In the dynamic world of financial markets, traders are continually seeking effective strategies to capitalize on price movements and generate profits. One highly regarded approach among day traders and short-term investors is the Opening Range Breakout (ORB) trading strategy. This method, often utilized with the help of a broker for forex trading, leverages the initial price action of a trading session to identify potential trading opportunities.
The opening range breakout strategy is based on the premise that the first few minutes or hours of a trading session often set the tone for the entire day. By carefully analyzing the price action during this crucial period, traders can position themselves to profit from subsequent breakouts or breakdowns.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the intricacies of the opening range breakout trading strategy, exploring its fundamental concepts, implementation techniques, risk management considerations, and potential pitfalls. Whether you’re a novice trader looking to expand your toolkit or an experienced market participant seeking to refine your approach, this article will provide valuable insights to enhance your trading prowess.
Understanding the Opening Range Breakout
Before we dive into the specifics of the opening range breakout strategy, it’s essential to grasp the concept of the opening range itself.

What is the Opening Range?
The opening range refers to the price range established by a financial instrument during the initial period of a trading session. This period can vary depending on the trader’s preference and the market being traded, but it typically spans from 5 minutes to an hour after the market opens.
The opening range is crucial because it often reflects the sentiment and expectations of market participants at the start of the trading day. It takes into account overnight news, economic data releases, and any other factors that may influence the asset’s price.
How the Opening Range Identifies Support and Resistance
One of the key reasons why traders pay close attention to the opening range is its ability to identify potential support and resistance levels. The high and low prices established during the opening range often serve as significant price levels throughout the trading day.
- The high of the opening range can act as a resistance level, potentially limiting upward price movements.
- The low of the opening range can function as a support level, possibly preventing further downside.
These levels are particularly important because many traders and automated trading systems use them as reference points for entering or exiting positions.
Timeframes for Defining the Opening Range
Traders can choose from various timeframes to define the opening range, depending on their trading style and the characteristics of the market they’re trading. Some common timeframes include:
- 5-minute opening range: Suitable for quick, intraday trades in fast-moving markets.
- 15-minute opening range: Offers a balance between capturing initial volatility and allowing for more price discovery.
- 30-minute opening range: Provides a broader view of the market’s initial direction and can be useful for longer intraday trades.
- 1-hour opening range: Appropriate for markets with slower price action or for traders looking to capture larger moves.
The choice of timeframe can significantly impact the effectiveness of the strategy, so it’s essential to experiment and find the one that best suits your trading objectives and risk tolerance.
The Role of Volatility in Opening Range Breakouts
Volatility plays a crucial role in the success of opening range breakout trades. Higher volatility can lead to more significant breakouts and potentially larger profits, but it also comes with increased risk. Conversely, lower volatility may result in fewer false breakouts but could limit profit potential.
Traders often use volatility indicators, such as the Average True Range (ATR), to gauge market conditions and adjust their trading parameters accordingly. Understanding and adapting to different volatility regimes is key to consistently profiting from opening range breakouts.
Trading the Opening Range Breakout
Now that we’ve covered the fundamentals of the opening range, let’s explore how to implement the opening range breakout trading strategy.
Read More: Mastering the ICT Turtle Soup Trading Strategy
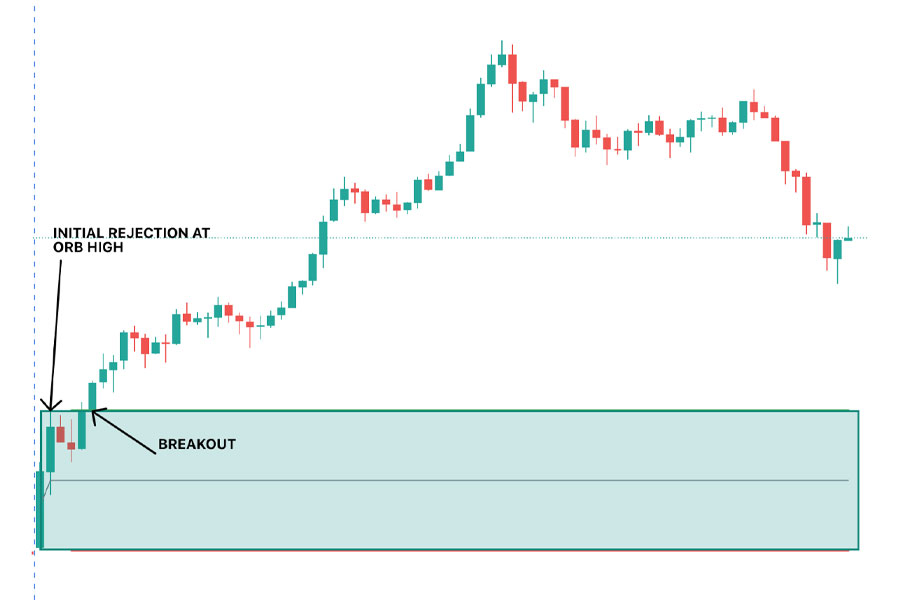
Long Entry Triggers: Breakouts Above the Opening Range High
A long (buy) entry is triggered when the price breaks above the high of the opening range. This breakout suggests that bullish momentum is overcoming the initial resistance, potentially leading to further upside.
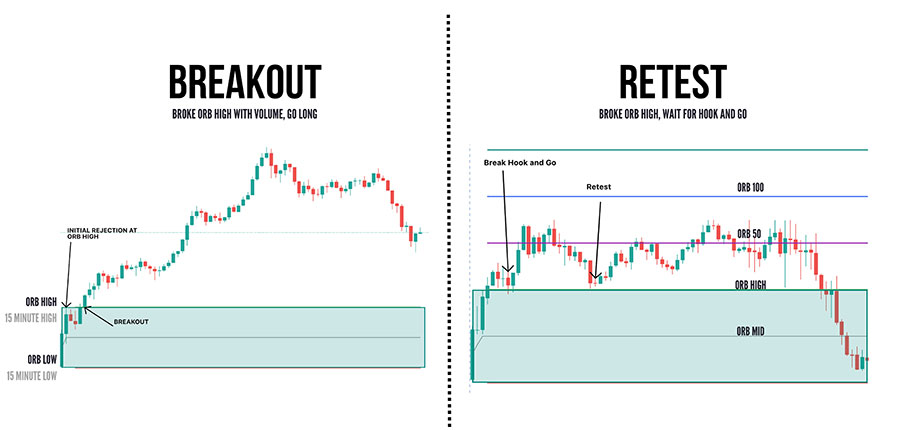
Key considerations for long entries:
- Confirmation: Wait for a candle to close above the opening range high to reduce the risk of false breakouts.
- Volume: Look for increased trading volume during the breakout to validate the move.
- Market context: Consider the overall market trend and any relevant support/resistance levels.
Short Entry Triggers: Breakouts Below the Opening Range Low
Conversely, a short (sell) entry is signaled when the price breaks below the low of the opening range. This breakdown indicates that bearish pressure is intensifying, possibly leading to further downside.
Key considerations for short entries:
- Confirmation: Wait for a candle to close below the opening range low to minimize false breakdown risks.
- Volume: Seek increased trading volume to confirm the validity of the breakdown.
- Market context: Assess the broader market trend and any significant support/resistance levels.
Order Placement Strategies
Effective order placement is crucial for successfully executing opening range breakout trades. Traders typically choose between two main order types:
- Limit Orders: These orders are placed at specific price levels, usually just above the opening range high for long entries or just below the opening range low for short entries. Limit orders offer better price control but may result in missed opportunities if the price moves quickly.
- Market Orders: These orders are executed at the best available price when the breakout occurs. Market orders ensure entry into the trade but may result in slippage, especially in fast-moving markets.
Some traders use a combination of both order types, placing limit orders initially and switching to market orders if the breakout appears strong and sustained.
Incorporating Price Action Analysis
While the opening range breakout strategy provides clear entry signals, incorporating price action analysis can enhance its effectiveness. Traders should pay attention to:
- Candlestick patterns: Look for bullish or bearish candlestick formations that support the breakout direction.
- Price momentum: Assess the strength of the price move using indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
- Previous day’s high and low: These levels can act as additional support or resistance points.
By combining opening range breakouts with thorough price action analysis, traders can increase their confidence in potential trades and improve their overall success rate.
Risk Management for Opening Range Breakouts
Proper risk management is essential for long-term success in trading, and the opening range breakout strategy is no exception. Here are key risk management principles to consider:

Importance of Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are crucial for limiting potential losses in case a trade moves against you. They help protect your capital and ensure that a single losing trade doesn’t significantly impact your overall trading account.
Placement of Stop-Loss Orders
For long trades:
- Place the stop-loss below the opening range low or a recent swing low.
- Consider using a percentage of the opening range’s height as a buffer to account for minor price fluctuations.
For short trades:
- Set the stop-loss above the opening range high or a recent swing high.
- As with long trades, add a small buffer to avoid premature stopouts.
Read More: Mastering the ICT Judas Swing
Position Sizing Considerations
Proper position sizing is critical for managing risk effectively. Consider the following approaches:
- Fixed percentage risk: Risk a set percentage of your trading account on each trade (e.g., 1% or 2%).
- Volatility-based sizing: Adjust position size based on market volatility, using indicators like the ATR.
- Fixed dollar risk: Risk a specific dollar amount on each trade, regardless of the account size.
Regardless of the method chosen, ensure that your position size allows for appropriate stop-loss placement without risking an excessive portion of your trading capital.
Setting Profit Targets
While stop-losses protect you from significant losses, profit targets help you lock in gains. Common approaches to setting profit targets include:
- Fixed risk-reward ratios: Aim for a specific ratio, such as 1:2 or 1:3, where the potential profit is 2 or 3 times the risk.
- Technical levels: Use key support and resistance levels, Fibonacci extensions, or pivot points as profit targets.
- Trailing stops: Implement a trailing stop to let profits run while protecting gains.
Additional Considerations
To maximize the effectiveness of the opening range breakout strategy, traders should be aware of several additional factors:
False Breakouts and How to Identify Them
False breakouts occur when the price briefly moves beyond the opening range but quickly reverses. To minimize the impact of false breakouts:
- Wait for confirmation: Require a candle close beyond the opening range before entering.
- Monitor volume: Low volume breakouts are more likely to fail.
- Use multiple timeframes: Confirm the breakout on both lower and higher timeframes.
- Consider market structure: Be cautious of breakouts into significant support or resistance levels.
Combining Opening Range Breakouts with Other Technical Indicators
While the opening range breakout strategy can be effective on its own, combining it with other technical indicators can enhance its performance. Consider incorporating:
- Moving averages: Use them to confirm the overall trend direction.
- Momentum indicators: RSI or Stochastic Oscillator can help identify overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: These can provide additional context for breakout strength and potential reversal points.
- Volume indicators: On-Balance Volume (OBV) or Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) can confirm breakout strength.
Market-Specific Considerations
The opening range breakout strategy may perform differently across various markets and asset classes. Consider these market-specific factors:
- Stocks: Individual company news and sector trends can impact breakout validity.
- Forex: Economic releases and central bank decisions can cause significant volatility.
- Futures: Contract rollover periods and seasonal patterns may affect breakout dynamics.
- Cryptocurrencies: High volatility and 24/7 trading can influence the definition of the opening range.
Adapt your approach based on the specific characteristics of the market you’re trading.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Opening Range Breakout Strategy
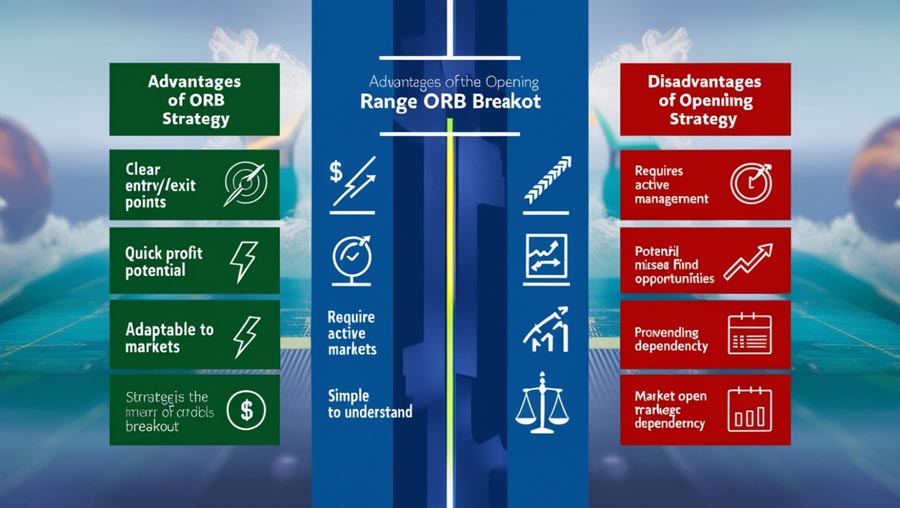
Like any trading strategy, the opening range breakout approach has its strengths and weaknesses:
Advantages:
- Clearly defined entry and exit points: The strategy provides objective criteria for trade entry and stop-loss placement.
- Potential for quick profits: Successful breakout trades can lead to rapid price movements and quick gains.
- Adaptability: The strategy can be applied to various timeframes and market conditions.
- Simplicity: The core concept is easy to understand, making it accessible to traders of all experience levels.
Disadvantages:
- Increased risk of false breakouts: Especially in choppy or low-volatility markets.
- Requires active trading: The strategy often necessitates quick decision-making and frequent monitoring.
- Potential for missed opportunities: Waiting for confirmation can sometimes result in late entries.
- Dependency on market open dynamics: The strategy may be less effective in markets without a clear opening period.
Conclusion
The opening range breakout trading strategy offers a powerful approach to capitalizing on early market moves and identifying potential trends. By carefully analyzing the initial price action of a trading session, traders can position themselves to profit from subsequent breakouts or breakdowns.
Key takeaways from this comprehensive guide include:
- Understanding the significance of the opening range in establishing support and resistance levels.
- Implementing proper entry techniques for both long and short trades.
- The critical importance of risk management through stop-loss orders and position sizing.
- Enhancing the strategy’s effectiveness by combining it with price action analysis and other technical indicators.
- Recognizing and adapting to market-specific considerations and potential pitfalls like false breakouts.
While the opening range breakout strategy can be suitable for various trader types, it is particularly well-suited for day traders and active short-term investors who can dedicate time to monitoring market opens and managing intraday positions.
As with any trading approach, it’s crucial to thoroughly test and practice the opening range breakout strategy in a simulated environment before risking real capital. This allows you to refine your technique, develop confidence in your decision-making, and identify any necessary adjustments to suit your trading style and risk tolerance.
By mastering the opening range breakout strategy and incorporating it into your broader trading toolkit, you can enhance your ability to identify and capitalize on high-probability trading opportunities in the dynamic world of financial markets.
Read More: Mastering the ICT Power of 3 (PO3)
How does the opening range breakout strategy perform in different market conditions, such as trending vs. ranging markets?
The opening range breakout strategy can perform differently depending on market conditions. In trending markets, breakouts are more likely to continue in the direction of the trend, potentially leading to larger profits. However, in ranging markets, breakouts may be more prone to failure, resulting in false signals. Traders should adapt their approach based on the prevailing market conditions, potentially using additional indicators to confirm the market state before executing trades.
Can the opening range breakout strategy be automated, and what are the challenges in doing so?
Yes, the opening range breakout strategy can be automated through algorithmic trading systems. However, there are several challenges to consider:
Defining the opening range precisely, especially in 24-hour markets.
Implementing effective filters to reduce false breakouts.
Adapting to changing market volatility and conditions.
Handling technical issues such as data feeds and order execution.
Successful automation requires extensive testing, robust risk management, and ongoing monitoring to ensure the system performs as intended.
How do earnings announcements and other significant news events impact the effectiveness of the opening range breakout strategy?
Earnings announcements and major news events can significantly impact the opening range breakout strategy. These events often lead to increased volatility and gap openings, which can affect the formation and validity of the opening range. Traders should be cautious when applying the strategy around such events, as price movements may be more erratic and less predictable. It’s often advisable to avoid trading during major announcements or to adjust your strategy to account for the increased volatility and potential for rapid price reversals.







