels.
- Competitive spreads: Benefit from tight spreads across a wide range of currency pairs. OpoFinance offers spreads as low as 0.0 pips on major pairs, allowing for cost-effective trading.
- Educational resources: Enhance your trading skills with OpoFinance’s extensive library of educational materials. From beginner guides to advanced strategy webinars, there’s something for every trader.
- Dedicated customer support: Receive prompt assistance from a team of experienced professionals. OpoFinance offers 24/5 customer support in multiple languages.
One of OpoFinance’s standout features is its innovative social trading service. This platform allows traders to connect with and learn from successful investors, opening up new opportunities for both novice and experienced traders alike. By leveraging the power of community and shared knowledge, OpoFinance’s social trading feature can help you make more informed trading decisions and potentially improve your overall performance in the forex market.
Conclusion
Forex trading is legal in most countries, but it operates within a complex regulatory framework designed to protect traders and maintain market integrity. As a trader, it’s crucial to understand the legal landscape, choose a reputable broker, and comply with local regulations to ensure a safe and lawful trading experience.
By staying informed about the legal aspects of forex trading and working with regulated brokers like OpoFinance, you can confidently participate in the global currency market while minimizing legal and financial risks. Remember that forex trading carries inherent risks, and it’s essential to approach it with caution, proper education, and a well-thought-out strategy.
As the forex market continues to evolve, staying up-to-date with regulatory changes and best practices will be key to your long-term success as a trader. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your trading approach, always prioritize legality, safety, and compliance in your forex trading journey.
The world of forex trading offers exciting opportunities, but it’s crucial to navigate it with care and knowledge. By understanding the legal framework, choosing the right broker, and staying informed about market developments, you can position yourself for success in this dynamic global marketplace.
Can I face legal consequences for forex trading in countries where it’s restricted?
Yes, engaging in forex trading in countries where it’s restricted or banned can lead to legal consequences. Some nations have strict capital controls or religious prohibitions against certain financial activities, including forex trading. Penalties can range from fines to imprisonment, depending on the severity of the violation and local laws. It’s crucial to research and comply with the laws in your country of residence and any country where you plan to conduct forex trading activities.
Are there any age restrictions for legal forex trading?
Age restrictions for forex trading vary by country and broker. In most jurisdictions, the minimum age to open a forex trading account is 18. However, some countries and brokers may require traders to be 21 or older. It’s important to check the specific requirements of your chosen broker and local regulations. Trading as a minor or allowing minors to trade on your behalf can lead to account closure and potential legal issues.
How does the legality of forex trading differ for individual traders versus institutional investors?
The legal framework for forex trading often differs between individual (retail) traders and institutional investors. Institutional investors, such as banks, hedge funds, and large corporations, may face less stringent regulations in some areas due to their presumed sophistication and resources. For example, leverage limits and reporting requirements might be more relaxed for institutional investors. However, they may also be subject to additional oversight and compliance measures, particularly if they manage funds for others. Retail traders typically benefit from more consumer protection measures but may face stricter trading conditions and leverage limits to mitigate risks.






