The world of forex trading, where currencies are constantly bought and sold, can be both challenging and rewarding. To truly succeed in this market, there’s one key concept you need to grasp: the spread in forex. This guide will dive deep into everything about the spread in forex – what it is, why it’s important, how it impacts your trading plans, and more. Understanding the role of a reliable forex trading broker is also crucial, as their spread offerings can significantly influence your trading costs and overall profitability. Buckle up, and let’s get started!

What is Spread in Forex?
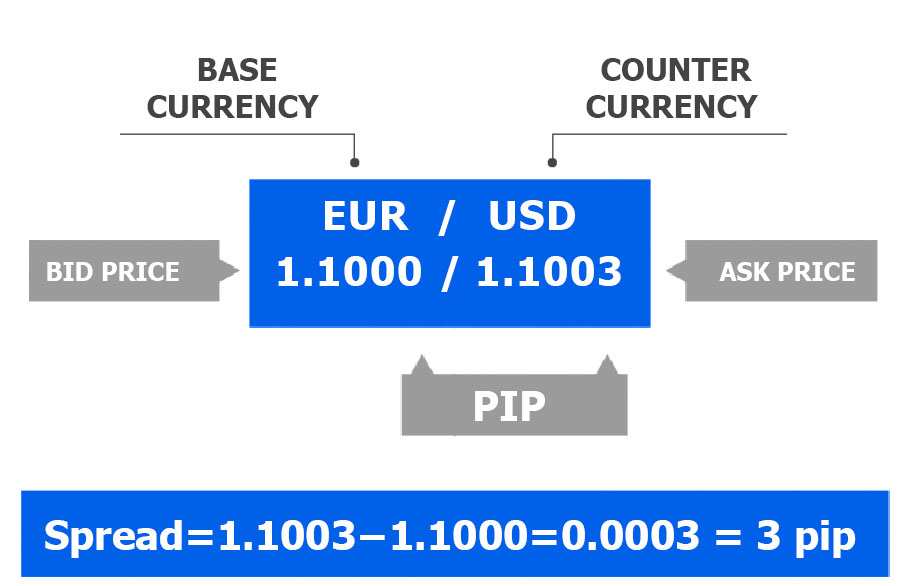
In forex trading, the spread in forex is the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair. The bid price represents what the market is willing to pay to buy the currency pair from you, while the ask price is the price at which the market will sell the currency pair to you. For instance, if the EUR/USD pair has a bid price of 1.1000 and an ask price of 1.1002, the spread in forex is 2 pips.
How to Calculate Spread
Calculating the spread is pretty simple. Here’s the formula:
Spread=Ask Price−Bid Price
So, if the EUR/USD bid price is 1.1000 and the ask price is 1.1003, the spread would be:
Spread=1.1003−1.1000=0.0003
This 0.0003 is typically expressed in pips, which in this example would be 3 pips.
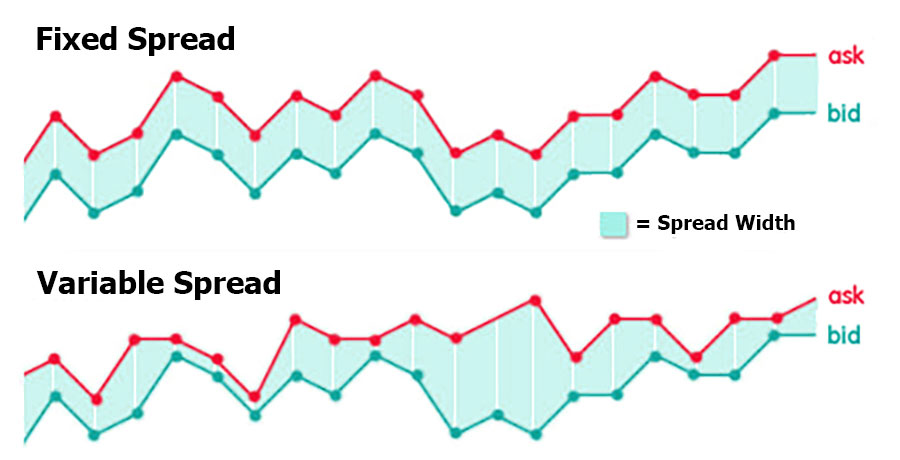
Types of Spread
Fixed Spread
Fixed spreads in forex stay constant no matter the market conditions. Brokers who offer fixed spreads in forex usually operate as market makers. Fixed spreads are beneficial for traders who need predictability in their trading costs.
Pros of Fixed Spreads
- Predictability: Fixed spreads allow you to know your trading costs upfront, aiding in precise risk management.
- No Surprises: You won’t face unexpected cost increases during volatile market periods.
- Ideal for Beginners: Fixed spreads are simpler to understand, making them perfect for new traders.
Cons of Fixed Spreads
- Potentially Higher Costs: Fixed spreads can be higher than variable spreads when the market is stable.
- Less Competitive for High-Volume Trades: Traders executing large orders might find fixed spreads more expensive than variable ones, which can tighten during high liquidity.
- Possible Requotes: Some brokers might issue requotes during volatile times to maintain the fixed spread, leading to execution delays.
Variable Spread
Variable spreads in forex change based on market volatility and liquidity. When liquidity is high, the spread in forex can narrow significantly, making trading cheaper. However, during high volatility, the spread in forex can widen, increasing costs.
Pros of Variable Spreads
- Lower Costs in Stable Markets: Variable spreads can be lower than fixed spreads when the market is stable.
- Market Transparency: Variable spreads reflect current market conditions more accurately.
- Favorable for Scalpers: Scalpers and high-frequency traders can benefit from tighter spreads during periods of high liquidity.
Read More: What are Pips and Pipettes? Overview and Calculation
Cons of Variable Spreads
- Unpredictability: Spreads can widen unexpectedly during volatile market conditions, increasing trading costs.
- Complexity for Beginners: Managing variable spreads can be more challenging for novice traders.
- Higher Costs During Volatility: Major economic events can cause spreads to widen significantly, raising trading costs.
Why Spread Matters in Forex Trading
Cost of Trading
The spread in forex is essentially the cost of trading. Each time you enter a trade, you pay the spread, impacting your overall profitability. For example, if the spread in forex for the EUR/USD pair is 2 pips and you buy 1 lot, you need the market to move 2 pips in your favor just to break even.
Impact on Scalping Strategies
Scalpers, who make multiple trades within short time frames to capture small price movements, are particularly sensitive to spreads. Low spreads are crucial for scalpers since even small spreads can erode profits due to the high frequency of trades.
Influence on Trading Style
Traders with longer-term strategies might be less affected by the spread since they aim to capture larger price movements over time. However, understanding spreads is still essential for accurate risk management and cost calculation.
How to Minimize Spread Costs
Choose the Right Broker
Selecting a broker with competitive spreads in forex is critical. Look for brokers offering low variable spreads in forex during your preferred trading times. Some brokers offer accounts with raw spreads in forex and charge a commission instead, which can be more cost-effective for high-volume traders.
Trade During High Liquidity Times
Forex markets experience periods of high liquidity, such as the overlap between the London and New York sessions. Trading during these times can help you benefit from narrower spreads.
Monitor Economic Events
Major economic announcements can cause spreads to widen due to increased volatility. Staying informed about the economic calendar allows you to avoid trading during these times or adjust your strategy accordingly.
Use Limit Orders
Using limit orders instead of market orders can help you avoid paying the spread. A limit order allows you to specify the price at which you want to enter or exit a trade, potentially reducing your trading costs.
Spread and Different Market Conditions
Normal Market Conditions
During normal market conditions, liquidity is generally high, and spreads are narrower. This is ideal for traders, especially those using high-frequency strategies, as trading costs are minimized.
Volatile Market Conditions
During high volatility, such as during major economic announcements or geopolitical events, spreads can widen significantly. Traders need to be cautious as trading costs can increase unexpectedly, affecting overall profitability.
Low Liquidity Periods
During periods of low liquidity, such as holidays or outside major trading sessions, spreads can widen due to the lack of market participants. Traders should be aware of these times and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Read More: Margin in Forex: A Comprehensive Guide
Practical Examples of Spread in Forex Trading
Example 1: Trading EUR/USD with a Fixed Spread
Suppose your broker offers a fixed spread of 2 pips on the EUR/USD pair. If the bid price is 1.1000, the ask price will be 1.1002. When you place a buy order, you enter the market at 1.1002. To break even, the market needs to move up by 2 pips to 1.1004.
Example 2: Trading GBP/USD with a Variable Spread
Assume your broker offers variable spreads on the GBP/USD pair. During a period of high liquidity, the spread might be as low as 1 pip. If the bid price is 1.2500, the ask price could be 1.2501. However, during a volatile market condition, the spread might widen to 4 pips, with the bid price at 1.2500 and the ask price at 1.2504.
Spread in Different Types of Forex Accounts
Standard Accounts
Standard accounts typically have wider spreads compared to other account types. They are suitable for beginners and those trading with smaller volumes. The trading costs are incorporated into the spread, with no additional commission charged.
ECN Accounts
ECN (Electronic Communication Network) accounts offer tighter spreads because they connect traders directly to the interbank market. These accounts usually charge a commission on each trade in addition to the spread. ECN accounts are preferred by professional traders and those trading large volumes due to lower trading costs.
STP Accounts
STP (Straight Through Processing) accounts route traders’ orders directly to liquidity providers. Spreads on STP accounts are variable and can be competitive, especially during high liquidity periods. These accounts are a middle ground between standard and ECN accounts, suitable for intermediate traders.
The Role of Spreads in Risk Management
Understanding and managing spreads in forex is crucial for effective risk management in forex trading. Here are some strategies to consider:
Position Sizing
Adjust your position size based on the spread in forex to ensure that trading costs do not excessively erode your potential profits. Smaller position sizes can help mitigate the impact of wider spreads in forex during volatile periods.
Stop-Loss Orders
Place stop-loss orders at levels that account for the spread in forex to avoid being stopped out prematurely. For example, if you place a stop-loss order 10 pips away from your entry price, and the spread in forex is 2 pips, consider placing the stop-loss 12 pips away to accommodate the spread.
Spread Monitoring Tools
Use spread monitoring tools or trading platforms that provide real-time spread information. This can help you make informed decisions and avoid entering trades when spreads are excessively wide.
Advanced Strategies for Spread Management
Hedging
Hedging involves taking offsetting positions in related currency pairs to mitigate risk. By understanding the spread and its impact on different pairs, traders can implement effective hedging strategies to protect against adverse market movements.
Read More: Forex Terminology for Beginners
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading systems can be programmed to monitor spreads and execute trades when spreads are favorable. This can be particularly useful for high-frequency trading strategies that rely on minimal trading costs.
Arbitrage
Arbitrage strategies involve taking advantage of price discrepancies between different markets or brokers. By understanding and monitoring spreads, traders can identify arbitrage opportunities and execute trades to capture risk-free profits.
Other Trading Fees: Commission and Swap
Commission
In addition to spreads in forex, some brokers charge a commission per trade. This is common with ECN accounts where the spreads in forex are very tight. The commission is usually a fixed amount per traded lot and can be advantageous for high-volume traders because it can result in lower overall trading costs compared to wider spreads.
Swap
Swap, also known as rollover interest, is the fee paid or earned for holding a position overnight. Depending on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in a pair, you may either receive or pay this fee. It’s crucial to factor in swap rates, especially if you hold positions for multiple days, as they can affect your profitability.
Conclusion
Understanding the spread in forex trading is essential for all traders, as it directly affects your trading costs and profitability. By choosing the right broker, trading during high liquidity times, and being mindful of economic events, you can manage and minimize the impact of spreads on your trading strategy.
Both fixed and variable spreads in forex have their pros and cons, and the choice between them depends on your trading style, strategy, and risk tolerance. Fixed spreads offer predictability, making them suitable for beginners and those who prefer stable trading costs. Variable spreads, on the other hand, can offer lower costs during stable market conditions but require careful management during volatile periods.
Additionally, being aware of other trading fees such as commissions and swaps in forex is vital for comprehensive cost management. Commissions can make ECN accounts with tight spreads in forex attractive to high-volume traders, while swap fees can impact longer-term trades.
For those looking to enhance their forex trading knowledge and stay ahead in the market, mastering the concept of spread in forex is a fundamental step. Stay informed, stay strategic, and optimize your trading for better outcomes.
What is the typical spread range for major currency pairs?
The spread range for major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, typically varies between 0.1 to 3 pips depending on market conditions, broker type, and trading volume.
How does spread affect my profitability in forex trading?
The spread directly impacts your trading costs. A wider spread increases the cost of entering and exiting trades, requiring a larger price movement to achieve profitability. Conversely, a narrower spread reduces these costs, making it easier to turn a profit.
Can the spread change during economic news releases?
Yes, spreads can widen significantly during economic news releases due to increased volatility and lower liquidity. It’s crucial to monitor such events and adjust your trading strategy accordingly to manage the potential increase in trading costs.
Is it possible to trade forex with zero spreads?
Some brokers offer zero spread accounts, where the spread is essentially zero or very tight. However, these accounts usually charge a commission per trade to compensate for the absence of a spread, which can still impact overall trading costs.
How do I choose between a broker with fixed spreads and one with variable spreads?
The choice depends on your trading style and needs. Fixed spreads provide cost predictability, which is beneficial for beginners and during volatile periods. Variable spreads can be lower during stable market conditions, which can be advantageous for experienced traders who can manage spread fluctuations effectively.







