In the ever-volatile world of commodities, mastering the best trading strategy for crude oil is essential for traders seeking to capitalize on this lucrative market. Crude oil, often referred to as “black gold,” presents unique opportunities and challenges due to its global economic significance and sensitivity to various factors. Partnering with an online forex broker can further enhance your trading journey by providing access to valuable resources and market insights. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of crude oil trading, equipping you with the knowledge and tools necessary to develop a winning strategy.

The best trading strategy for crude oil combines a deep understanding of market dynamics, technical analysis proficiency, and robust risk management techniques. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear roadmap to navigate the complexities of oil trading and potentially achieve consistent profits. Let’s embark on this journey to unlock the profit potential of crude oil trading
Understanding the Crude Oil Market
Fundamental Factors Influencing Crude Oil Prices

Crude oil prices are primarily driven by supply and demand dynamics. Key factors include:
- Global Production Levels: OPEC decisions, production rates from major oil-producing countries, and technological advancements in extraction. OPEC’s ability to control supply through production quotas can lead to significant price changes. For instance, when OPEC decides to cut production, prices typically rise due to reduced supply.
- Economic Growth: Economic activity in major oil-consuming countries, such as the U.S., China, and India, affects demand. Economic growth leads to higher industrial activity, increasing demand for crude oil. Conversely, economic downturns reduce demand and cause prices to fall.
- Geopolitical Events: Conflicts, sanctions, and political instability in oil-producing regions can disrupt supply and cause price volatility. For example, tensions in the Middle East, which is a major oil-producing region, can lead to fears of supply disruptions and push prices higher.
- Natural Disasters: Hurricanes, earthquakes, and other natural events can impact oil production and transportation infrastructure. The impact of Hurricane Katrina on Gulf Coast oil production in 2005 is a prime example of how natural disasters can cause significant price spikes.
Technical Analysis Tools for Predicting Price Movements
Technical analysis is crucial for traders to predict future price movements based on historical data. Common tools include:
- Moving Averages: Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA) help identify trends. The 50-day and 200-day moving averages are popular choices for identifying long-term trends.
- Parabolic SAR (Stop and Reverse): Indicates potential reversal points in the market. Traders use the Parabolic SAR to determine the direction of the trend and potential entry and exit points.
- Fibonacci Retracement Levels: Used to identify potential support and resistance levels. Traders draw Fibonacci retracement levels to find price levels where the market is likely to reverse.
- Volatility Indicators: Bollinger Bands and Average True Range (ATR) measure market volatility. Bollinger Bands expand and contract based on volatility, helping traders identify periods of high and low volatility.
Read More: Best Trading Strategy for EURUSD
Risk Management Strategies for Oil Trading

Effective risk management is essential for long-term success. Key strategies include:
- Position Sizing: Determine the appropriate trade size based on your risk tolerance and account size. Proper position sizing ensures that a single trade does not have an outsized impact on your overall portfolio.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Protect your capital by setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Stop-loss orders are placed at predetermined levels to automatically close a trade if the market moves against you.
- Diversification: Spread risk by trading multiple assets and strategies. Diversification reduces the impact of any single trade or market event on your overall portfolio.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Ensure potential rewards outweigh risks before entering a trade. A good risk-reward ratio ensures that your potential profits justify the risks taken.
Read More: best trading strategy for us30
Popular Crude Oil Trading Strategies
Moving Average and Parabolic SAR Strategy
This strategy combines moving averages and the Parabolic SAR to identify trends and potential reversal points.
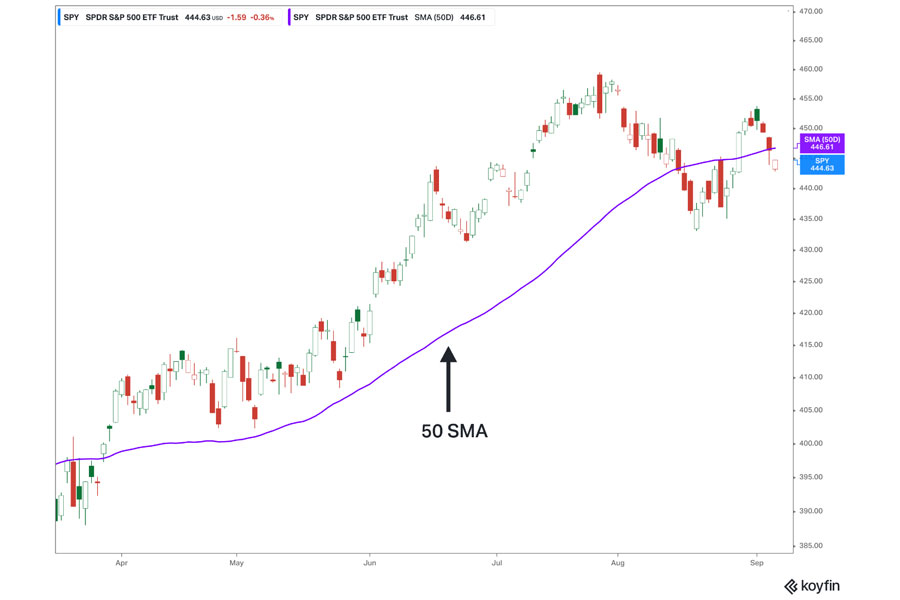
How to Implement:
- Identify the Trend: Use a long-term moving average (e.g., 50-day SMA) to determine the overall trend. For example, if the 50-day SMA is trending upward, it indicates a bullish market.
- Confirm with Parabolic SAR: Use the Parabolic SAR to identify entry and exit points within the trend. If the Parabolic SAR dots are below the price, it suggests an uptrend, while dots above the price indicate a downtrend.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Place stop-loss orders below the Parabolic SAR dots to protect against sudden reversals. This ensures that your losses are minimized if the market moves against you.
Trading Oil with Fibonacci Levels
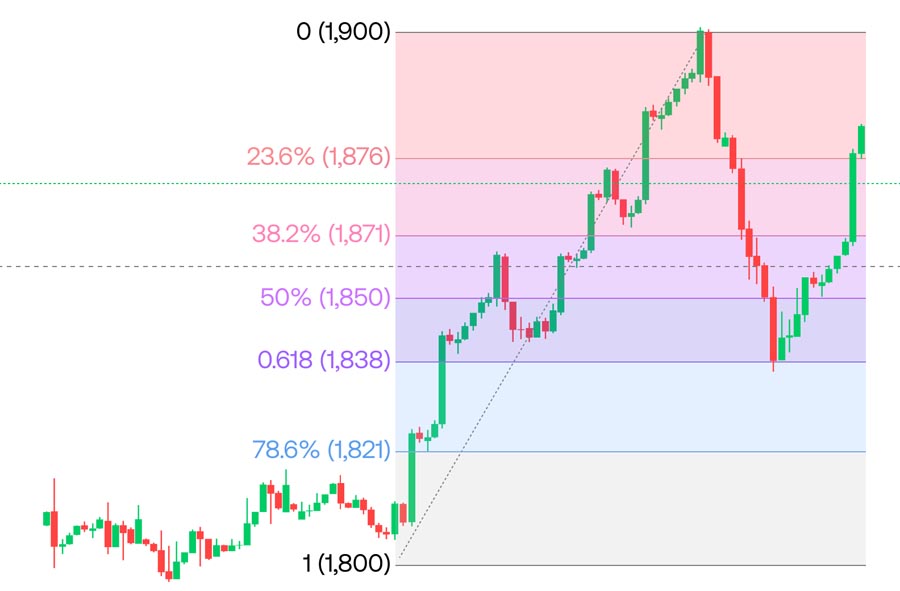
Fibonacci retracement levels help traders identify potential support and resistance levels, aiding in decision-making.
How to Implement:
- Identify Key Levels: Plot Fibonacci retracement levels on significant price movements. For example, if the price of crude oil has moved from $50 to $70, plot the Fibonacci levels from the low to the high.
- Enter Trades at Retracement Levels: Buy at key support levels (e.g., 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%) and sell at resistance levels. These levels are considered potential reversal points where the price may change direction.
- Set Targets and Stops: Place stop-loss orders below the next Fibonacci level and set profit targets near key resistance levels. This ensures that your trades have a clear plan for exit.
Volatility-Based Trading Strategies
Volatility-based strategies focus on capitalizing on periods of high market volatility.
How to Implement:
- Use Bollinger Bands: Identify periods of low volatility (narrow bands) and anticipate potential breakouts. When the bands are narrow, it indicates low volatility, and a breakout is likely.
- Trade the Breakout: Enter trades when the price breaks above or below the bands, indicating increased volatility. This suggests a new trend is forming, and you can capitalize on the price movement.
- Manage Risk: Set stop-loss orders based on the ATR to account for increased price swings. The ATR provides an estimate of the market’s recent volatility, helping you set appropriate stop-loss levels.
Read More: best trading strategy for xauusd
Trading Oil Through ETFs and Options
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and options provide alternative ways to trade crude oil without directly trading futures contracts.
How to Implement:
- Choose the Right ETF: Select ETFs that track crude oil prices (e.g., USO, OIL). These ETFs provide exposure to crude oil without the need to trade futures contracts directly.
- Trade Options: Use options strategies like calls, puts, and spreads to leverage price movements with limited risk. Options allow you to benefit from price movements while controlling risk.
- Diversify: Combine ETFs and options with other trading strategies to spread risk. Diversifying your approach can reduce the impact of any single strategy on your overall portfolio.
Case Study: Successful Implementation of a Breakout Strategy
In early 2020, crude oil prices experienced significant volatility due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Traders using a breakout strategy were able to capitalize on the sharp price movements. For instance, when oil prices broke below the $50 support level, traders who shorted the market saw substantial profits as prices continued to decline. This case study highlights the importance of having a strategy in place to take advantage of market volatility.
Building a Robust Trading Plan

Setting Clear Trading Objectives and Risk Tolerance
Establishing clear goals and understanding your risk tolerance is the foundation of a successful trading plan.
- Define Objectives: Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. For example, a SMART goal could be to achieve a 10% return on investment within six months.
- Assess Risk Tolerance: Determine how much risk you are willing to take on each trade and overall portfolio. Understanding your risk tolerance helps you make informed decisions and avoid emotional trading.
Developing a Disciplined Approach to Trading
Discipline is crucial for consistent trading success.
- Create a Trading Routine: Follow a structured routine that includes market analysis, planning, and execution. A routine helps you stay focused and avoid impulsive decisions.
- Stick to Your Plan: Avoid emotional decisions and adhere to your trading plan. Consistency in following your plan is key to long-term success.
Importance of Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The oil market is dynamic, and continuous learning is essential for staying ahead.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with market news, economic indicators, and geopolitical events. Staying informed helps you anticipate market movements and make better trading decisions.
- Review and Adapt: Regularly review your trading performance and adjust strategies as needed. Continuous improvement ensures that your strategies remain effective in changing market conditions.
Additional Considerations

Role of Geopolitical Events in Oil Price Fluctuations
Geopolitical events can cause significant price volatility in the crude oil market.
- Conflicts and Wars: Military conflicts in oil-producing regions can disrupt supply and spike prices. For example, tensions in the Middle East often lead to fears of supply disruptions and higher prices.
- Sanctions: Economic sanctions on countries like Iran and Venezuela can reduce global oil supply. Sanctions limit the ability of these countries to export oil, affecting global supply and prices.
- OPEC Decisions: Production quotas and agreements among OPEC members can influence prices. OPEC’s ability to control supply through production decisions has a direct impact on oil prices.
Impact of Economic Indicators on Crude Oil Market
Economic indicators provide insights into oil demand and supply dynamics.
- GDP Growth: Strong economic growth increases oil demand, while recessions reduce it. For instance, rapid industrial growth in China has significantly increased global oil demand.
- Industrial Production: Higher industrial activity boosts oil consumption. Economic reports on manufacturing output can provide insights into future oil demand.
- Unemployment Rates: Low unemployment typically correlates with higher economic activity and oil demand. As more people are employed, economic activity increases, leading to higher oil consumption.
Leveraging Trading Platforms and Tools for Success
Utilizing advanced trading platforms and tools can enhance your trading performance.
- Trading Platforms: Use platforms like MetaTrader, TradingView, and ThinkorSwim for analysis and execution. These platforms offer advanced charting tools, technical indicators, and real-time data.
- Automated Trading Systems: Implement automated systems to execute trades based on predefined criteria. Automated trading removes emotion from the equation and ensures consistent execution of your strategy.
- Data Analytics: Leverage data analytics tools to gain deeper insights into market trends. Analyzing historical data can help you identify patterns and improve your trading decisions.
Conclusion
Mastering the best trading strategy for crude oil requires a multifaceted approach that combines market understanding, technical proficiency, and disciplined risk management. By integrating the strategies and considerations outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the complexities of the oil market and potentially achieve consistent profits.
Remember, successful crude oil trading is not just about finding the perfect strategy – it’s about continuous learning, adaptation, and maintaining emotional discipline. Start by implementing these strategies on a demo account, refine your approach based on results, and gradually transition to live trading as you gain confidence and consistency.
Key takeaways for success in crude oil trading:
- Develop a deep understanding of fundamental and technical factors influencing oil prices
- Implement robust risk management techniques to protect your capital
- Utilize a combination of trading strategies to capitalize on different market conditions
- Build and stick to a comprehensive trading plan
- Stay informed about geopolitical events and economic indicators
- Continuously educate yourself and adapt your strategies to changing market dynamics
By following these principles and dedicating yourself to ongoing improvement, you’ll be well-positioned to thrive in the challenging yet rewarding world of crude oil trading. Remember, patience and persistence are key – success in trading is a marathon, not a sprint. Start your journey today, and may your trades be profitable and your risks well-managed.
What is the best time to trade crude oil?
The best time to trade crude oil is during periods of high liquidity and volatility, typically overlapping with the opening hours of major oil exchanges such as the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) and the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE).
How do geopolitical events affect crude oil prices?
Geopolitical events such as conflicts, sanctions, and political instability in oil-producing regions can disrupt supply, leading to significant price volatility.
What are the advantages of trading crude oil ETFs over futures contracts?
Trading crude oil ETFs offers exposure to oil prices without the complexity and risk associated with futures contracts. ETFs are more accessible and provide opportunities for diversification and risk management.








One Response
This is really interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I have joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your wonderful post. Also, I have shared your web site in my social networks!