The foreign exchange (forex) market is filled with unique specialized terminology and words. If you are new to forex, it is better to initially commit yourself to learning them.
One of these unique terms is “lot.” In forex, trading is done in a specific size or quantity of currency units, which are referred to as lots. A lot in forex or trading is a measurement unit for the volume of a position or a fixed amount of the base currency in the forex market. This quantity is always specified in lots. Remember that the size of your lot directly affects your risk level. The larger your lot size, the higher your risk will be. Risk management is essentially a model that allows you to calculate the optimal standard lot size in forex based on the estimated risk level, fluctuations (stop-loss amount), and leverage.
What is Lot in Forex trading?

In simple terms, a lot is the unit of measurement for the amount of a trade. In the normal case, a lot is a standard unit for measuring the volume of a position opened by traders. In forex, you can only open positions in specific volumes of trading units, which are referred to as lots.
Let’s give an example to clarify the concept. In the outside world of forex, almost everything is measured with its own unit of measurement. When you go to a specialized fruit and vegetable market to buy a quantity of fruit, you usually use the term “kilogram.” For example, you ask the seller to give you a few kilograms of apples.
Similarly, in forex, the lot is the designated unit of measurement for trading volumes. It helps standardize the size of positions and allows for easier calculation and comparison of trade sizes. Different types of lots, such as standard lots, mini lots, or micro lots, are used to determine the volume of trades in forex.
Training Lot in Forex
The concept of lots in forex refers to the standard unit of measurement for currency trades. A standard lot equals 100,000 units of the base currency in a forex pair.
In addition to standard lots, there are also mini-lots and micro-lots. A mini lot represents 10,000 units of the base currency, while a micro lot represents 1,000 units. These smaller sizes allow traders to trade with less capital and enable better risk management.
Understanding the concept of leverage is essential when trading with lot sizes. Leverage allows traders to trade a larger amount of money with a relatively small capital. In forex, leverage is typically provided by brokers and can go up to 1:500. This means that a trader can trade $500 for every $1 in their account balance.
It’s important to remember that while leverage can potentially increase profits, it also increases the potential losses. Therefore, understanding how to manage risk when trading with lot sizes is crucial. Using risk management tools such as stop-loss orders is important to limit potential losses.
In conclusion, a lot in forex is the standard unit of measurement for trade in the currency market, and understanding the concept of leverage and risk management when trading with larger lot sizes is important.
Lot sizes forex

In the digital currency market, it is important to know that each lot in Forex represents one hundred thousand units of the base currency. For example, when you trade on the EUR/USD currency pair and buy one lot, you are essentially purchasing 100,000 dollars. This metric unit has various types, including standard lots, mini lots, and micro-lots.
Types of lots in Forex include:
Standard Lots:
The standard lot represents the predefined and standard amount for each lot. The size of a standard lot is equal to 100,000 units, as mentioned in the previous explanation.
Mini Lots:
Mini lots have a value equal to half the size of standard lots. The size of a mini lot is 10,000 units and is displayed as 0.1 lots.
Micro Lots:
The smallest unit of measurement is the micro lot. The size of a micro lot is equal to 1,000 units and is displayed as 0.01 lots. It is the lowest volume that can be traded in Forex.
Nano Lots:
Nano lots are larger than micro lots but smaller than mini lots. One nano lot has a value of 100 units. It’s important to note that nano lots are not tradable in the digital currency market unless in nano accounts created for practice and testing purposes.
Fractional Lots:
Some brokers offer fractional lots, allowing traders to trade lot sizes smaller than nano lots. For example, some brokers allow trading below 0.01 lots.
These different types of lots provide flexibility in position sizing and allow traders with various capital levels to participate in Forex trading.
Forex lot size chart
Here’s a chart that provides a general overview of the lot sizes commonly used in forex trading:
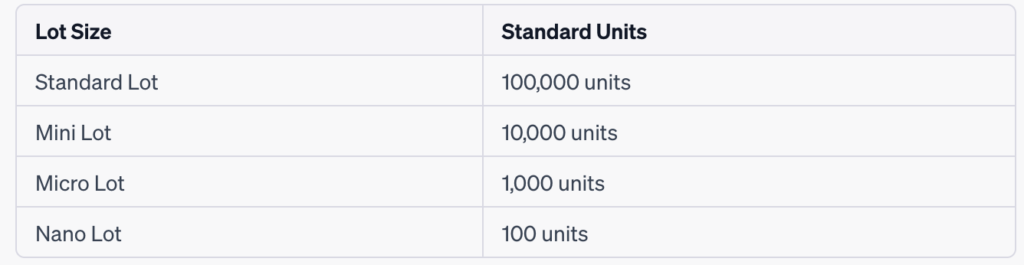
Please note that the above chart represents the standard lot sizes, but some brokers may offer variations or additional options. Additionally, different brokers may have their own terminology for lot sizes, so it’s important to familiarize yourself with your specific broker’s terminology and specifications.
When trading, it’s crucial to consider your risk tolerance, account size, and trading strategy to determine the appropriate lot size for your specific circumstances.
How to Choose Lot Size in Forex?

Choosing the appropriate lot size in forex trading is an important decision that depends on several factors, including your risk tolerance, account size, trading strategy, and market conditions. Here are some steps to help you determine the appropriate lot size:
- Understand Lot Size: In forex trading, a lot refers to the standardized trading size. The three main types of lot sizes are:
- Standard Lot: 100,000 units of the base currency.
- Mini Lot: 10,000 units of the base currency.
- Micro Lot: 1,000 units of the base currency.
- Assess Risk Tolerance: Consider your risk tolerance and the amount of capital you are willing to risk on each trade. This will help you determine the percentage of your trading account you are comfortable risking per trade. Risking 1-2% of your trading account per trade is a common guideline, but you can adjust this based on your personal preferences and risk management strategy.
- Determine Stop-Loss Level: Identify the appropriate placement for your stop-loss order based on your trading strategy, technical analysis, and market conditions. The distance between your entry point and the stop-loss level will impact your risk per trade.
- Calculate Position Size: To calculate the position size, you can use the following formula: Position Size = (Account Balance x Risk Percentage) / (Distance to Stop Loss x Pip Value)
- Account Balance: Your total trading account balance.
- Risk Percentage: The portion of your account balance you are willing to risk per trade (e.g., 1% or 2%).
- Distance to Stop Loss: The number of pips between your entry point and the stop-loss level.
- Pip Value: The value of a single pip for the currency pair you are trading.
By plugging in the appropriate values, you can calculate the position size that aligns with your risk management strategy.
- Consider Leverage: If you are using leverage, be aware that it amplifies both potential profits and losses. Adjust your lot size accordingly, considering the leverage ratio you are utilizing.
- Adapt to Market Conditions: Market conditions can influence your lot size selection. During periods of higher volatility or when trading more exotic currency pairs, you may want to adjust your position size accordingly to account for increased risk.
- Demo Testing: Before implementing your chosen lot size in live trading, it’s advisable to test your strategy and position sizing with a demo trading account. This allows you to assess the effectiveness of your risk management and make adjustments if necessary.
Conclusion
Remember, risk management is a crucial aspect of successful forex trading. Choosing an appropriate lot size is just one component of effective risk management. It’s important to combine it with other risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders, diversifying your trades, and avoiding excessive concentration in a single currency pair.
Always trade within your financial means, consider seeking guidance from experienced traders or professionals, and continuously evaluate and adjust your risk management approach as needed.