The ICT (Inner Circle Trader) Market Maker Model is a powerful framework that helps traders understand how large financial institutions—often referred to as ‘Smart Money’—influence market movements. This model provides insights into how these institutions accumulate and distribute positions, allowing traders to predict and capitalize on market trends more effectively. In this article, we’ll explore both the buy and sell strategies within the ICT Market Maker Model, providing you with practical steps to identify high-probability trading opportunities in various financial markets. Partnering with a regulated forex broker ensures that you have a trustworthy platform to apply these strategies, enabling you to trade with confidence and security.

If you’re looking to gain an edge in your trading by understanding and leveraging institutional behavior, this guide will offer the tools and strategies needed to align your trades with the market’s underlying forces. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear roadmap for implementing the ICT Market Maker Model in your trading, helping you to make more informed decisions and increase your potential for success.
The ICT Market Maker Buy Model (MMBM)
The ICT Market Maker Buy Model (MMBM) is a sophisticated approach designed to identify and capitalize on bullish market conditions. It provides a structured framework that helps traders understand how institutional players accumulate positions and drive prices higher. The model is broken down into several key phases, each representing a critical stage in the market’s evolution from consolidation to expansion.
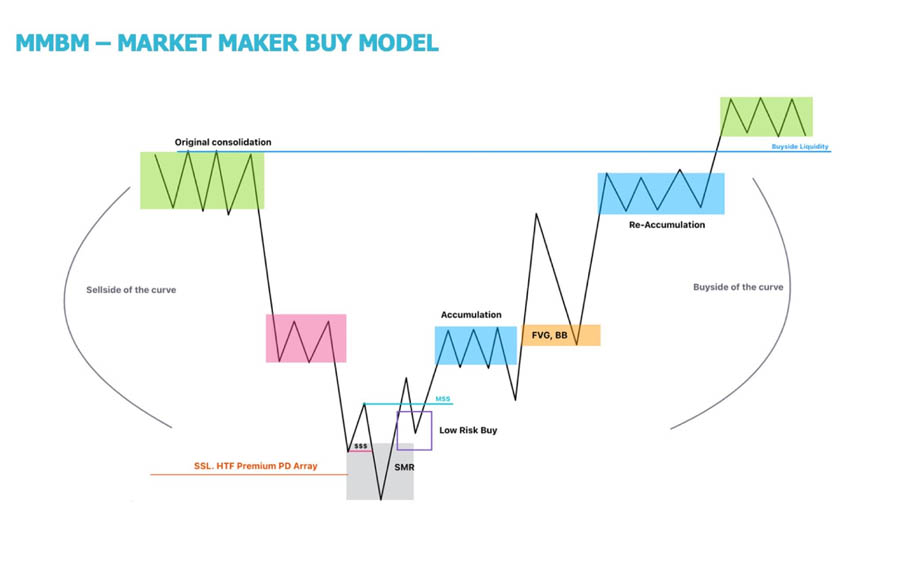
Phases of the MMBM
- Original Consolidation: The initial phase, where the market often moves sideways, is marked by the engineering of pending Buy-Side Liquidity (BSL) and Sell-Side Liquidity (SSL). During this phase, institutions are setting the stage for future price movements, creating a pool of stop orders on both sides of the market.
- Distribution: In this phase, sell orders exceed buy orders, typically occurring as the market moves to premium prices. This is where smart money begins to distribute their positions, selling to retail traders who are entering late, driven by the momentum of the uptrend.
- Smart Money Reversal (SMR): This is a pivotal point in the model, where institutions reverse their positions. The SMR phase is used by institutions to mitigate short positions, rebalance old imbalances (such as Buy-Side Imbalance and Sell-Side Inefficiency), and conduct Sell-Side Liquidity Raids. These actions are designed to shake out retail traders and create favorable conditions for the next phase of the market.
- Buy Program: The final phase represents net long positioning by institutions, divided into three parts:
- Accumulation (1st leg): Here, buy orders begin to exceed sell orders, indicating the start of a new bullish phase.
- Re-Accumulation (2nd leg): The dominance of buy orders continues, reinforcing the uptrend.
- Terminus: This is the final stage where institutions add their last orders to their positions, preparing for the next cycle of distribution.
Understanding and Implementing the Buy Model
To effectively use the MMBM, traders must develop a keen understanding of market structure and institutional behavior. Here’s how to implement the Buy Model:
- Identify Higher Timeframe (HTF) Institutional Order Flow (IOF) as bullish: This involves analyzing longer timeframes to determine the overall market direction. Higher timeframe analysis helps in aligning trades with the broader market trend, which is crucial for the success of the Buy Model.
- Recognize the Direction of Liquidity (DOL) as higher: Liquidity direction is a key indicator of where the market is likely to move next. By identifying areas where liquidity is concentrated, traders can anticipate potential price movements and position themselves accordingly.
- Observe an initial curve representing a Sell Program with Distribution/Redistribution: This is the early indication that institutions are beginning to distribute their positions, leading to a temporary downtrend before the market resumes its upward trajectory.

The primary goal of the Buy Model is to efficiently deliver price to the HTF draw while generating liquidity pools above the market. These liquidity pools are created during the sell curve and will later be used to pair institutional orders post-SMR. By understanding the formation of these pools, traders can better anticipate where the market is likely to reverse.
Once a Smart Money Reversal is identified through a Market Structure Shift (MSS), traders can apply one of three entry models to capitalize on the expected upward movement:
- 2022 Model: A contemporary strategy that targets entries by capitalizing on fair value gaps created after triggering key liquidity draw levels.
- IOFED (Institutional Order Flow Entry Drill): A methodical entry strategy that aligns with the overall institutional order flow.
- Breaker + Fair Value Gap: A combination of breaker block and fair value gaps in the market to capture early entry points.
The ICT Market Maker Sell Model (MMSM)
The ICT Market Maker Sell Model (MMSM) is the counterpart to the Buy Model, focusing on identifying and profiting from bearish market conditions. It shares a similar structure but with inverse characteristics, making it essential for traders looking to profit from downward market movements.
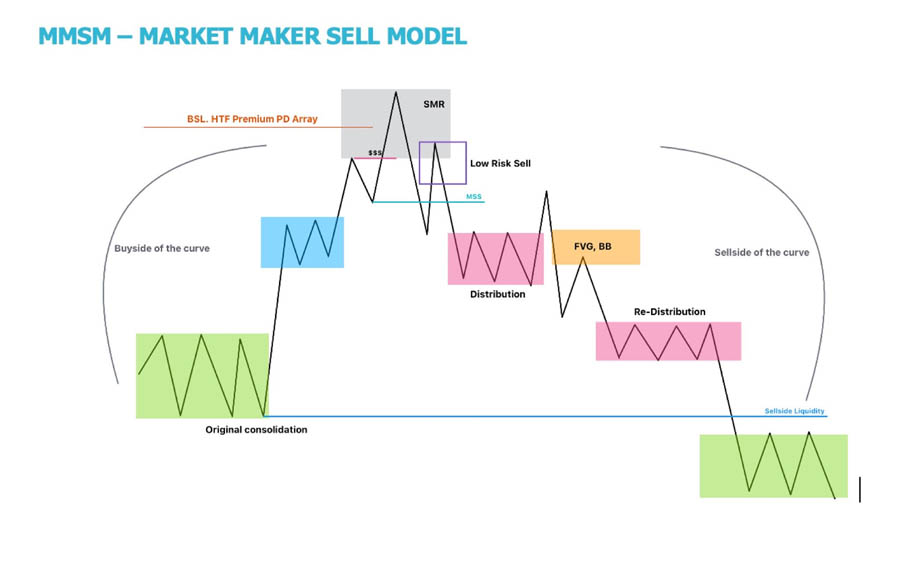
Phases of the MMSM
- Original Consolidation: Like the Buy Model, the sell model begins with consolidation, where the market is engineered to create pending Sell-Side Liquidity (SSL) and Buy-Side Liquidity (BSL). During this phase, institutions are setting up the market for a significant price decline, trapping retail traders in long positions.
- Accumulation: In this phase, buy orders exceed sell orders, often through accumulation at discount market prices. This is where smart money begins to accumulate short positions, anticipating a future downtrend.
- Smart Money Reversal (SMR): This phase is where institutions reverse their long positions, similar to the buy model but with a focus on driving prices lower. The SMR is used for mitigating long positions, rebalancing old imbalances (such as Sell-Side Imbalance and Buy-Side Inefficiency), and conducting Buy-Side Liquidity Raids. These actions are designed to trap retail traders who are late to the uptrend.
- Sell Program: The final phase represents net short positioning by institutions:
- Distribution (1st leg): This is where sell orders begin to exceed buy orders, signaling the start of a new bearish phase.
- Redistribution (2nd leg): The dominance of sell orders continues, reinforcing the downtrend.
- Terminus/Completion: This is the final stage where institutions add their last orders to their positions, preparing for the next cycle of accumulation.
Read more: Mastering the ICT Asian Range Strategy
Implementing the Sell Model
To effectively use the MMSM, traders must develop a keen understanding of bearish market structure and institutional behavior. Here’s how to implement the Sell Model:
- Identify HTF IOF as bearish: This involves analyzing longer timeframes to determine the overall market direction. Higher timeframe analysis helps in aligning trades with the broader market trend, which is crucial for the success of the Sell Model.
- Recognize DOL as lower: Liquidity direction is a key indicator of where the market is likely to move next. By identifying areas where liquidity is concentrated, traders can anticipate potential price movements and position themselves accordingly.
- Observe an initial curve representing a Buy Program with Accumulation/Re-Accumulation: This is the early indication that institutions are beginning to accumulate their short positions, leading to a temporary uptrend before the market resumes its downward trajectory.
The Sell Model aims to efficiently deliver price to the HTF draw while generating liquidity pools below the market. These pools, created during the buy curve, will be used to pair institutional orders post-SMR. By understanding the formation of these pools, traders can better anticipate where the market is likely to reverse.
After identifying a Smart Money Reversal through a Market Structure Shift (MSS) or Market Structure Break (MSB), traders can apply the same entry models as in the Buy Model. These entry models help traders capitalize on the downtrend, ensuring they are positioned correctly for maximum profit potential.
Read more: Mastering ICT Optimal Trade Entry
Advanced Concepts and Strategies
To fully leverage the ICT Market Maker Model, it is essential to understand and implement advanced concepts that go beyond the basic buy and sell models. These strategies provide deeper insights into market dynamics and can significantly enhance trading performance.
- Liquidity Engineering: Understanding how institutions create and exploit liquidity pools is crucial for predicting market movements. Liquidity pools are areas where a large number of stop orders are placed, and institutions often target these pools to execute their trades at favorable prices. By identifying these pools, traders can anticipate potential reversals and position themselves accordingly.
- Order Block Identification: Recognizing significant areas of institutional interest and order placement is vital for understanding market structure. Order blocks are areas where institutions have placed large orders, and these levels often act as strong support or resistance zones. Trading around these levels can provide high-probability setups, as the market tends to react strongly when revisiting these areas.
- Fair Value Gaps: Identifying and trading price discrepancies created by rapid market movements can be highly profitable. Fair value gaps occur when the market moves so quickly that it leaves behind unfilled orders, creating a price gap. These gaps often act as magnets for price, as the market seeks to fill them before continuing in its original direction.
- Multi-Timeframe Analysis: Aligning trades with higher timeframe institutional order flow and market structure increases the probability of success. By analyzing multiple timeframes, traders can gain a more comprehensive view of the market, ensuring their trades are aligned with the broader trend. This approach helps in filtering out false signals and improving overall trading accuracy.
- Correlation Management: Considering relationships between different markets can enhance decision-making and risk management. Certain markets tend to move in correlation with each other, and understanding these relationships can help traders anticipate price movements across different assets. By managing correlations effectively, traders can diversify their portfolios and reduce risk.
Risk Management in the ICT Market Maker Model
Effective risk management is crucial when implementing the ICT Market Maker Model. Without proper risk management, even the best trading strategies can result in significant losses. The following principles should be adhered to:
- Position Sizing: Adjust position sizes based on the strength of the setup and overall market conditions. Larger positions should be taken when the setup is strong, and market conditions are favorable. Conversely, smaller positions should be taken when the setup is less certain or market conditions are volatile.
- Stop Loss Placement: Set stops beyond key liquidity levels to avoid premature exits. Stop losses should be placed at levels where liquidity is likely to be concentrated, ensuring that the market has to move significantly against the trade before the stop is hit. This approach helps in avoiding false stop-outs caused by temporary price fluctuations.
- Take Profit Targets: Align take profit levels with identified fair value gaps and potential expansion zones. By setting take profit targets at logical levels, traders can maximize their gains while minimizing the risk of the market reversing before their targets are hit.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Maintain a favorable risk-reward ratio, typically aiming for at least 1:2 or higher. A good risk-reward ratio ensures that even if only a portion of trades are successful, the overall profitability remains positive. This approach helps in managing risk while maximizing potential returns.
- Hedging Strategies: Consider using hedging techniques to protect positions during volatile market conditions. Hedging involves taking offsetting positions in correlated markets, reducing the overall risk. This strategy can be particularly useful during periods of high volatility, where the market may move unpredictably.
OpoFinance Services: Elevating Your Trading Experience
For traders looking to implement the ICT Market Maker Model effectively, choosing the right broker is crucial. OpoFinance, an ASIC-regulated broker, offers a suite of services designed to enhance your trading journey. With advanced tools and resources, OpoFinance helps traders optimize their market analysis and execution capabilities.

- Advanced Charting Tools: Access sophisticated charting software to identify key ICT model components. These tools provide real-time data and advanced technical analysis features, allowing traders to apply the ICT model with precision.
- Competitive Spreads: Benefit from tight spreads, which are crucial for capturing small price movements in the model. Lower spreads mean that traders can enter and exit positions with minimal slippage, improving overall profitability.
- Educational Resources: Leverage comprehensive materials to deepen your understanding of market dynamics. OpoFinance offers a wealth of educational content, including webinars, tutorials, and articles, helping traders stay informed and improve their skills.
- Social Trading: Engage with OpoFinance’s social trading feature to learn from experienced ICT model practitioners. Social trading allows traders to follow and replicate the strategies of successful traders, providing valuable insights and opportunities for learning.
- Risk Management Suite: Utilize advanced tools to protect your capital while implementing complex ICT strategies. OpoFinance offers a range of risk management features, including customizable stop losses, take profit orders, and margin protection tools, ensuring that traders can manage their risk effectively.
Read more: Decoding SMT Divergence
By combining the insights from the ICT Market Maker Model with OpoFinance’s robust trading infrastructure, traders can potentially optimize their market analysis and execution capabilities. This combination of knowledge and tools can lead to more informed decisions and improved trading outcomes, making OpoFinance an ideal partner for traders using the ICT model.
Conclusion
The ICT Market Maker Model offers a profound understanding of market dynamics, providing traders with a framework to anticipate and capitalize on institutional behavior. By mastering both the buy and sell models, traders can gain a significant edge in identifying high-probability setups across various market conditions. However, success with this model requires dedication, continuous learning, and disciplined risk management.
As you integrate the ICT Market Maker Model into your trading approach, consider leveraging the advanced tools and services offered by regulated brokers like OpoFinance. With persistence, practice, and a commitment to ongoing education, the ICT Market Maker Model can become a powerful asset in your trading arsenal, potentially leading to more informed decisions and improved trading outcomes. This model not only equips traders with the knowledge to navigate the markets confidently but also empowers them to adapt to changing market conditions, ultimately enhancing their trading success.
How does the ICT Market Maker Model differ from traditional technical analysis?
The ICT Market Maker Model focuses on understanding institutional behavior and market structure, whereas traditional technical analysis primarily relies on chart patterns and indicators. The ICT model provides a framework for anticipating price movements based on the actions of large market participants, offering a unique perspective that can complement traditional analysis methods. By understanding the underlying forces driving market movements, traders can make more informed decisions, rather than relying solely on historical price data.
Can the ICT Market Maker Model be used for day trading?
Yes, the ICT Market Maker Model can be adapted for day trading. While it’s often used for swing trading and longer-term analysis, the principles can be applied to shorter timeframes. Day traders can focus on identifying intraday liquidity pools, stop hunts, and fair value gaps to inform their trading decisions. However, it’s important to note that shorter timeframes may require quicker decision-making and a solid understanding of the model’s core concepts. Day trading with the ICT model also demands a high level of discipline and the ability to quickly adapt to rapidly changing market conditions.
How long does it typically take to become proficient in using the ICT Market Maker Model?
The time required to become proficient in the ICT Market Maker Model varies depending on individual factors such as trading experience, dedication to learning, and market familiarity. Generally, traders may need several months to a year of consistent study and practice to gain a solid understanding of the model and its applications. Continuous learning, backtesting, and real-market experience are essential for developing proficiency and confidence in using the model effectively. Proficiency also involves not just understanding the model but being able to apply it consistently in live market conditions, which can take time and experience to master.







